This article appears to be a dictionary definition .(January 2024) |
A traction component in a vehicular sense, is a type of transducer. [1] [2]
This article appears to be a dictionary definition .(January 2024) |
A traction component in a vehicular sense, is a type of transducer. [1] [2]
Parasolid is a geometric modeling kernel originally developed by Shape Data Limited, now owned and developed by Siemens Digital Industries Software. It can be licensed by other companies for use in their 3D computer graphics software products.

In computational modelling, multiphysics simulation is defined as the simultaneous simulation of different aspects of a physical system or systems and the interactions among them. For example, simultaneous simulation of the physical stress on an object, the temperature distribution of the object and the thermal expansion which leads to the variation of the stress and temperature distributions would be considered a multiphysics simulation. Multiphysics simulation is related to multiscale simulation, which is the simultaneous simulation of a single process on either multiple time or distance scales.

COMSOL Multiphysics is a finite element analysis, solver, and simulation software package for various physics and engineering applications, especially coupled phenomena and multiphysics. The software facilitates conventional physics-based user interfaces and coupled systems of partial differential equations (PDEs). COMSOL provides an IDE and unified workflow for electrical, mechanical, fluid, acoustics, and chemical applications.
Poroelasticity is a field in materials science and mechanics that studies the interaction between fluid flow and solids deformation within a linear porous medium and it is an extension of elasticity and porous medium flow. The deformation of the medium influences the flow of the fluid and vice versa. The theory was proposed by Maurice Anthony Biot as a theoretical extension of soil consolidation models developed to calculate the settlement of structures placed on fluid-saturated porous soils. The theory of poroelasticity has been widely applied in geomechanics, hydrology, biomechanics, tissue mechanics, cell mechanics, and micromechanics.

Germund Dahlquist was a Swedish mathematician known primarily for his early contributions to the theory of numerical analysis as applied to differential equations.

Autodesk Simulation is a general-purpose multiphysics finite element analysis software package initially developed by ALGOR Incorporated and acquired by Autodesk in January 2009. It is intended for use with Microsoft Windows and Linux operating systems. It is distributed in a number of different core packages to cater to specific applications, such as mechanical event simulation and computational fluid dynamics.
code_saturne is a general-purpose computational fluid dynamics free computer software package. Developed since 1997 at Électricité de France R&D, code_saturne is distributed under the GNU GPL licence. It is based on a co-located finite-volume approach that accepts meshes with any type of cell and any type of grid structure.

Range Software is finite element analysis software package.

Synopsys Simpleware ScanIP is a 3D image processing and model generation software program developed by Synopsys Inc. to visualise, analyse, quantify, segment and export 3D image data from magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computed tomography (CT), microtomography and other modalities for computer-aided design (CAD), finite element analysis (FEA), computational fluid dynamics (CFD), and 3D printing. The software is used in the life sciences, materials science, nondestructive testing, reverse engineering and petrophysics.
OptiY is a design environment software that provides modern optimization strategies and state of the art probabilistic algorithms for uncertainty, reliability, robustness, sensitivity analysis, data-mining and meta-modeling.
Swedish Iranians or Swedish Persians consist of people of Iranian nationality who have settled in Sweden, as well as Swedish residents and citizens of Iranian heritage. As of 2019, there were 80,136 residents of Sweden born in Iran, as well as 40,883 born in Sweden with at least one Iranian-born parent.

SU2 is a suite of open-source software tools written in C++ for the numerical solution of partial differential equations (PDE) and performing PDE-constrained optimization. The primary applications are computational fluid dynamics and aerodynamic shape optimization, but has been extended to treat more general equations such as electrodynamics and chemically reacting flows. SU2 supports continuous and discrete adjoint for calculating the sensitivities/gradients of a scalar field.
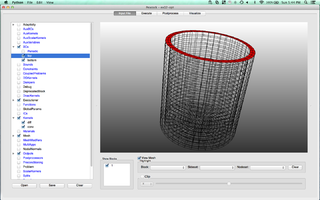
MOOSE is an object-oriented C++ finite element framework for the development of tightly coupled multiphysics solvers from Idaho National Laboratory. MOOSE makes use of the PETSc non-linear solver package and libmesh to provide the finite element discretization.
Ashish Kishore Lele is an Indian chemical engineer, rheologist and the Director of the National Chemical Laboratory, Pune. He is known for his researches on micro and mesostructure of polymers and is an elected fellow of the Indian Academy of Sciences, and the Indian National Academy of Engineering. The Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, the apex agency of the Government of India for scientific research, awarded him the Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Prize for Science and Technology, one of the highest Indian science awards for his contributions to Engineering Sciences in 2006. He received the Infosys Prize in 2012.
Electromagnetically induced acoustic noise (and vibration), electromagnetically excited acoustic noise, or more commonly known as coil whine, is audible sound directly produced by materials vibrating under the excitation of electromagnetic forces. Some examples of this noise include the mains hum, hum of transformers, the whine of some rotating electric machines, or the buzz of fluorescent lamps. The hissing of high voltage transmission lines is due to corona discharge, not magnetism.
FEATool Multiphysics is a physics, finite element analysis (FEA), and partial differential equation (PDE) simulation toolbox. FEATool Multiphysics features the ability to model fully coupled heat transfer, fluid dynamics, chemical engineering, structural mechanics, fluid-structure interaction (FSI), electromagnetics, as well as user-defined and custom PDE problems in 1D, 2D (axisymmetry), or 3D, all within a graphical user interface (GUI) or optionally as script files. FEATool has been employed and used in academic research, teaching, and industrial engineering simulation contexts.
In the theory of radiative transfer, of either thermal or neutron radiation, a position and direction-dependent intensity function is usually sought for the description of the radiation field. The intensity field can in principle be solved from the integrodifferential radiative transfer equation (RTE), but an exact solution is usually impossible and even in the case of geometrically simple systems can contain unusual special functions such as the Chandrasekhar's H-function and Chandrasekhar's X- and Y-functions. The method of discrete ordinates, or the Sn method, is one way to approximately solve the RTE by discretizing both the xyz-domain and the angular variables that specify the direction of radiation. The methods were developed by Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar when he was working on radiative transfer.