
Training is teaching, or developing in oneself or others, any skills and knowledge or fitness that relate to specific useful competencies. Training has specific goals of improving one's capability, capacity, productivity and performance. It forms the core of apprenticeships and provides the backbone of content at institutes of technology. In addition to the basic training required for a trade, occupation or profession, training may continue beyond initial competence to maintain, upgrade and update skills throughout working life. People within some professions and occupations may refer to this sort of training as professional development. Training also refers to the development of physical fitness related to a specific competence, such as sport, martial arts, military applications and some other occupations.

Carpentry is a skilled trade and a craft in which the primary work performed is the cutting, shaping and installation of building materials during the construction of buildings, ships, timber bridges, concrete formwork, etc. Carpenters traditionally worked with natural wood and did rougher work such as framing, but today many other materials are also used and sometimes the finer trades of cabinetmaking and furniture building are considered carpentry. In the United States, 98.5% of carpenters are male, and it was the fourth most male-dominated occupation in the country in 1999. In 2006 in the United States, there were about 1.5 million carpentry positions. Carpenters are usually the first tradesmen on a job and the last to leave. Carpenters normally framed post-and-beam buildings until the end of the 19th century; now this old-fashioned carpentry is called timber framing. Carpenters learn this trade by being employed through an apprenticeship training—normally 4 years—and qualify by successfully completing that country's competence test in places such as the United Kingdom, the United States, Canada, Switzerland, Australia and South Africa. It is also common that the skill can be learned by gaining work experience other than a formal training program, which may be the case in many places.
A national qualifications framework is a formal system describing qualifications. 47 countries participating in the Bologna Process are committed to producing a national qualifications framework. Other countries not part of this process also have national qualifications frameworks.

SME is a non-profit student and professional association for educating and advancing the manufacturing industry in North America.
Skills management is the practice of understanding, developing and deploying people and their skills. Well-implemented skills management should identify the skills that job roles require, the skills of individual employees, and any gap between the two.
Digital literacy refers to an individual's ability to find, evaluate, and communicate information through typing and other media on various digital platforms. It is evaluated by an individual's grammar, composition, typing skills and ability to produce text, images, audio and designs using technology. The American Library Association (ALA) defines digital literacy as "the ability to use information and communication technologies to find, evaluate, create, and communicate information, requiring both cognitive and technical skills." While digital literacy initially focused on digital skills and stand-alone computers, the advent of the internet and use of social media, has resulted in the shift in some of its focus to mobile devices. Similar to other expanding definitions of literacy that recognise cultural and historical ways of making meaning, digital literacy does not replace traditional forms of literacy, but instead builds upon and expands the skills that form the foundation of traditional forms of literacy. Digital literacy should be considered to be a part of the path to knowledge.
The Workforce Skills Qualifications (WSQ) system is a national continuing education and training system designed for adult workers in Singapore, complementing the formal education system for students. WSQ training is accessible to all workers and does not require academic pre-requisites. The WSQ provides training for skills upgrading and also recognition and certification of workers' existing skills. There are seven qualification levels from basic Certificate to graduate Diploma and these spell out the upgrading and career advancement pathways for workers. Workers can also be certified with Statements of Attainment for individual modules to fill gaps in their skills.
The National Skill Standards Board (NSSB) was a coalition of community, business, labor, education, and civil rights leaders. It was tasked with building a national voluntary system of skill standards, assessment, and certification to enhance the ability of the United States workforce to compete effectively in the global economy.
Career Pathways is a workforce development strategy used in the United States to support workers’ transitions from education into and through the workforce. This strategy has been adopted at the federal, state and local levels in order to increase education, training and learning opportunities for America’s current and emerging workforce.

The Workplace Safety and Health Council(WSHC) is an industry-led statutory body in Singapore responsible for the encouragement, regulation and enforcement of workplace health, safety and welfare. The WSHC can be considered as a successor institution to the Workplace Safety and Health Advisory Committee (WSHAC), which was formed in September 2005.

The Mining Industry Human Resources Council (MiHR) is a not-for-profit organization that drives collaboration among mining and exploration companies, organized labour, contractors, educational institutions, industry associations and Indigenous groups to identify opportunities and address the human resource and labour market challenges facing the Canadian minerals and metals sector. MiHR contributes to the sustainability of the Canadian mining sector by collaborating with its stakeholders and communities of interest, to develop solutions tailored to human resources needs in the mining sector. Its vision is to build a diverse, sustainable, safe and skilled Canadian Mining workforce that is recognized globally.
Registered Apprenticeship is a program of the United States Department of Labor that connects job seekers looking to learn new skills with employers looking for qualified workers. Employers, employer associations, and joint labor-management organizations, known collectively as "sponsors", provide apprentices with paid on-the-job learning and academic instruction that reflects industry needs. The goal of such instruction is to provide workers with advanced skillsets that meet the specific needs of their employers.
Vocational education is that form of instruction designed to prepare people for industrial or commercial employment. It can be acquired either formally in trade schools, technical secondary schools, or in on-the-job training programs or, more informally, by picking up the necessary skills on the job.
Industrial and production engineering (IPE) is an interdisciplinary engineering discipline that includes manufacturing technology, engineering sciences, management science, and optimization of complex processes, systems, or organizations. It is concerned with the understanding and application of engineering procedures in manufacturing processes and production methods. Industrial engineering dates back all the way to the industrial revolution, initiated in 1700s by Sir Adam Smith, Henry Ford, Eli Whitney, Frank Gilbreth and Lilian Gilbreth, Henry Gantt, F.W. Taylor, etc. After the 1970s, industrial and production engineering developed worldwide and started to widely use automation and robotics. Industrial and production engineering includes three areas: Mechanical engineering, industrial engineering, and management science.
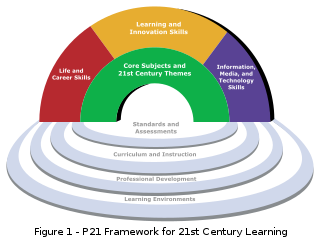
21st century skills comprise skills, abilities, and learning dispositions that have been identified as being required for success in 21st century society and workplaces by educators, business leaders, academics, and governmental agencies. This is part of a growing international movement focusing on the skills required for students to master in preparation for success in a rapidly changing, digital society. Many of these skills are also associated with deeper learning, which is based on mastering skills such as analytic reasoning, complex problem solving, and teamwork. These skills differ from traditional academic skills in that they are not primarily content knowledge-based.

Fabricators & Manufacturers Association, International (FMA) is a 501(c)3 nonprofit professional association serving both company and individual members in the metal processing, forming, and fabricating industries.
The National Policy on Skill Development is an umbrella framework devised by the Government of India to develop employable skills among the youth of the country through learning and producing workers adequately skilled to meet the requirements of industry. India has traditionally had a lower percentage of population of appropriately skilled workers comparable to other economies of the world. In its 11th five-year plan for the financial year 2007-12 suggested actions to increase the skilled workforce in the country to 15 million annually and targeted to skill 150 million people by 2022. In line with the recommendations in the five-year plan and to mitigate the challenges faced by the economy of the shortage of the skilled workforce. The government formulated a skill development policy in 2009, with emphasis given to special courses to be imparted through Industrial Training Institutes in partnership with the private sector.
Apprenticeships have a long tradition in the United Kingdom, dating back to around the 12th century. They flourished in the 14th century and were expanded during the industrial revolution. In modern times, apprenticeships were formalised in 1964 by act of parliament and they continue to be in widespread use to this day.
Apprenticeship programs in the United States are regulated by the Smith–Hughes Act (1917), The National Industrial Recovery Act (1933), and National Apprenticeship Act, also known as the "Fitzgerald Act."
Skilled through alternative routes (STAR) is a term to describe adults in the United States without bachelor's degrees who have work experience and skills that position them for transitions to higher-wage jobs. First identified in a 2020 research paper in the National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER), STARs made up approximately 70 million workers in the U.S. economy as of 2021.






