Related Research Articles

Peroxyacetyl nitrate is a peroxyacyl nitrate. It is a secondary pollutant present in photochemical smog. It is thermally unstable and decomposes into peroxyethanoyl radicals and nitrogen dioxide gas. It is a lachrymatory substance, meaning that it irritates the lungs and eyes.

Global dimming is a decline in the amount of sunlight reaching the Earth's surface. It is caused by atmospheric particulate matter, predominantly sulfate aerosols, which are components of air pollution. Global dimming was observed soon after the first systematic measurements of solar irradiance began in the 1950s. This weakening of visible sunlight proceeded at the rate of 4–5% per decade until the 1980s. During these years, air pollution increased due to post-war industrialization. Solar activity did not vary more than the usual during this period.

MOPITT is an ongoing astronomical instrument aboard NASA's Terra satellite that measures global tropospheric carbon monoxide levels. It is part of NASA's Earth Observing System (EOS), and combined with the other payload remote sensors on the Terra satellite, the spacecraft monitors the Earth's environment and climate changes. Following its construction in Canada, MOPITT was launched into Earth's orbit in 1999 and utilizes gas correlation spectroscopy to measure the presence of different gases in the troposphere. The fundamental operations occur in its optical system composed of two optical tables holding the bulk of the apparatus. Results from the MOPITT enable scientists to better understand carbon monoxide's effects on a global scale, and various studies have been conducted based on MOPITT's measurements.
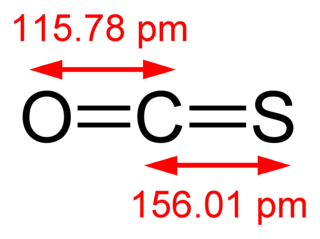
Carbonyl sulfide is the chemical compound with the linear formula O=C=S. It is a colorless flammable gas with an unpleasant odor. It is a linear molecule consisting of a carbonyl double bonded to a sulfur atom. Carbonyl sulfide can be considered to be intermediate between carbon dioxide and carbon disulfide, both of which are valence isoelectronic with it.
Fluoroform, or trifluoromethane, is the chemical compound with the formula CHF3. It is a hydrofluorocarbon as well as being a part of the haloforms, a class of compounds with the formula CHX3 with C3v symmetry. Fluoroform is used in diverse applications in organic synthesis. It is not an ozone depleter but is a greenhouse gas.
John Adrian Pyle is a British atmospheric scientist, Director of the Centre for Atmospheric Science in Cambridge, England. He is a Professor in the Department of Chemistry at the University of Cambridge, and since 2007 has held the 1920 Chair of Physical Chemistry in the Chemistry Department. He is also a Fellow of the Royal Society and of St Catharine's College, Cambridge.

Tropospheric ozone depletion events are phenomena that reduce the concentration of ozone in the earth's troposphere. Ozone (O3) is a trace gas which has been of concern because of its unique dual role in different layers of the lower atmosphere. Apart from absorbing UV-B radiation and converting solar energy into heat in the stratosphere, ozone in the troposphere provides greenhouse effect and controls the oxidation capacity of the atmosphere.
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) are the gases in the atmosphere that raise the surface temperature of planets such as the Earth. What distinguishes them from other gases is that they absorb the wavelengths of radiation that a planet emits, resulting in the greenhouse effect. The Earth is warmed by sunlight, causing its surface to radiate heat, which is then mostly absorbed by greenhouse gases. Without greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, the average temperature of Earth's surface would be about −18 °C (0 °F), rather than the present average of 15 °C (59 °F).

Tihomir Novakov, Ph.D known also as Tica Novakov was a Serbian-born American physicist. As a scientist, Novakov is known for his black carbon, air quality, and climate change research. James Hansen dubbed him "the godfather of black carbon".

Stratospheric aerosol injection is a proposed method of solar geoengineering to reduce global warming. This would introduce aerosols into the stratosphere to create a cooling effect via global dimming and increased albedo, which occurs naturally from volcanic winter. It appears that stratospheric aerosol injection, at a moderate intensity, could counter most changes to temperature and precipitation, take effect rapidly, have low direct implementation costs, and be reversible in its direct climatic effects. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change concludes that it "is the most-researched [solar geoengineering] methodagreement that it could limit warming to below 1.5 °C (2.7 °F)." However, like other solar geoengineering approaches, stratospheric aerosol injection would do so imperfectly and other effects are possible, particularly if used in a suboptimal manner.

Frost flowers are ice crystals commonly found growing on young sea ice and thin lake ice in cold, calm conditions. The ice crystals are similar to hoar frost, and are commonly seen to grow in patches around 3–4 cm in diameter. Frost flowers growing on sea ice have extremely high salinities and concentrations of other sea water chemicals and, because of their high surface area, are efficient releasers of these chemicals into the atmosphere.

Particulates or atmospheric particulate matter are microscopic particles of solid or liquid matter suspended in the air. The term aerosol commonly refers to the particulate/air mixture, as opposed to the particulate matter alone. Sources of particulate matter can be natural or anthropogenic. They have impacts on climate and precipitation that adversely affect human health, in ways additional to direct inhalation.

An aethalometer is an instrument for measuring the concentration of optically absorbing (‘black’) suspended particulates in a gas colloid stream; commonly visualized as smoke or haze, often seen in ambient air under polluted conditions. The word aethalometer is derived from the Classical Greek verb aethaloun, meaning "to blacken with soot". The aethalometer, a device used for measuring black carbon in atmospheric aerosols, was initially deployed in 1980 and was first commercialized by Magee Scientific.

Space-based measurements of carbon dioxide are used to help answer questions about Earth's carbon cycle. There are a variety of active and planned instruments for measuring carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere from space. The first satellite mission designed to measure CO2 was the Interferometric Monitor for Greenhouse Gases (IMG) on board the ADEOS I satellite in 1996. This mission lasted less than a year. Since then, additional space-based measurements have begun, including those from two high-precision satellites. Different instrument designs may reflect different primary missions.

Anne Mee Thompson is an American scientist, who specializes in atmospheric chemistry and climate change. Her work focuses on how human activities have changed the chemistry of the atmosphere, climate forcing, and the Earth's oxidizing capacity. Thompson is an elected fellow of the American Meteorological Society, American Geophysical Union, and AAAS.
Arlene M. Fiore is an atmospheric chemist whose research focuses on issues surrounding air quality and climate change.

Johannes "Jos" Lelieveld is a Dutch atmospheric chemist. Since 2000, he has been a Scientific Member of the Max Planck Society and director of the Atmospheric Chemistry Department at the Max Planck Institute for Chemistry in Mainz. He is also professor at the University of Mainz and at the Cyprus Institute in Nicosia.

Beate Gertrud Liepert is a research scientist at Columbia University, as well as in North West Research Associates, Redmond and a lecturer at Seattle University. Her research focuses on climate variability: inter-annual changes, centennial time scales, the water and energy cycles.
Jennifer Logan is an atmospheric scientist known for her research on how human activities influence the atmosphere, particularly with respect to biomass burning and the ozone hole.
Glenn Edmond Shaw is an American scientist specializing in atmospheric physics, especially relating to global climate change and long-range transport of aerosol material. He is Emeritus Professor of Physics and Atmospheric Science at the University of Alaska Fairbanks and a member of the scientific staff of the Geophysical Institute. He conducted research on global atmospheric transport of aerosols and feedback of biogenic aerosols on global climate. He and Kenneth Rahn did research on the sources and climatic effect of Arctic haze. He did pioneering work on the scientific concept of climate homeostasis through the sulfur cycle and atmospheric aerosol.
References
- ↑ Belelie, M.D.; Piketh, S.J.; Burger, R.P.; Venter, A.D.; Naidoo, M. (1 January 2019). "Characterisation of ambient Total Gaseous Mercury concentrations over the South African Highveld". Atmospheric Pollution Research. 10 (1): 12–23. doi: 10.1016/j.apr.2018.06.001 .
- ↑ Seo, Yong-Seok; Jeong, Seung-Pyo; Holsen, Thomas M.; Han, Young-Ji; Choi, Eunhwa; Park, Eun Ha; Kim, Tae Young; Eum, Hee-Sang; Park, Dae Gun; Kim, Eunhye; Kim, Soontae; Kim, Jeong-Hun; Choi, Jaewon; Yi, Seung-Muk (2016). "Characteristics of total gaseous mercury (TGM) concentrations in an industrial complex in South Korea: impacts from local sources". Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics. 16 (15): 10215–10228. doi: 10.5194/acp-16-10215-2016 .
- ↑ Garcia-Sanchez, Antonio; Contreras, Felicia; Adams, Meliton; Santos, Fernando (2006). "Airborne total gaseous mercury and exposure in a Venezuelan mining area". International Journal of Environmental Health Research. 16 (5): 361–373. doi:10.1080/09603120600869315.
- ↑ Gill, G. A.; Guentzel, J. L.; Landing, W. M.; Pollman, C. D. (1995). "Total gaseous mercury measurements in Florida: The FAMS project (1992?1994)". Water, Air, & Soil Pollution. 80 (1–4): 235–244. doi:10.1007/BF01189673.
- ↑ Slemr, F.; Brunke, E.-G.; Labuschagne, C.; Ebinghaus, R. (2008). "Total gaseous mercury concentrations at the Cape Point GAW station and their seasonality". Geophysical Research Letters. 35 (11). doi: 10.1029/2008GL033741 .
- ↑ Feng, Xinbin; Shang, Lihai; Wang, Shaofeng; Tang, Shunlin; Zheng, Wei (2004). "Temporal variation of total gaseous mercury in the air of Guiyang, China". Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres. 109 (D3). doi:10.1029/2003JD004159.