
A commodity market is a market that trades in the primary economic sector rather than manufactured products, such as cocoa, fruit and sugar. Hard commodities are mined, such as gold and oil. Futures contracts are the oldest way of investing in commodities. Commodity markets can include physical trading and derivatives trading using spot prices, forwards, futures, and options on futures. Farmers have used a simple form of derivative trading in the commodity market for centuries for price risk management.
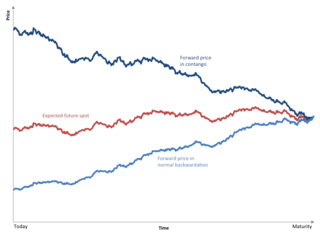
Contango is a situation where the futures price of a commodity is higher than the expected spot price of the contract at maturity. In a contango situation, arbitrageurs or speculators are "willing to pay more [now] for a commodity [to be received] at some point in the future than the actual expected price of the commodity [at that future point]. This may be due to people's desire to pay a premium to have the commodity in the future rather than paying the costs of storage and carry costs of buying the commodity today." On the other side of the trade, hedgers are happy to sell futures contracts and accept the higher-than-expected returns. A contango market is also known as a normal market, or carrying-cost market.

The derivatives market is the financial market for derivatives, financial instruments like futures contracts or options, which are derived from other forms of assets.

A hedge is an investment position intended to offset potential losses or gains that may be incurred by a companion investment. A hedge can be constructed from many types of financial instruments, including stocks, exchange-traded funds, insurance, forward contracts, swaps, options, gambles, many types of over-the-counter and derivative products, and futures contracts.
The forward market is the informal over-the-counter financial market by which contracts for future delivery are entered into. It is mainly used for trading in foreign currencies, where the contracts are used to hedge against foreign exchange risk. Commodities are also traded on forward markets. Examples include agricultural products such as rice, and energy futures, such as oil and natural gas. Transactions on a forward market are typically not standardized, and contracts are customised to the needs of the trading parties. In contrast, standardized forward contracts are called futures contracts and traded on a futures exchange.

The Commodity Futures Modernization Act of 2000 (CFMA) is United States federal legislation that ensured financial products known as over-the-counter (OTC) derivatives remained unregulated. It was signed into law on December 21, 2000 by President Bill Clinton. It clarified the law so most OTC derivative transactions between "sophisticated parties" would not be regulated as "futures" under the Commodity Exchange Act of 1936 (CEA) or as "securities" under the federal securities laws. Instead, the major dealers of those products would continue to have their dealings in OTC derivatives supervised by their federal regulators under general "safety and soundness" standards. The Commodity Futures Trading Commission's (CFTC) desire to have "functional regulation" of the market was also rejected. Instead, the CFTC would continue to do "entity-based supervision of OTC derivatives dealers". The CFMA's treatment of OTC derivatives such as credit default swaps has become controversial, as those derivatives played a major role in the financial crisis of 2008 and the subsequent 2008–2012 global recession.
In finance, a contract for difference (CFD) is a legally binding agreement that creates, defines, and governs mutual rights and obligations between two parties, typically described as "buyer" and "seller", stipulating that the buyer will pay to the seller the difference between the current value of an asset and its value at contract time. If the closing trade price is higher than the opening price, then the seller will pay the buyer the difference, and that will be the buyer’s profit. The opposite is also true. That is, if the current asset price is lower at the exit price than the value at the contract’s opening, then the seller, rather than the buyer, will benefit from the difference.
Crack spread is a term used on the oil industry and futures trading for the differential between the price of crude oil and petroleum products extracted from it. The spread approximates the profit margin that an oil refinery can expect to make by "cracking" the long-chain hydrocarbons of crude oil into useful shorter-chain petroleum products.
An energy derivative is a derivative contract based on an underlying energy asset, such as natural gas, crude oil, or electricity. Energy derivatives are exotic derivatives and include exchange-traded contracts such as futures and options, and over-the-counter derivatives such as forwards, swaps and options. Major players in the energy derivative markets include major trading houses, oil companies, utilities, and financial institutions.

The Kansas City Board of Trade (KCBT), was an American commodity futures and options exchange regulated by the Commodity Futures Trading Commission. Specializing in the hard-red winter wheat contract, it was located at 4800 Main Street in Kansas City, Missouri.

StoneX Group Inc. is a financial services organization. The company operates in six areas: commercial hedging, global payments, securities, physical commodities, foreign exchange and clearing and execution services (CES). The company ranked No. 58 in the 2021 Fortune 500 list of the largest United States corporations by total revenue. In July 2020, the company rebranded and changed its name to StoneX Group Inc.

Intercontinental Exchange, Inc. (ICE) is an American company formed in 2000 that operates global financial exchanges and clearing houses and provides mortgage technology, data and listing services. Listed on the Fortune 500, S&P 500, and Russell 1000, the company owns exchanges for financial and commodity markets, and operates 12 regulated exchanges and marketplaces. This includes ICE futures exchanges in the United States, Canada and Europe, the Liffe futures exchanges in Europe, the New York Stock Exchange, equity options exchanges and OTC energy, credit and equity markets.
A master's degree in quantitative finance concerns the application of mathematical methods to the solution of problems in financial economics. There are several like-titled degrees which may further focus on financial engineering, computational finance, mathematical finance, and/or financial risk management.

Mercuria Energy Group Ltd is a Cypriot-domiciled multinational commodity trading company active in a wide spectrum of global energy markets including crude oil and refined petroleum products, natural gas, power, biodiesel, base metals and agricultural products. The company is one of the world's five largest independent energy traders and asset operators and is based in Geneva, Switzerland, with 37 additional offices worldwide. The group operates in 50 different countries.
Weather risk management is a type of risk management done by organizations to address potential financial losses caused by unusual weather.

Sean O'Brien Cota is an American businessman, energy market expert, financial commentator, and policy advisor on American energy and financial market transparency and reform measures. As the President of a third generation family-owned oil company, Cota & Cota Oil, Inc. in Bellows Falls, VT, whom he has worked for since 1977, he became extremely involved in energy commodity trading in 1988. In 2010, he was named Chairman of the Petroleum Marketers Association of America.
Danske Commodities (DC) is an energy trading house. The company is an international trader of energy-related commodities such as electric power, gas and climate market products with activities in 40 countries.

Richard L. Sandor is an American businessman, economist, and entrepreneur. He is chairman and CEO of the American Financial Exchange (AFX) established in 2015, which is an electronic exchange for direct interbank/financial institution lending and borrowing. The AFX flagship product, the AMERIBOR benchmark index, reflects the actual borrowing costs of thousands of regional and community banks across the U.S. and is one of the short-term borrowing rates, along with the Secured Overnight Financing Rate, vying to replace U.S. dollar Libor as a benchmark in the U.S.
Live cattle is a type of futures contract that can be used to hedge and to speculate on fed cattle prices. Cattle producers, feedlot operators, and merchant exporters can hedge future selling prices for cattle through trading live cattle futures, and such trading is a common part of a producer's price risk management program. Conversely, meat packers, and merchant importers can hedge future buying prices for cattle. Producers and buyers of live cattle can also enter into production and marketing contracts for delivering live cattle in cash or spot markets that include futures prices as part of a reference price formula. Businesses that purchase beef as an input could also hedge beef price risk by purchasing live cattle futures contracts.







