See also
![]() The dictionary definition of tolkusha at Wiktionary
The dictionary definition of tolkusha at Wiktionary
Tolkusha is a traditional food of the Chukotko-Kamchatkan peoples in the Russian Far East, especially Kamchatka. It is made of dried fish meat or fish roe mixed with fat (seal or reindeer) and berries (bilberry or crowberry) extended with edible plant bulbs or stems, ground and pounded together for a long time to yield a white paste. [1]
Tolkusha (Russian : толкуша) is a Russian word, coming from the verb толочь [toloch’] = to bruise, to crush, to pound, to tamp. The indigenous names for tolkusha include Chukchi: rilqəril, Kerek: jilq, Koryak: jilqəjil, Alutor: tilqətil, Palana: təlqətəl or Itelmen: silqsilq. [2]
![]() The dictionary definition of tolkusha at Wiktionary
The dictionary definition of tolkusha at Wiktionary

Koryaks are an Indigenous people of the Russian Far East who live immediately north of the Kamchatka Peninsula in Kamchatka Krai and inhabit the coastlands of the Bering Sea. The cultural borders of the Koryaks include Tigilsk in the south and the Anadyr basin in the north.

Pemmican is a mixture of tallow, dried meat, and sometimes dried berries. A calorie-rich food, it can be used as a key component in prepared meals or eaten raw. Historically, it was an important part of indigenous cuisine in certain parts of North America and it is still prepared today.
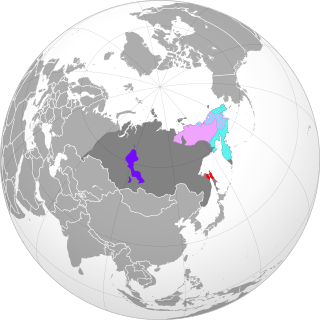
The Paleo-Siberian languages are several language isolates and small language families spoken in parts of Siberia. They are not known to have any genetic relationship to each other; their only common link is that they are held to have antedated the more dominant languages, particularly Tungusic and latterly Turkic languages, that have largely displaced them. Even more recently, Turkic and especially Tungusic have been displaced in their turn by Russian.

The Chukotko-Kamchatkan or Chukchi–Kamchatkan languages are a language family of extreme northeastern Siberia. Its speakers traditionally were indigenous hunter-gatherers and reindeer-herders. Chukotko-Kamchatkan is endangered. The Kamchatkan branch is moribund, represented only by Western Itelmen, with less than a hundred speakers left. The Chukotkan branch had close to 7,000 speakers left, with a reported total ethnic population of 25,000.

The Nivkh, or Gilyak, are an Indigenous ethnic group inhabiting the northern half of Sakhalin Island and the lower Amur River and coast on the adjacent Russian mainland. Historically, they may have inhabited parts of Manchuria.

The Itelmens, Russian: Ительмены, romanized: Itel'meny) are an Indigenous ethnic group of the Kamchatka Peninsula in Russia. The Itelmen language is distantly related to Chukchi and Koryak, forming the Chukotko-Kamchatkan language family, but it is now virtually extinct, the vast majority of ethnic Itelmens being native speakers of Russian.

Alyutor or Alutor is a language of Russia that belongs to the Chukotkan branch of the Chukotko-Kamchatkan languages, by the Alyutors. It is moribund, as only 25 speakers were reported in the 2010 Russian census.

Koryak, also known as Nymylan, Korjakische, Chavchuven and Koræiki, is a Chukotko-Kamchatkan language spoken by 1,665 people as of 2010 in the easternmost extremity of Siberia, mainly in Koryak Okrug. It is mostly spoken by Koryaks. Its close relative, the Chukchi language, is spoken by about three times that number. The language together with Chukchi, Alyutor and Itelmen forms the Chukotko-Kamchatkan language family. Its native name in Koryak is нымылан nymylan, but variants of the Russian name "Koryak" are most commonly used in English and other languages. The Chukchi and Koryaks form a cultural unit with an economy based on reindeer herding and both have autonomy within the Russian Federation.

Uralo-Siberian is a hypothetical language family consisting of Uralic, Yukaghir, and Eskaleut. It was proposed in 1998 by Michael Fortescue, an expert in Eskaleut and Chukotko-Kamchatkan, in his book Language Relations across Bering Strait. Some have attempted to include Nivkh in Uralo-Siberian. Until 2011, it also included Chukotko-Kamchatkan. However, after 2011 Fortescue only included Uralic, Yukaghir and Eskaleut in the theory, although he argued that Uralo-Siberian languages have influenced Chukotko-Kamchatkan.

Itelmen or Western Itelmen, formerly known as Western Kamchadal, is a language of the Chukotko-Kamchatkan family spoken on the western coast of the Kamchatka Peninsula. Fewer than a hundred native speakers, mostly elderly, in a few settlements in the southwest of Koryak Autonomous Okrug, remained in 1993. The 2021 Census counted 2,596 ethnic Itelmens, virtually all of whom are now monolingual in Russian. However, there are attempts to revive the language, and it is being taught in a number of schools in the region.

Kerek is an extinct language in Russia of the northern branch of the Chukotko-Kamchatkan languages. Before its extinction, it was spoken by the Kereks of the Russian Far East. It went extinct in 2005 with the death of Ekaterina Khatkana.
Geographically, Siberia includes the Russian Urals, Siberian, and Far Eastern Federal Districts.
Mosan is a hypothetical language family consisting of the Salishan, Wakashan, and Chimakuan languages of the Pacific Northwest region of North America. It was proposed by Edward Sapir in 1929 in the Encyclopædia Britannica. Little evidence has been adduced in favor of such a grouping, no progress has been made in reconstructing it, and it is now thought to reflect a language area rather than a genetic relationship. The term persists outside academic linguistic literature because of Sapir's stature.
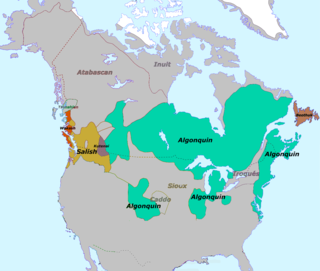
Algonquian–Wakashan is a hypothetical language family composed of several established language families that was proposed in 1929. The proposal consists of the following:

Chukotkan is a dialect cluster that forms one branch of the Chukotko-Kamchatkan language family. It is spoken in two autonomous regions at the extreme northeast of Russia, bounded on the east by the Pacific and on the north by the Arctic.

Kamchatkan (Kamchatic) is a former dialect cluster spoken on the Kamchatka Peninsula. It now consists of a single language, Western Itelmen. It had 100 or fewer speakers in 1991, mostly of the older generation. The Russian census of 2010 still reported 80 speakers.
Michael David Fortescue is a British-born linguist specializing in Arctic and native North American languages, including Kalaallisut, Inuktun, Chukchi and Nitinaht.
Proto-Chukotko-Kamchatkan is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Chukotko-Kamchatkan languages. It is purported to have broken up into the Northern (Chukotian) and Southern (Itelmen) branches around 2000 BCE, when western reindeer herders moved into the Chukotko-Kamchatkans' homeland and its inland people adopted the new lifestyle.
Siberian languages may refer to any languages spoken in Siberia, including:
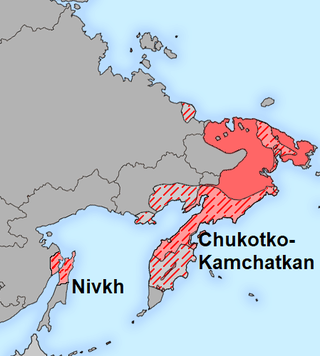
The Chukotko-Kamchatko-Amuric or Chukotko-Kamchatkan-Amuric languages form a hypothetical language family including Nivkh and Chukotko-Kamchatkan. A relationship between these two language groups was proposed by Michael Fortescue in a 2011 paper. He theorized that their common ancestor might have been spoken around 4000 years ago. However Glottolog says that the evidence is insufficient to conclude a genealogical relationship between Nivkh and Chukotko-Kamchatkan.