Related Research Articles
Blue Stream is a major trans-Black Sea gas pipeline that carries natural gas to Turkey from Russia. The pipeline has been constructed by the Blue Stream Pipeline B.V., the Netherlands based joint venture of Russian Gazprom and Italian Eni. The Blue Stream Pipeline B.V. is an owner of the subsea section of pipeline, including Beregovaya compressor station, while Gazprom owns and operates the Russian land section of the pipeline and the Turkish land section is owned and operated by the Turkish energy company BOTAŞ. According to Gazprom the pipeline was built with the intent of diversifying Russian gas delivery routes to Turkey and avoiding third countries.
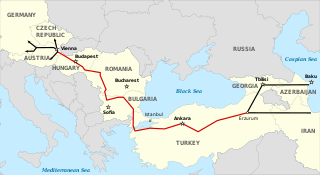
The Nabucco pipeline was a failed natural gas pipeline project from Erzurum, Turkey to Baumgarten an der March, Austria to diversify natural gas suppliers and delivery routes for Europe. The pipeline was to lessen European dependence on Russian energy. The project was backed by several European Union states and the United States and was seen as rival to the Gazprom-Eni South Stream pipeline project. The main supplier was to be Iraq with potential supplies from Azerbaijan, Turkmenistan, and Egypt.

The South Caucasus Pipeline is a natural gas pipeline from the Shah Deniz gas field in the Azerbaijan sector of the Caspian Sea to Turkey. It runs parallel to the Baku–Tbilisi–Ceyhan pipeline (oil).

The Yamal–Europe natural gas pipeline is a 4,107-kilometre-long (2,552 mi) pipeline connecting Russian natural gas fields in the Yamal Peninsula and Western Siberia with Poland and Germany, through Belarus. The Poland portion ceased operating in 2022.
The Power of Siberia 2 is a proposed natural gas pipeline to export natural gas from Russia's Western Siberia Altai region to North-Eastern China.

South Stream is a canceled pipeline project to transport natural gas of the Russian Federation through the Black Sea to Bulgaria and through Serbia, Hungary and Slovenia further to Austria. It was never finished.
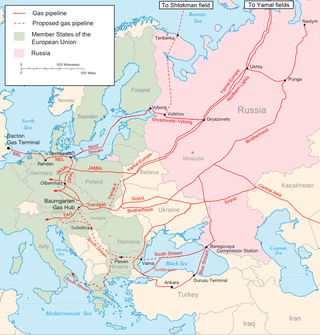
The Urengoy–Pomary–Uzhhorod pipeline is one of Russia's main natural gas export pipelines, partially owned and operated by Ukraine. It was part of the "gas in exchange for pipes program", and the Soviet-controlled bank "Ost-West Handelsbank" was opened in Frankfurt on 1 March 1973 to support the project.

Russia supplies a significant volume of fossil fuels to other European countries. In 2021, it was the largest exporter of oil and natural gas to the European Union, (90%) and 40% of gas consumed in the EU came from Russia.

Ukraine extracts about 20 billion cubic meters of fossil gas each year, and since 2022 this has almost met demand. Ukraine has been estimated to possess natural gas reserves of over 670 billion cubic meters (in 2022), and gas is an important part of energy in Ukraine. In 2021, Ukraine produced 19.8 billion cubic meters (bcm or Gm3) of natural gas. To satisfy domestic demand of 27.3 bcm that year, Ukraine relied on gas imports (2.6 bcm) and withdrawal from underground storage (4.9 bcm). Winter demand can reach 150 mcm per day.

With few natural energy resources, Moldova imports almost all of its energy supplies. 50% of the country's national energy company, Moldovagaz, is owned by Russian oil and natural gas supplier Gazprom, the remaining 36% split between the Moldovan government (36.6%) and the unrecognised government of Transnistria (13.4%). Moldova's historic dependence on Russian energy is underscored by a debt of more than US$709 million to Gazprom as well as a further US$7 billion by Transnistria. Russia supplies the breakaway pro-Russian region with oil and natural gas without requiring them to pay, with the cost levied as debt against the Moldovan state as a form of economic warfare. The Moldovan government disputes the figures, and has identified more than US$100 million in fraudulent claims by Gazprom.

The Trans-Anatolian Natural Gas Pipeline is a natural gas pipeline in Turkey. It is the central part of the Southern Gas Corridor, which connects the giant Shah Deniz gas field in Azerbaijan to Europe through the South Caucasus Pipeline and the Trans Adriatic Pipeline. The pipeline has a strategic importance for both Azerbaijan and Turkey. It allows the first Azerbaijani gas exports to Europe, beyond Turkey. It also strengthens the role of Turkey as a regional energy hub.
Gas Interconnector Greece–Bulgaria is a natural gas pipeline from the Greek to the Bulgarian natural gas pipeline network. It became operational on 1 October 2022.

In 2021 Russia was the world's second-largest producer of natural gas, producing an estimated 701 billion cubic meters (bcm) of gas a year, and the world's largest natural gas exporter, shipping an estimated 250 bcm a year. In 2022 the export market was significantly downsized, following the Russian invasion of Ukraine and Russia reducing exports after countries refused to pay in rubles.
TurkStream is a natural gas pipeline running from Russia to Turkey. It starts from Russkaya compressor station near Anapa in Russia's Krasnodar Region, crossing the Black Sea to the receiving terminal at Kıyıköy. Some gas flows onwards to the European Union.

The natural gas transmission system of Ukraine is a complex of pipelines for import and transit of gas in Ukraine. It is one of the largest gas transmission systems in the world. The system is linked with the systems of Poland, Romania, Moldova, Hungary and Slovakia, and was formerly linked with the natural gas transmission systems of Russia and Belarus. The system is owned by Government of Ukraine and operated by Gas Transmission System Operator of Ukraine. Some local transmission lines together with distribution sets are owned by regional gas companies.
Balkan Stream is a pipeline which transports Russian natural gas from Turkey to Bulgaria, Serbia and Hungary. It is an extension of Turk Stream. Annual capacity is almost 16 bcm from Turkey and 1.8 bcm onwards to Serbia.

Natural gas supplies over a quarter of Turkey's energy. The country consumes 50 to 60 billion cubic metres of this natural gas each year, nearly all of which is imported. A large gas field in the Black Sea however started production in 2023.

The Russia–EU gas dispute flared up in March 2022 following the invasion of Ukraine on 24 February 2022. Russia and the major EU countries clashed over the issue of payment for natural gas pipelined to Europe by Russia's Gazprom, amidst sanctions on Russia that were expanded in response to Russia's 2022 invasion of Ukraine. In June, Gazprom claimed it was obliged to cut the flow of gas to Germany by more than half, as a result of such sanctions that prevented the Russian company from receiving its turbine component from Canada. On 26 September 2022, three of the four pipes of the Nord Stream 1 and 2 gas pipelines were sabotaged. This resulted in a record release of 115,000 tonnes of methane (CH4) – an equivalent of 15 million tonnes of carbon dioxide (CO2) – and is believed to have made a contribution to global warming.
As part of the sanctions imposed on the Russian Federation as a result of the Russo-Ukrainian War, on 3 December 2022, the European Union (EU) agreed to cap the price of natural gas in order to reduce the volatility created by Russia in the gas market.
The Iași–Chișinău pipeline, also known as the Iași–Ungheni–Chișinău pipeline, is a natural gas pipeline going from Iași in Romania to Chișinău in Moldova. The pipeline was inaugurated in 2014 and connected Iași with the Moldovan town of Ungheni. It was extended to the capital Chișinău in 2019, with the compressor stations being put into operation in 2021. However, it was not used until the 2022–2023 Moldovan energy crisis.
References
- ↑ Sabadus, Aura (2020-12-17). "Why East European gas markets should integrate". Atlantic Council . Retrieved 2021-01-07.
- ↑ "The Trans-Balkan pipeline reimagined [GGP]". www.naturalgasworld.com. Retrieved 2021-01-07.
- ↑ "Gas_25 / Trans-Balkan Corridor bi-directional flow Moldova – Ukraine". www.energy-community.org. Retrieved 2021-01-07.
- ↑ Sabadus, Aura. "Ukraine, Turkey emerging as eastern European gas transit options". ICIS Explore. Retrieved 2022-10-24.
- ↑ Korchemkin, Mikhail (2009-01-16). "Gazprom insists on using just one specific pipeline". East European Gas Analysis. Retrieved 2016-02-06.
- ↑ "Master Plan. Ukrainian Gas Transmission System (UGTS). Priority Objects. Modernisation and Reconstruction" (PDF). Naftogaz . Energy Charter Secretariat. 2009. Retrieved 2016-02-06.
- ↑ "Ankara to complete TurkStream by end of 2019". Hürriyet Daily News . 18 November 2019. Retrieved 13 December 2019.
- ↑ Barsukov, Yuri (2018-11-22). «Газпром» сделал трубный выбор [Gazprom made a pipe choice]. Kommersant (in Russian). Retrieved 2019-12-13.
- ↑ Geropoulos, Kostis (2020-12-11). "Europe turns the tables on Russian gas". New Europe. Retrieved 2021-01-07.
- ↑ Nikolov, Krassen (2022-04-29). "Bulgaria becomes regional hub for gas supplies". www.euractiv.com. Retrieved 2022-10-23.
- ↑ Sabadus, Aura. "Moldova, Ukraine backhaul to unlock Trans-Balkan gas corridor". ICIS Explore. Retrieved 2022-10-22.
- ↑ "High Costs Cloud Outlook for Trans-Balkan Gas Pipeline". Energy Intelligence. 2020-11-20. Retrieved 2022-10-24.
- ↑ 11 Companies Interested In Transporting Gas From Romania To Ukraine Via Trans-Balkan Pipeline
- ↑ Roberts, John; Bowden, Julian (2022-12-12). "Europe and the Caspian: The gas supply conundrum". Atlantic Council . Retrieved 2022-12-12.
- ↑ Donaldson, Alex (2023-05-18). "Moldova no longer using Russian natural gas, announces PM Recean". Power Technology. Retrieved 2025-01-01.
- ↑ "Republic of Moldova on the brink of an energy crisis". www.bursa.ro (in Romanian). Retrieved 2025-01-01.
- ↑ "Kyiv proposes reversing Trans-Balkan gas pipeline flows through Ukraine". www.naturalgasworld.com. Retrieved 2023-12-30.