A simulation is an approximate imitation of the operation of a process or system; the act of simulating first requires a model is developed. This model is a well-defined description of the simulated subject, and represents its key characteristics, such as its behaviour, functions and abstract or physical properties. The model represents the system itself, whereas the simulation represents its operation over time.
Educational games are games explicitly designed with educational purposes, or which have incidental or secondary educational value. All types of games may be used in an educational environment. Educational games are games that are designed to help people to learn about certain subjects, expand concepts, reinforce development, understand a historical event or culture, or assist them in learning a skill as they play. Game types include board, card, and video games. An educational game is a game designed to teach humans about a specific subject and to teach them a skill. As educators, governments, and parents realize the psychological need and benefits of gaming have on learning, this educational tool has become mainstream. Games are interactive play that teach us goals, rules, adaptation, problem solving, interaction, all represented as a story. They satisfy our fundamental need to learn by providing enjoyment, passionate involvement, structure, motivation, ego gratification, adrenaline, creativity, social interaction and emotion in the game itself while the learning takes place.
A virtual airline (VA) is a dedicated hobby organization that uses flight simulation to model the operations of an airline. Virtual airlines generally have a presence on the Internet, similar to a real airline. Many hundreds of virtual airlines of significance are currently active, with tens of thousands of participants involved at any one time.
In computer network research, network simulation is a technique whereby a software program models the behavior of a network by calculating the interaction between the different network entities. Most simulators use discrete event simulation - the modeling of systems in which state variables change at discrete points in time. The behavior of the network and the various applications and services it supports can then be observed in a test lab; various attributes of the environment can also be modified in a controlled manner to assess how the network / protocols would behave under different conditions.

VBS2 is the successor of the battlefield simulation system VBS1. It was developed in close cooperation with the USMC, Australian Defence Force and other military customers of VBS1. VBS2 was officially launched on 17 April 2007.
A computer architecture simulator is a program that simulates the execution of computer architecture.
Simulation software is based on the process of modeling a real phenomenon with a set of mathematical formulas. It is, essentially, a program that allows the user to observe an operation through simulation without actually performing that operation. Simulation software is used widely to design equipment so that the final product will be as close to design specs as possible without expensive in process modification. Simulation software with real-time response is often used in gaming, but it also has important industrial applications. When the penalty for improper operation is costly, such as airplane pilots, nuclear power plant operators, or chemical plant operators, a mock up of the actual control panel is connected to a real-time simulation of the physical response, giving valuable training experience without fear of a disastrous outcome.
A Practice Enterprise is a practice company that runs like a real business silhouetting a real enterprise's business procedures, products and services. A Practice Enterprise resembles a real company in its form, organization and function. Each Practice Enterprise trades with other Practice Enterprises, following standard commercial business procedures in the Practice Enterprise worldwide economic environment. It offers a ‘learning-by-doing’ training programme with the aim to better prepare young people for their future careers and to increase their entrepreneurship potential through running their own Practice Enterprise.

Medical simulation, or more broadly, healthcare simulation, is a branch of simulation related to education and training in medical fields of various industries. Simulations can be held in the classroom, in situational environments, or in spaces built specifically for simulation practice. It can involve simulated human patients - artificial, human or a combination of the two, educational documents with detailed simulated animations, casualty assessment in homeland security and military situations, emergency response, and support virtual health functions with holographic simulation. In the past, its main purpose was to train medical professionals to reduce error during surgery, prescription, crisis interventions, and general practice. Combined with methods in debriefing, it is now also used to train students in anatomy, physiology, and communication during their schooling.
An instructional simulation, also called an educational simulation, is a simulation of some type of reality but which also includes instructional elements that help a learner explore, navigate or obtain more information about that system or environment that cannot generally be acquired from mere experimentation. Instructional simulations are typically goal oriented and focus learners on specific facts, concepts, or applications of the system or environment. Today, most universities make lifelong learning possible by offering a virtual learning environment (VLE). Not only can users access learning at different times in their lives, but they can also immerse themselves in learning without physically moving to a learning facility, or interact face to face with an instructor in real time. Such VLEs vary widely in interactivity and scope. For example, there are virtual classes, virtual labs, virtual programs, virtual library, virtual training, etc. Researchers have classified VLE in 4 types:
Live, Virtual, & Constructive (LVC) Simulation is a broadly used taxonomy for classifying Models and Simulation (M&S). However, categorizing a simulation as a live, virtual, or constructive environment is problematic since there is no clear division between these categories. The degree of human participation in a simulation is infinitely variable, as is the degree of equipment realism. The categorization of simulations also lacks a category for simulated people working real equipment.
Human-in-the-loop or HITL is defined as a model that requires human interaction. HITL is associated with modeling and simulation (M&S) in the live, virtual, and constructive taxonomy. HITL models may conform to human factors requirements as in the case of a mockup. In this type of simulation a human is always part of the simulation and consequently influences the outcome in such a way that is difficult if not impossible to reproduce exactly. HITL also readily allows for the identification of problems and requirements that may not be easily identified by other means of simulation.
Virtual Worlds are 3D computer environments where each user is represented with a character - avatar. Traditionally, virtual worlds have been used for entertainment. However, starting from approximately 2004 both corporate world and academia started to recognize business value of virtual worlds for training and education, collaboration, and marketing. Development and maturity of most popular virtual world - Second Life - played a significant role in corporate movement towards virtual worlds for several reasons:
The ADMS is an emergency and disaster management training simulation system designed to train incident commanders, first responders, and incident command teams in a real-time, interactive virtual reality(VR) environment. ADMS was first introduced by Environmental Tectonics Corporation (ETCC:US) in 1992. The development of ADMS was in response to the crash of British Airtours Flight 28M at the Manchester airport in 1985, in which 55 people died. Following the accident research indicated that first responder training should include realistic scenarios. The first ADMS system was produced for the UK Ministry of Defence, and delivered to Royal Air Force’s (RAF) Manston Facility. Since its inception, ADMS has evolved into a modular, expandable disaster simulation platform, with systems in use worldwide.

Boston Virtual ARTCC (BVA) is a non-profit community of aviation enthusiasts, students, and professionals. The organization connects virtual pilots and virtual air traffic controllers through the VATSIM network for the purposes of flight simulation and training.
In business, training simulation is a virtual medium through which various types of skills can be acquired. Training simulations can be used in a variety of genres; however they are most commonly used in corporate situations to improve business awareness and management skills. They are also common in academic environments as an integrated part of a business or management course.

Harvey was one of the earliest medical simulators available for training of health care professionals. Harvey was created in 1968 by Dr. Michael Gordon at the University of Miami. Harvey is currently sold by the Laerdal Corporation.
A surgery simulator is computer technology developed to simulate surgical procedures for the purpose of training medical professionals, without the need of a patient, cadaver or animal. The concept goes back to the 1980s with video games, but only in the 1990s with three-dimensional graphics and the 2000s with the use of motion sensors for realistic movements has the technology been able to simulate the real situation. The most common type of surgery taught through this method is laparoscopic surgery, although it has also been used to do a trial run before other kinds of procedures.
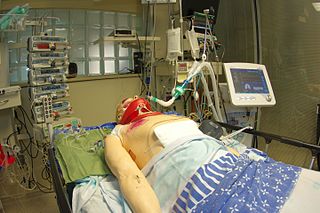
MSR - The Israel Center for Medical Simulation is Israel's national institute for Simulation-Based Medical Education (SBME) and Patient Safety training. It is located at the Chaim Sheba Medical Center in the Tel HaShomer neighborhood of Ramat Gan, in the Tel Aviv District. MSR is internationally recognized as leader in patient safety simulation-based training.







