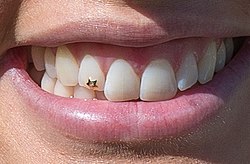
A tooth gem is a gemstone glued onto the enamel of a person's tooth. It can be a single gemstone, or multiple arranged into shapes. They are semi-permanent, lasting from several months to several years. [1] [2] [3] [4] Over time the bond between the tooth and an improperly applied gem may weaken, creating a gap which cannot be cleaned, allowing bacteria to accumulate and can eventually lead to tooth decay.[ citation needed ] Tooth gems cannot be placed on veneers as they are too smooth. [3]