
A bus stop is a designated place where buses stop for passengers to board or alight from a bus. The construction of bus stops tends to reflect the level of usage, where stops at busy locations may have shelters, seating, and possibly electronic passenger information systems; less busy stops may use a simple pole and flag to mark the location. Bus stops are, in some locations, clustered together into transport hubs allowing interchange between routes from nearby stops and with other public transport modes to maximise convenience.
ISO 20022 is an ISO standard for electronic data interchange between financial institutions. It describes a metadata repository containing descriptions of messages and business processes, and a maintenance process for the repository content. The standard covers financial information transferred between financial institutions that includes payment transactions, securities trading and settlement information, credit and debit card transactions and other financial information.

The National Public Transport Access Node (NaPTAN) database is a UK nationwide system for uniquely identifying all the points of access to public transport in the UK. The database is closely associated with the National Public Transport Gazetteer.

Vehicle and Operator Services Agency (VOSA) was an executive agency granted trading fund status in the United Kingdom sponsored by the Department for Transport of the United Kingdom Government.

The Transport Direct Programme was a division of the UK Department for Transport (DfT) to develop standards, data and better information technology systems to support public transport. It developed and operates the Transport Direct Portal which is a public facing multi-modal journey planner. It also supports the creation and management of comprehensive databases of all public transport movements in the United Kingdom with Traveline. During 2010 two key datasets were released as Open Data and published on www.data.gov.uk.

A transport hub is a place where passengers and cargo are exchanged between vehicles or/and between transport modes. Public transport hubs include train stations, rapid transit stations, bus stops, tram stop, airports and ferry slips. Freight hubs include classification yards, airports, seaports and truck terminals, or combinations of these. For private transport, the parking lot functions as a hub.

A public transport timetable is a document setting out information on public transport service times, to assist passengers with planning a trip. Typically, the timetable will list the times when a service is scheduled to arrive at and depart from specified locations. It may show all movements at a particular location or all movements on a particular route or for a particular stop. Traditionally this information was provided in printed form, for example as a leaflet or poster. It is now also often available in a variety of electronic formats.
The Service Interface for Real Time Information or SIRI is an XML protocol to allow distributed computers to exchange real time information about public transport services and vehicles.
Transmodel is the CEN European Reference Data Model for Public Transport Information; it provides a conceptual model of common public transport concepts and data structures that can be used to build many different kinds of public transport information system, including for timetabling, fares, operational management, real time data, journey planning etc.
IFOPT is a CEN Technical Specification that provides a Reference Data Model for describing the main fixed objects required for public access to Public transport, that is to say Transportation hubs. Such a model is a fundamental component of the modern Public transport information systems needed both to operate Public transport and to inform passengers about services.
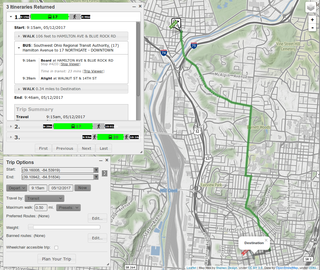
A journey planner, trip planner, or route planner is a specialised search engine used to find an optimal means of travelling between two or more given locations, sometimes using more than one transport mode. Searches may be optimised on different criteria, for example fastest, shortest, fewest changes, cheapest. They may be constrained, for example, to leave or arrive at a certain time, to avoid certain waypoints, etc. A single journey may use a sequence of several modes of transport, meaning the system may know about public transport services as well as transport networks for private transportation. Trip planning or journey planning is sometimes distinguished from route planning, where route planning is typically thought of as using private modes of transportation such as cycling, driving, or walking, normally using a single mode at a time. Trip or journey planning, in contrast, would make use of at least one public transport mode which operates according to published schedules; given that public transport services only depart at specific times, an algorithm must therefore not only find a path to a destination, but seek to optimise it so as to minimise the waiting time incurred for each leg. In European Standards such as Transmodel, trip planning is used specifically to describe the planning of a route for a passenger, to avoid confusion with the completely separate process of planning the operational journeys to be made by public transport vehicles on which such trips are made.
Stagecoach in Huntingdonshire is the trading name of Stagecoach in The Fens Limited, which runs services throughout Huntingdon, the Fens and surrounding areas. It is part of Stagecoach East, itself a subsidiary of the larger Stagecoach Group Plc.

Public transport bus services are generally based on regular operation of transit buses along a route calling at agreed bus stops according to a published public transport timetable.
CycleNetXChange provides a standard format with which to exchange cycle path data, together with information about the quality of routes; This enables computerised transport systems to provide cycle routes.
Bus transport in Bromsgrove has a long and varied history, dating back to Midland Red operations. In recent years, however, First Midland Red, which has evolved from the original Midland Red company, has severely reduced operations, leaving many independent operators running in the town.

Traveline is a public transport route planner service provided by a partnership between local authorities and transport operators in the UK to provide impartial and comprehensive information about public transport which has operated since 2000. It prepares comprehensive public transport data for the UK and provides a number of regional public transport journey planners.

The General Transit Feed Specification (GTFS) defines a common format for public transportation schedules and associated geographic information.

railML is an open, XML based data exchange format for data interoperability of railway applications.
NeTEx is the CEN Technical standard for exchanging Public Transport Information as XML documents. it provides a W3C XML schema based on the Transmodel abstract model of common public transport concepts and data structures and can be used to exchange many different kinds of data between passenger information systems, including data describing for stops, facilities, timetabling and fares. Such data can be used by both operational management systems and customer facing systems for journey planning etc.










