
The Dutch West India Company was a chartered company of Dutch merchants as well as foreign investors. Among its founders was Willem Usselincx (1567–1647) and Jessé de Forest (1576–1624). On 3 June 1621, it was granted a charter for a trade monopoly in the Dutch West Indies by the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands and given jurisdiction over Dutch participation in the Atlantic slave trade, Brazil, the Caribbean, and North America.

The British colonization of the Americas was the history of establishment of control, settlement, and colonization of the continents of the Americas by England, Scotland and, after 1707, Great Britain. Colonization efforts began in the 17th century with failed attempts by England to establish permanent colonies in the North. The first permanent English colony was established in Jamestown, Virginia in 1607. Approximately 30,000 Algonquian peoples lived in the region at the time. Over the next several centuries more colonies were established in North America, Central America, South America, and the Caribbean. Though most British colonies in the Americas eventually gained independence, some colonies have opted to remain under Britain's jurisdiction as British Overseas Territories.

New Spain, officially the Viceroyalty of New Spain, or Kingdom of New Spain, was an integral territorial entity of the Spanish Empire, established by Habsburg Spain during the Spanish colonization of the Americas and having its capital in Mexico City. Its jurisdiction comprised a huge area that included what is now Mexico, much of the Southwestern U.S. and California in North America; Central America, northern parts of South America, and several territorial Pacific Ocean archipelagos.
Ávila is a province of central-western Spain, in the southern part of the autonomous community of Castile and León. It is bordered on the south by the provinces of Toledo and Cáceres, on the west by Salamanca, on the north by Valladolid, and on the east by Segovia and Madrid. Ávila has a population of 158,265 (2018) and is ranked 47th out of 50 of Spanish provinces in population. Its capital is Ávila.

The Mosquito Coast, also known as the Mosquitia, Mosquito Shore and the Mosquito Kingdom, historically included the area along the eastern coast of present-day Nicaragua and Honduras. It formed part of the Western Caribbean Zone. It was named after the local Miskitu Nation and was long dominated by British interests. The Mosquito Coast was militarily incorporated into Nicaragua in November 1894; however, in 1960, the northern part was granted to Honduras by the International Court of Justice.

Throughout the history of the British Isles, the land that is now the United Kingdom has been a major music producer, drawing inspiration from church music and traditional folk music, using instruments of England, Scotland, Northern Ireland, and Wales. Each of the four countries of the United Kingdom has its own diverse and distinctive folk music forms, which flourished until the era of industrialisation when it began to be replaced by new forms of popular music, including music hall and brass bands. Many British musicians have influenced modern music on a global scale, and the UK has one of the world's largest music industries. British music such as British brass music and English, Scottish, Irish, and Welsh folk music directly and heavily influenced American music such as American folk music, American march music, old-time music, ragtime, blues, country music, and bluegrass. The UK has birthed many popular music genres such as beat music, power pop, psychedelic music, progressive rock and progressive pop, heavy metal, new wave, and electropop to name a few.
The Leeward Islands are a group of islands situated where the northeastern Caribbean Sea meets the western Atlantic Ocean. Starting with the Virgin Islands east of Puerto Rico, they extend southeast to Guadeloupe and its dependencies. In English, the term Leeward Islands refers to the northern islands of the Lesser Antilles chain. The more southerly part of this chain, starting with Dominica, is called the Windward Islands. Dominica was originally considered a part of the Leeward Islands, but was transferred from the British Leeward Islands to the British Windward Islands in 1940.

The Treaty of Nerchinsk of 1689 was the first treaty between the Tsardom of Russia and the Qing dynasty of China. The Russians gave up the area north of the Amur River as far as the Stanovoy Range and kept the area between the Argun River and Lake Baikal. This border along the Argun River and Stanovoy Range lasted until the Amur Annexation via the Treaty of Aigun in 1858 and the Convention of Peking in 1860. It opened markets for Russian goods in China, and gave Russians access to Chinese supplies and luxuries.

The Miskitos are a native people in Central America. Their territory extends from Cape Camarón, Honduras, to Río Grande de Matagalpa, Nicaragua, along the Mosquito Coast, in the Western Caribbean Zone. Their population is estimated at 700,000 people as of 2021 according to the official Miskito Database.

In Geography, the Caribbean Basin is generally defined as the area running from Florida westward along the Gulf coast, then south along the Mexican coast through Central America and then eastward across the northern coast of South America. This region includes the islands of the archipelago of the West Indies. Bermuda is also included within the region even though it is in the west-central Atlantic, due to its common cultural history created by European colonization of the region, and in most of the region by the presence of a significant group of African descent.

The Guianas, sometimes called by the Spanish loan-word Guayanas, is a region in north-eastern South America which includes the following three territories:

Mission San José de Tumacácori is a historic Spanish mission preserved in its present form by Franciscans in 1828.

The Alapaha River is a 202-mile-long (325 km) river in southern Georgia and northern Florida in the United States. It is a tributary of the Suwannee River, which flows to the Gulf of Mexico.
Domingo Francisco de San Antón Muñón Chimalpahin Quauhtlehuanitzin, usually referred to simply as Chimalpahin or Chimalpain, was a Nahua annalist from Chalco. His Nahuatl names mean "Runs Swiftly with a Shield" and "Rising Eagle", respectively, and he claimed descent from the lords of Tenango-Amecameca-Chalco. He was the grandson of the late Don Domingo Hernández Ayopochtzin, a seventh-generation descendant of the founding king of the polity. Don Domingo was learned and esteemed, especially for his education and his record-keeping skills in the ancient tradition.

The West Indies is a subregion of North America, surrounded by the North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea that includes 13 independent island countries and 18 dependencies and other territories in three major archipelagos: the Greater Antilles, the Lesser Antilles, and the Lucayan Archipelago.
The Halchidhoma are an Indian tribe now living mostly on the Salt River reservation, but formerly native to the area along the lower Colorado River in California and Arizona when first contacted by Europeans. In the early nineteenth century, under pressure from their hostile Mohave and Quechan neighbors, they moved to the middle Gila River, where some merged with the Maricopa, and others went on to Salt River and maintained an independent identity.

Moros is a municipality in the province of Zaragoza, Aragon. Its population was 304 in 2021.

The General Crisis is a term used by some historians to describe an alleged period of widespread global conflict and instability that occurred from the early 17th century to the early 18th century in Europe, and in more recent historiography in the world at large.
The western Caribbean zone is a region consisting of the Caribbean coasts of Central America and Colombia, from the Yucatán Peninsula in southern Mexico to the Caribbean region in northern Colombia, and the islands west of Jamaica are also included. The zone emerged in the late sixteenth century as the Spanish failed to completely conquer many sections of the coast, and northern European powers supported opposition to Spain, sometimes through alliances with local powers.
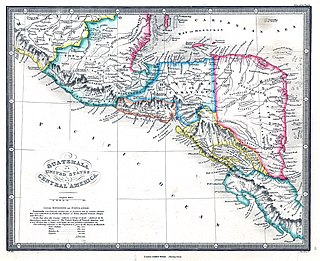
The Province ofTaguzgalpa, also called New Cartago, was created by Royal Order of February 10, 1576. The entire province stretched from east of Trujillo, or the Aguan or Roman River, as far as the San Juan River, but was believed to be only from the east of Trujillo to the Wanks or Coco River. It also included the Province of Tologalpa, which stretched from the Coco River to the San Juan River. It was bordered to the north and east by the Caribbean Sea; by the south by the Province of Costa Rica; and by the west by the Province of Honduras and Province of Nicaragua. It appeared on the Dutch map of Montanus in 1671 with an alternate spelling of "Tiguzigalpa."
















