
Adobe Flash is a multimedia software platform used for production of animations, rich web applications, desktop applications, mobile apps, mobile games, and embedded web browser video players. Flash displays text, vector graphics, and raster graphics to provide animations, video games, and applications. It allows streaming of audio and video, and can capture mouse, keyboard, microphone, and camera input.
An HTML editor is a program for editing HTML, the markup of a web page. Although the HTML markup in a web page can be controlled with any text editor, specialized HTML editors can offer convenience and added functionality. For example, many HTML editors handle not only HTML, but also related technologies such as CSS, XML and JavaScript or ECMAScript. In some cases they also manage communication with remote web servers via FTP and WebDAV, and version control systems such as Subversion or Git. Many word processing, graphic design and page layout programs that are not dedicated to web design, such as Microsoft Word or Quark XPress, also have the ability to function as HTML editors.

Adobe Dreamweaver is a proprietary web development tool from Adobe Inc. It was created by Macromedia in 1997 and developed by them until Macromedia was acquired by Adobe Systems in 2005.

A favicon, also known as a shortcut icon, website icon, tab icon, URL icon, or bookmark icon, is a file containing one or more small icons, associated with a particular website or web page. A web designer can create such an icon and upload it to a website by several means, and graphical web browsers will then make use of it. Browsers that provide favicon support typically display a page's favicon in the browser's address bar and next to the page's name in a list of bookmarks. Browsers that support a tabbed document interface typically show a page's favicon next to the page's title on the tab, and site-specific browsers use the favicon as a desktop icon.
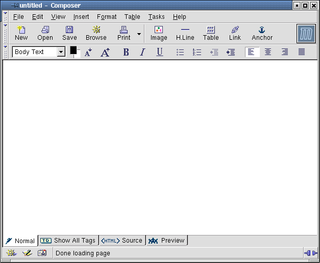
Mozilla Composer is the free and open-source HTML editor and web authoring module of the Mozilla Application Suite. It is used to create and to edit web pages, e-mail, and text documents easily. It is compatible with Windows, macOS and Linux. Composer is a graphical WYSIWYG HTML editor. One also can view, write and edit HTML source code with Composer.

HomeSite was an HTML editor originally developed by Nick Bradbury. Unlike WYSIWYG HTML editors such as FrontPage and Dreamweaver, HomeSite was designed for direct editing, or "hand coding", of HTML and other website languages.
Mozilla Firefox has features that allow it to be distinguished from other web browsers, such as Chrome and Internet Explorer.

Acid2 is a webpage that test web browsers' functionality in displaying aspects of HTML markup, CSS 2.1 styling, PNG images, and data URIs. The test page was released on 13 April 2005 by the Web Standards Project. The Acid2 test page will be displayed correctly in any application that follows the World Wide Web Consortium and Internet Engineering Task Force specifications for these technologies. These specifications are known as web standards because they describe how technologies used on the web are expected to function.

Microsoft developed 11 versions of Internet Explorer for Windows from 1995 to 2013. Microsoft also developed Internet Explorer for Mac, Internet Explorer for UNIX, and Internet Explorer Mobile respectively for Apple Macintosh, Unix, and mobile devices; the first two are discontinued but the latter runs on Windows CE, Windows Mobile, and Windows Phone.
The following tables compare general and technical information for a number of HTML editors.
In computing, quirks mode is a technique used by some web browsers for the sake of maintaining backward compatibility with web pages designed for old web browsers instead of strictly complying with W3C and IETF standards in standards mode. This behavior has since been codified in the standard, so what was previously standards mode is now referred to as simply no quirks mode.

Microsoft Expression Web is a discontinued HTML editor and general web design software product by Microsoft. It was discontinued on December 20, 2012, and subsequently made available free of charge from Microsoft. It was a component of the also discontinued Expression Studio.

The Acid3 test is a web test page from the Web Standards Project that checks a web browser's compliance with elements of various web standards, particularly the Document Object Model (DOM) and JavaScript.

Internet Explorer 9 or IE9 is a web browser for Windows. It was released by Microsoft on March 14, 2011, as the ninth version of Internet Explorer and the successor to Internet Explorer 8, and can replace previous versions of Internet Explorer on Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008, Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 but unlike its predecessor, this version does not support Windows XP and Windows Server 2003. It and older versions of Internet Explorer are no longer supported on any Microsoft OS except Windows Server 2008 SP2. Microsoft released Internet Explorer 9 as a major out-of-band version that was not tied to the release schedule of any particular version of Windows, unlike previous versions. It is the first version of Internet Explorer not to be bundled with a Windows operating system, although some OEMs have installed it with Windows 7 on their PCs, as well as new Windows 7 laptops.
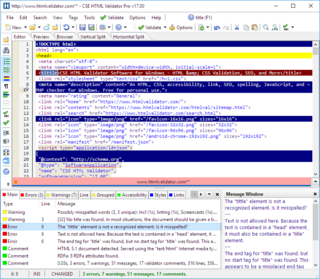
CSS HTML Validator is an HTML editor and CSS editor for Windows that helps web developers create syntactically correct and accessible HTML, XHTML, and CSS documents by locating errors, potential problems, and common mistakes. It is also able to check links, suggest improvements, alert developers to deprecated, obsolete, or proprietary tags, attributes, and CSS properties, and find issues that can affect search engine optimization.
Modern HTML5 has feature-parity with the now-obsolete Adobe Flash. Both include features for playing audio and video within web pages. Flash was specifically built to integrate vector graphics and light games in a web page, features that HTML5 also supports.
Encrypted Media Extensions (EME) is a W3C specification for providing a communication channel between web browsers and the Content Decryption Module (CDM) software which implements digital rights management (DRM). This allows the use of HTML5 video to play back DRM-wrapped content such as streaming video services without the use of heavy third-party media plugins like Adobe Flash or Microsoft Silverlight. The use of a third-party key management system may be required, depending on whether the publisher chooses to scramble the keys.

Nick Bradbury is an American software developer and entrepreneur. Bradbury is noted for creating the early web-development editors HomeSite and TopStyle, and FeedDemon, the RSS news aggregator for Microsoft Windows. Currently, he is a mobile developer at the software company Automattic. He is a graduate of the University of Tennessee, Knoxville and currently resides in Knoxville, Tennessee.









