Related Research Articles

Acoustics is a branch of physics that deals with the study of mechanical waves in gases, liquids, and solids including topics such as vibration, sound, ultrasound and infrasound. A scientist who works in the field of acoustics is an acoustician while someone working in the field of acoustics technology may be called an acoustical engineer. The application of acoustics is present in almost all aspects of modern society with the most obvious being the audio and noise control industries.

Sonar is a technique that uses sound propagation to navigate, measure distances (ranging), communicate with or detect objects on or under the surface of the water, such as other vessels.
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hear it. This limit varies from person to person and is approximately 20 kilohertz in healthy young adults. Ultrasound devices operate with frequencies from 20 kHz up to several gigahertz.
A hydrophone is a microphone designed to be used underwater for recording or listening to underwater sound. Most hydrophones are based on a piezoelectric transducer that generates an electric potential when subjected to a pressure change, such as a sound wave. Some piezoelectric transducers can also serve as a sound projector, but not all have this capability, and some may be destroyed if used in such a manner.

Echo sounding or depth sounding is the use of sonar for ranging, normally to determine the depth of water (bathymetry). It involves transmitting acoustic waves into water and recording the time interval between emission and return of a pulse; the resulting time of flight, along with knowledge of the speed of sound in water, allows determining the distance between sonar and target. This information is then typically used for navigation purposes or in order to obtain depths for charting purposes.

A bulbous bow is a protruding bulb at the bow of a ship just below the waterline. The bulb modifies the way the water flows around the hull, reducing drag and thus increasing speed, range, fuel efficiency, and stability. Large ships with bulbous bows generally have twelve to fifteen percent better fuel efficiency than similar vessels without them. A bulbous bow also increases the buoyancy of the forward part and hence reduces the pitching of the ship to a small degree.

A fishfinder or sounder (Australia) is an instrument used to locate fish underwater by detecting reflected pulses of sound energy, as in sonar. A modern fishfinder displays measurements of reflected sound on a graphical display, allowing an operator to interpret information to locate schools of fish, underwater debris, and the bottom of body of water. Fishfinder instruments are used both by sport and commercial fishermen. Modern electronics allows a high degree of integration between the fishfinder system, marine radar, compass and GPS navigation systems.
A scientific echosounder is a device which uses sonar technology for the measurement of underwater physical and biological components—this device is also known as scientific sonar. Applications include bathymetry, substrate classification, studies of aquatic vegetation, fish, and plankton, and differentation of water masses.
Sound from ultrasound is the name given here to the generation of audible sound from modulated ultrasound without using an active receiver. This happens when the modulated ultrasound passes through a nonlinear medium which acts, intentionally or unintentionally, as a demodulator.

A multibeam echosounder (MBES) is a type of sonar that is used to map the seabed. It emits acoustic waves in a fan shape beneath its transceiver. The time it takes for the sound waves to reflect off the seabed and return to the receiver is used to calculate the water depth. Unlike other sonars and echo sounders, MBES uses beamforming to extract directional information from the returning soundwaves, producing a swath of depth soundings from a single ping.

Underwater acoustics or hydroacoustics is the study of the propagation of sound in water and the interaction of the mechanical waves that constitute sound with the water, its contents and its boundaries. The water may be in the ocean, a lake, a river or a tank. Typical frequencies associated with underwater acoustics are between 10 Hz and 1 MHz. The propagation of sound in the ocean at frequencies lower than 10 Hz is usually not possible without penetrating deep into the seabed, whereas frequencies above 1 MHz are rarely used because they are absorbed very quickly.

Frederick Vinton Hunt was an inventor, a scientist and a professor at Harvard University who worked in the field of acoustic engineering.
Salvage diving is the diving work associated with the recovery of all or part of ships, their cargoes, aircraft, and other vehicles and structures which have sunk or fallen into water. In the case of ships it may also refer to repair work done to make an abandoned or distressed but still floating vessel more suitable for towing or propulsion under its own power. The recreational/technical activity known as wreck diving is generally not considered salvage work, though some recovery of artifacts may be done by recreational divers.

The interactions between marine mammals and sonar have been a subject of debate since the invention of the technology.
An underwater acoustic positioning system is a system for the tracking and navigation of underwater vehicles or divers by means of acoustic distance and/or direction measurements, and subsequent position triangulation. Underwater acoustic positioning systems are commonly used in a wide variety of underwater work, including oil and gas exploration, ocean sciences, salvage operations, marine archaeology, law enforcement and military activities.
A Fessenden oscillator is an electro-acoustic transducer invented by Reginald Fessenden, with development starting in 1912 at the Submarine Signal Company of Boston. It was the first successful acoustical echo ranging device. Similar in operating principle to a dynamic voice coil loudspeaker, it was an early kind of transducer, capable of creating underwater sounds and of picking up their echoes.
A sound velocity probe is a device that is used for measuring the speed of sound, specifically in the water column, for oceanographic and hydrographic research purposes.

Frank Massa (1906–1990) was an American engineer who contributed greatly to the development of the field of acoustical engineering. He is perhaps best known for the development of recorded sound technology for the motion picture industry and, during World War II, the development of the first towed sonar transducers and hydrophones used by the U.S. Navy to detect and defeat German U-boat submarines.
Ultrasonic antifouling is a technology that uses high frequency sound (ultrasound) to prevent or reduce biofouling on underwater structures, surfaces, and medium. Ultrasound is just high frequency sound. Ultrasound has the same physical properties as human-audible sound. The method has two primary forms: sub-cavitation intensity and cavitation intensity. Sub-cavitation methods create high frequency vibrations, whilst cavitation methods cause more destructive microscopic pressure changes. Both methods inhibit or prevent biofouling by algae and other single-celled organisms.
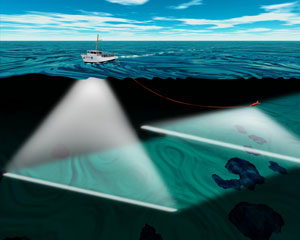
An underwater survey is a survey performed in an underwater environment or conducted remotely on an underwater object or region. Survey can have several meanings. The word originates in Medieval Latin with meanings of looking over and detailed study of a subject. One meaning is the accurate measurement of a geographical region, usually with the intention of plotting the positions of features as a scale map of the region. This meaning is often used in scientific contexts, and also in civil engineering and mineral extraction. Another meaning, often used in a civil, structural, or marine engineering context, is the inspection of a structure or vessel to compare actual condition with the specified nominal condition, usually with the purpose of reporting on the actual condition and compliance with, or deviations from, the nominal condition, for quality control, damage assessment, valuation, insurance, maintenance, and similar purposes. In other contexts it can mean inspection of a region to establish presence and distribution of specified content, such as living organisms, either to establish a baseline, or to compare with a baseline.
References
- ↑ Wilson, O. B. (1988). Introduction to Theory and Design of Sonar Transducers. Peninsula Publishing.
- ↑ EP 0473480,"Electroacoustic transducer for use under water and comprising a system for automatically compensating the hydrostatic pressure"