
A tax is a compulsory financial charge or some other type of levy imposed on a taxpayer by a governmental organization in order to fund government spending and various public expenditures. A failure to pay, along with evasion of or resistance to taxation, is punishable by law. Taxes consist of direct or indirect taxes and may be paid in money or as its labour equivalent. The first known taxation took place in Ancient Egypt around 3000–2800 BC.
A tariff is a tax imposed by a government of a country or of a supranational union on imports or exports of goods. Besides being a source of revenue for the government, import duties can also be a form of regulation of foreign trade and policy that taxes foreign products to encourage or safeguard domestic industry. Tariffs are among the most widely used instruments of protectionism, along with import and export quotas.

Free trade is a trade policy that does not restrict imports or exports. It can also be understood as the free market idea applied to international trade. In government, free trade is predominantly advocated by political parties that hold liberal economic positions while economically left-wing and nationalist political parties generally support protectionism, the opposite of free trade.

In economics, an externality is a cost or benefit that is imposed on a third party who did not agree to incur that cost or benefit. For the purpose of these statements, overall cost and benefit to society is defined as the sum of the imputed monetary value of benefits and costs to all parties involved. The concept of externality was first developed by economist Arthur Pigou in the 1920s. Air pollution from motor vehicles is an example of a negative externality. The costs of the air pollution for the rest of society is not compensated for by either the producers or users of motorized transport.
The law of comparative advantage describes how, under free trade, an agent will produce more of and consume less of a good for which they have a comparative advantage.
The Incoterms or International Commercial Terms are a series of pre-defined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) relating to international commercial law. They are widely used in international commercial transactions or procurement processes and their use is encouraged by trade councils, courts and international lawyers. A series of three-letter trade terms related to common contractual sales practices, the Incoterms rules are intended primarily to clearly communicate the tasks, costs, and risks associated with the global or international transportation and delivery of goods. Incoterms inform sales contracts defining respective obligations, costs, and risks involved in the delivery of goods from the seller to the buyer, but they do not themselves conclude a contract, determine the price payable, currency or credit terms, govern contract law or define where title to goods transfers.

An export in international trade is a good or service produced in one country that is sold into another country. The seller of such goods and services is an exporter; the foreign buyer is an importer.
Cost–benefit analysis (CBA), sometimes also called benefit–cost analysis, is a systematic approach to estimating the strengths and weaknesses of alternatives used to determine options which provide the best approach to achieving benefits while preserving savings. A CBA may be used to compare completed or potential courses of actions, or to estimate the value against the cost of a decision, project, or policy. It is commonly used in commercial transactions, business or policy decisions, and project investments. For example, the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission has to conduct cost-benefit analysis before instituting regulations or de-regulations.

Trade barriers are government-induced restrictions on international trade.

FOB is a term in international commercial law specifying at what point respective obligations, costs, and risk involved in the delivery of goods shift from the seller to the buyer under the Incoterms standard published by the International Chamber of Commerce. FOB is only used in non-containerized sea freight or inland waterway transport. As with all Incoterms, FOB does not define the point at which ownership of the goods is transferred.

Non-tariff barriers to trade are trade barriers that restrict imports or exports of goods or services through mechanisms other than the simple imposition of tariffs.
PEST analysis describes a framework of macro-environmental factors used in the environmental scanning component of strategic management. It is part of an external analysis when conducting a strategic analysis or doing market research, and gives an overview of the different macro-environmental factors to be taken into consideration. It is a strategic tool for understanding market growth or decline, business position, potential and direction for operations.
The Ramsey problem, or Ramsey pricing, or Ramsey–Boiteux pricing, is a second-best policy problem concerning what prices a public monopoly should charge for the various products it sells in order to maximize social welfare while earning enough revenue to cover its fixed costs.

The iron law of prohibition is a term coined by Richard Cowan in 1986 which posits that as law enforcement becomes more intense, the potency of prohibited substances increases. Cowan put it this way: "the harder the enforcement, the harder the drugs."
Articles in economics journals are usually given classification codes according to a system originated by the Journal of Economic Literature. The JEL is published quarterly by the American Economic Association (AEA) and contains survey articles and information on recently published books and dissertations. The AEA maintains EconLit, a searchable data base of citations for articles, books, reviews, dissertations, and working papers classified by JEL codes for the years from 1969. A recent addition to EconLit is indexing of economics-journal articles from 1886 to 1968 parallel to the print series Index of Economic Articles.
A freight rate is a price at which a certain cargo is delivered from one point to another. The price depends on the form of the cargo, the mode of transport, the weight of the cargo, and the distance to the delivery destination. Many shipping services, especially air carriers, use dimensional weight for calculating the price, which takes into account both weight and volume of the cargo.
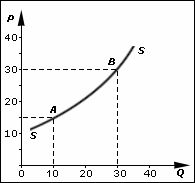
In economics, supply is the amount of a resource that firms, producers, labourers, providers of financial assets, or other economic agents are willing and able to provide to the marketplace or directly to another agent in the marketplace. Supply can be in currency, time, raw materials, or any other scarce or valuable object that can be provided to another agent. This is often fairly abstract. For example in the case of time, supply is not transferred to one agent from another, but one agent may offer some other resource in exchange for the first spending time doing something. Supply is often plotted graphically as a supply curve, with the quantity provided plotted horizontally and the price plotted vertically.
In electric power transmission, wheeling is the transportation of electric energy (megawatt-hours) from within an electrical grid to an electrical load outside the grid boundaries. Two types of wheeling are 1) a wheel-through, where the electrical power generation and the load are both outside the boundaries of the transmission system and 2) a wheel-out, where the generation resource is inside the boundaries of the transmission system but the load is outside. Wheeling often refers to the scheduling of the energy transfer from one Balancing Authority to another. Since the wheeling of electric energy requires use of a transmission system, there is often an associated fee which goes to the transmission owners. In a simpler sense, it refers to the process of transmission of electricity through the transmission lines.
Ecometrics is the quantitative analysis of economic, environmental, and societal systems based on the concurrent development of empirical theory, related by appropriate methods of inference in attempts to create more sustainable systems. Broadly defined, Ecometrics is a way to evaluate if an activity is contributing to more sustainable systems of production and consumption. Ecometrics is a system of statistical extrapolation and interpolation that uses principles of resource management in economic and environmental studies to analyze trends in consumption. With a comprehensive understanding of ecometrics, and thereby an understanding of the impacts of specific conscious or conventional opportunity costs, agents within economic systems can cause measurable change for the triple bottom line. The term was originally trademarked by Interface Global, a corporation founded by Ray Anderson. The parameters that cause change are often population, technology, transportation, consumption, public conscious, non-renewable or renewable resources, location, labor conditions, transportation and wealth. Ecometrics is used in labeling programs such as the US EPA Fuel Economy and Environment Label to determine the environmental and financial advantages of purchasing one car over another. There are many applications of Ecometrics for Environmental Impact Calculators infographics, and for political analysis. Because the parameters of ecometrics vary drastically for any activity, the applications of its resulting measurements are sometimes unilateral. Applied ecometrics exposes the complexity of making sustainable decisions, especially given other humanitarian goals such as third world economic development. In this way ecometrics shows any choice within consumption and production systems as wicked problems.
The Common Consolidated Corporate Tax Base (CCCTB) is a proposal for a common tax scheme for the European Union developed by the European Commission and first proposed in March 2011 that provides a single set of rules for how EU corporations calculate EU taxes, and provide the ability to consolidate EU taxes. Corporate tax rates in the EU would not be changed by the CCCTB, as EU countries would continue to have their own corporate tax rates.






