
The recorded history of the lands of what today is known as Catalonia begins with the development of the Iberian peoples while several Greek colonies were established on the coast before the Roman conquest. It was the first area of Hispania conquered by the Romans. It then came under Visigothic rule after the collapse of the western part of the Roman Empire. In 718, the area was occupied by the Umayyad Caliphate and became a part of Muslim ruled al-Andalus. The Frankish Empire conquered northern half of the area from the Muslims, ending with the conquest of Barcelona in 801, as part of the creation of a larger buffer zone of Christian counties against Islamic rule historiographically known as the Marca Hispanica. In the 10th century the County of Barcelona became progressively independent from Frankish rule.

The Catalan Countries are those territories where the Catalan language is spoken. They include the Spanish regions of Catalonia, the Balearic Islands, Valencian Community, and parts of Aragon and Murcia (Carche), as well as the Principality of Andorra, the department of Pyrénées-Orientales in France, and the city of Alghero in Sardinia (Italy). It is often used as a sociolinguistic term to describe the cultural-linguistic area where Catalan is spoken. In the context of Catalan nationalism, the term is sometimes used in a more restricted way to refer to just Catalonia, Valencia and the Balearic Islands. The Catalan Countries do not correspond to any present or past political or administrative unit, though most of the area belonged to the Crown of Aragon in the Middle Ages. Parts of Valencia (Spanish) and Catalonia (Occitan) are not Catalan-speaking.
The Republican Left of Catalonia is a pro-Catalan independence, social democratic political party in the Spanish autonomous community of Catalonia, with a presence also in Valencia, the Balearic Islands and the French department of Pyrénées-Orientales. It is also the main sponsor of the independence movement from France and Spain in the territories known as Catalan Countries, focusing in recent years on the creation of a Catalan Republic in Catalonia proper. Its current president is Oriol Junqueras and its secretary-general is Marta Rovira. The party is a member of the European Free Alliance.

The Senyera is a vexillological symbol based on the coat of arms of the Crown of Aragon, which consists of four red stripes on a yellow field. This coat of arms, often called bars of Aragon, or simply "the four bars", historically represented the King of the Crown of Aragon.

The Crown of Aragon was a composite monarchy ruled by one king, originated by the dynastic union of the Kingdom of Aragon and the County of Barcelona and ended as a consequence of the War of the Spanish Succession. At the height of its power in the 14th and 15th centuries, the Crown of Aragon was a thalassocracy controlling a large portion of present-day eastern Spain, parts of what is now southern France, and a Mediterranean empire which included the Balearic Islands, Sicily, Corsica, Sardinia, Malta, Southern Italy, and parts of Greece.

Catalans are a Romance ethnic group native to Catalonia, who speak Catalan. The current official category of "Catalans" is that of the citizens of Catalonia, an autonomous community in Spain and the inhabitants of the Roussillon historical region in southern France, today the Pyrénées Orientales department, also called Northern Catalonia and Pays Catalan in French.

The Principality of Catalonia was a medieval and early modern state in the northeastern Iberian Peninsula. During most of its history it was in dynastic union with the Kingdom of Aragon, constituting together the Crown of Aragon. Between the 13th and the 18th centuries, it was bordered by the Kingdom of Aragon to the west, the Kingdom of Valencia to the south, the Kingdom of France and the feudal lordship of Andorra to the north and by the Mediterranean Sea to the east. The term Principality of Catalonia was official until the 1830s, when the Spanish government implemented the centralized provincial division, but remained in popular and informal contexts. Today, the term Principat (Principality) is used primarily to refer to the autonomous community of Catalonia in Spain, as distinct from the other Catalan Countries, and usually including the historical region of Roussillon in Southern France.

The Reapers' War, also known as the Catalan Revolt, was a conflict that affected the Principality of Catalonia between the years of 1640 and 1659. It had an enduring effect in the Treaty of the Pyrenees (1659), which ceded the County of Roussillon and the northern half of the County of Cerdanya to France, splitting these northern Catalan territories off from the Principality of Catalonia and the Crown of Aragon, and thereby receding the borders of Spain to the Pyrenees.

The Catalan constitutions were the laws of the Principality of Catalonia promulgated by the Count of Barcelona and approved by the Catalan Courts. The Corts in Catalan have the same origin as courts in English but instead meaning the legislature. The first constitutions were promulgated by the Corts of 1283. The last ones were promulgated by the Corts of 1705. They had pre-eminence over the other legal rules and could only be revoked by the Catalan Courts themselves. The compilations of the constitutions and other rights of Catalonia followed the Roman tradition of the Codex.

Communist Movement was a political party in Spain. It was founded in 1972 as Movimiento Comunista de España (MCE).

Valentí Almirall i Llozer was a Catalan politician, considered one of the fathers of modern Catalan nationalism, and more specifically, of the left-wing variety.

United Left is a federative political movement in Spain that was first organized as a coalition in 1986, bringing together several left-wing political organizations, most notably the Communist Party of Spain.

The General Archive of the Crown of Aragon, originally Royal Archives of Barcelona, is an archive containing the background documents of the institutions of the former Crown of Aragon and currently also contains other historical resources.

The conquest of the island of Majorca on behalf of the Roman Catholic kingdoms was carried out by King James I of Aragon between 1229 and 1231. The pact to carry out the invasion, concluded between James I and the ecclesiastical and secular leaders, was ratified in Tarragona on 28 August 1229. It was open and promised conditions of parity for all who wished to participate.

The Catalan Courts or General Court of Catalonia were the policymaking and parliamentary body of the Principality of Catalonia from the 13th to the 18th century.
The 1931 Spanish local elections were held on 12 April throughout all municipalities in Spain to elect 80,472 councillors. The elections were perceived as a plebiscite on the monarchy of Alfonso XIII. After republican parties and their allies came away with a convincing victory, the king left the country and the Second Spanish Republic was proclaimed. A provisional government was formed shortly thereafter, with national elections scheduled for later in the year.

The Pacte Progressista, officially the Pacte Progressista d'Eivissa, is an electoral alliance formed in Ibiza by the Socialist Party of the Balearic Islands, United Left of Ibiza, The Greens of Ibiza, Entesa Nacionalista i Ecologista and Republican Left of Catalonia to contest the 1999 and 2003 regional elections. Previously, it had contested the 1996 Senate election in the Ibiza–Formentera constituency as Eivissa i Formentera al Senat, and it would also contest the 2000 Senate election as the Pacte per Eivissa i Formentera.
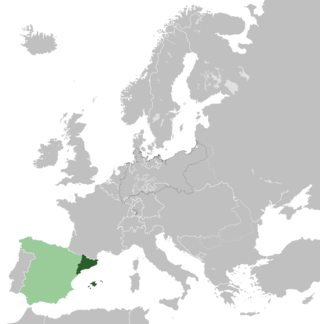
The Catalan State was a short-lived state proclaimed in 1873, during the First Spanish Republic, by the Provincial Deputation of Barcelona. It included the four provinces of Catalonia and the Balearic Islands.

Federalism in Spain began in the 1830s, although it has its roots in the 1790s. The first and only attempt to establish a federal state in Spain occurred during the First Spanish Republic (1873-1874). After this failure, federalism was a minority political current. In the Second Spanish Republic and in the Transition, an intermediate model was chosen between federalism and centralism — the integral state, in the first case; and the regional state in the second.
The history of the territorial organization of Spain, in the modern sense, is a process that began in the 16th century with the dynastic union of the Crown of Aragon and the Crown of Castile, the conquest of the Kingdom of Granada and later the Kingdom of Navarre. However, it is important to clarify the origin of the toponym Spain, as well as the territorial divisions that existed previously in the current Spanish territory.
















