
A wireless network is a computer network that uses wireless data connections between network nodes. Wireless networking allows homes, telecommunications networks and business installations to avoid the costly process of introducing cables into a building, or as a connection between various equipment locations. Admin telecommunications networks are generally implemented and administered using radio communication. This implementation takes place at the physical level (layer) of the OSI model network structure.

Wi-Fi is a family of wireless network protocols based on the IEEE 802.11 family of standards, which are commonly used for local area networking of devices and Internet access, allowing nearby digital devices to exchange data by radio waves. These are the most widely used computer networks, used globally in home and small office networks to link devices and to provide Internet access with wireless routers and wireless access points in public places such as coffee shops, hotels, libraries, and airports.

Wireless communication is the transfer of information (telecommunication) between two or more points without the use of an electrical conductor, optical fiber or other continuous guided medium for the transfer. The most common wireless technologies use radio waves. With radio waves, intended distances can be short, such as a few meters for Bluetooth or as far as millions of kilometers for deep-space radio communications. It encompasses various types of fixed, mobile, and portable applications, including two-way radios, cellular telephones, personal digital assistants (PDAs), and wireless networking. Other examples of applications of radio wireless technology include GPS units, garage door openers, wireless computer mouse, keyboards and headsets, headphones, radio receivers, satellite television, broadcast television and cordless telephones. Somewhat less common methods of achieving wireless communications involve other electromagnetic phenomena, such as light and magnetic or electric fields, or the use of sound.

The Toronto subway is a rapid transit system serving Toronto and the neighbouring city of Vaughan in Ontario, Canada, operated by the Toronto Transit Commission (TTC). As of September 2023, the subway system is a rail network consisting of three heavy-capacity rail lines operating predominantly underground. As of December 2022, three new lines are under construction: two light rail lines and one subway line.

A hotspot is a physical location where people can obtain Internet access, typically using Wi-Fi technology, via a wireless local-area network (WLAN) using a router connected to an Internet service provider.

Google WiFi was a municipal wireless network deployed in Mountain View, California. It was funded by Google and installed primarily on city lightposts. Google had committed to keeping the service free until 2010. The initial service was shut down by Google on May 3, 2014 at their Mountain View base, and provided a new public outdoor WiFi.

A municipal wireless network is a citywide wireless network. This usually works by providing municipal broadband via Wi-Fi to large parts or all of a municipal area by deploying a wireless mesh network. The typical deployment design uses hundreds of wireless access points deployed outdoors, often on poles. The operator of the network acts as a wireless internet service provider.
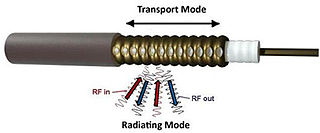
A leaky feeder is a communications system used in underground mining and other tunnel environments. Manufacturers and cabling professionals use the term "radiating cable" as this implies that the cable is designed to radiate: something that coaxial cable is not generally supposed to do.

Wi-Fi calling, also called VoWiFi, refers to mobile phone voice calls and data that are made over IP networks using Wi-Fi, instead of the cell towers provided by cellular networks. Using this feature, compatible handsets are able to route regular cellular calls through a wireless LAN (Wi-Fi) network with broadband Internet, while seamlessly change connections between the two where necessary. This feature makes use of the Generic Access Network (GAN) protocol, also known as Unlicensed Mobile Access (UMA).

A distributed antenna system (DAS) is a network of spatially separated antenna nodes connected to a common source via a transport medium that provides wireless service within a geographic area or structure. DAS antenna elevations are generally at or below the clutter level, and node installations are compact. A distributed antenna system may be deployed indoors or outdoors.

Alvarion Technologies is a global provider of autonomous Wi-Fi networks designed with self-organizing capabilities for carrier-grade Wi-Fi, enterprise connectivity, smart city planning, smart hospitality, connected campuses, and connected events.
Piggybacking on Internet access is the practice of establishing a wireless Internet connection by using another subscriber's wireless Internet access service without the subscriber's explicit permission or knowledge. It is a legally and ethically controversial practice, with laws that vary by jurisdiction around the world. While completely outlawed or regulated in some places, it is permitted in others.

Boingo Wireless, Inc. is an American company that designs, builds and manages wireless networks. Its public and private networks include distributed antenna systems (DAS), small cells, macro towers and more than one million Wi-Fi hotspots around the world. The company operates networks for airports, transit stations, stadiums, military bases, hospitals and commercial properties. In December 2022, the company announced it was moving its headquarters to Frisco, Texas, and would maintain regional offices in Los Angeles, New York, Chicago and Las Vegas. The company was listed on the Nasdaq until it was acquired by investment firm Digital Colony Management LLC in 2021.
The New York City Office of Technology and Innovation (OTI), formerly known as the Department of Information Technology and Telecommunications (DoITT), is the department of the government of New York City that oversees the City's "use of existing and emerging technologies in government operations, and its delivery of services to the public". Although the agency's primary purpose is to facilitate the technology needs of other New York City agencies, the department is best known by city residents for running the city's 311 "citizens' hotline," established in 2003. Its regulations are compiled in title 67 of the New York City Rules.
Towerstream Corporation is a Fixed Wireless Fiber Alternative company delivering high-speed Internet access to businesses. The company offers broadband services in 12 urban markets including New York City, Boston, Los Angeles, Chicago, Philadelphia, the San Francisco Bay area, Miami, Seattle, Dallas-Fort Worth, Houston, Las Vegas-Reno, and the greater Providence area, where the company is headquartered. In 2014, Towerstream launched its On-Net fixed-wireless service offering On-Net building tenants access to dedicated, symmetrical high-speed Internet connectivity, with a premier SLA, at market-setting prices. Founded in 1999 by Philip Urso and Jeffrey Thompson (eFortress), Towerstream held its first public offering in January 2007 and traded on the NASDAQ Capital Markets under symbol TWER. In November 2016 the stock had declined in price, was delisted from NASDAQ, and moved to the over-the-counter market.
Smartphone ad hoc networks are wireless ad hoc networks that use smartphones. Once embedded with ad hoc networking technology, a group of smartphones in close proximity can together create an ad hoc network. Smart phone ad hoc networks use the existing hardware in commercially available smartphones to create peer-to-peer networks without relying on cellular carrier networks, wireless access points, or traditional network infrastructure. Wi-Fi SPANs use the mechanism behind Wi-Fi ad-hoc mode, which allows phones to talk directly among each other, through a transparent neighbor and route discovery mechanism. SPANs differ from traditional hub and spoke networks, such as Wi-Fi Direct, in that they support multi-hop routing and relays and there is no notion of a group leader, so peers can join and leave at will without destroying the network.

LinkNYC is an infrastructure project providing free Wi-Fi service in New York City. The office of New York City Mayor Bill de Blasio announced the plan on November 17, 2014, and the installation of the first kiosks, or "Links," started in late 2015. The Links replace the city's network of 9,000 to 13,000 payphones, a contract for which expired in October 2014. The LinkNYC kiosks were devised after the government of New York City held several competitions to replace the payphone system. The most recent competition, in 2014, resulted in the contract being awarded to the CityBridge consortium, which comprises Qualcomm; Titan and Control Group, which now make up Intersection; and Comark.
BAI Communications, formerly Broadcast Australia, is an Australian telecommunications systems company.

Since the late 20th century, the Metropolitan Transportation Authority has started several projects to maintain and improve the New York City Subway. Some of these projects, such as subway line automation, proposed platform screen doors, the FASTRACK maintenance program, and infrastructural improvements proposed in 2015–2019 Capital Program, contribute toward improving the system's efficiency. Others, such as train-arrival "countdown clocks", "Help Point" station intercoms, "On the Go! Travel Station" passenger kiosks, wireless and cellular network connections in stations, MetroCard fare payment alternatives, and digital ads, are meant to benefit individual passengers. Yet others, including the various methods of subway construction, do not directly impact the passenger interface, but are used to make subway operations efficient.
Intersection is a smart cities technology and out-of-home advertising company. It was formed as a result of a merger between Control Group and Titan in June 2015. The Intersection is known for its product LinkNYC.















