
The Legion of Merit (LOM) is a military award of the United States Armed Forces that is given for exceptionally meritorious conduct in the performance of outstanding services and achievements. The decoration is issued to members of the eight uniformed services of the United States as well as to military and political figures of foreign governments.
The Commendation Medal is a mid-level United States military decoration presented for sustained acts of heroism or meritorious service. Each branch of the United States Armed Forces issues its own version of the Commendation Medal, with a fifth version existing for acts of joint military service performed under the Department of Defense.

The awards and decorations of the United States Armed Forces include various medals, service ribbons, ribbon devices, and specific badges which recognize military service and personal accomplishments of members of the U.S. Armed Forces. Such awards are a means to outwardly display the highlights of a service member's career.

The Air Medal (AM) is a military decoration of the United States Armed Forces. It was created in 1942 and is awarded for single acts of heroism or meritorious achievement while participating in aerial flight.
The Achievement Medal is a military decoration of the United States Armed Forces. The Achievement Medal was first proposed as a means to recognize outstanding achievement or meritorious service of military personnel who were not eligible to receive the higher Commendation Medal or the Meritorious Service Medal.
The Navy Arctic Service Ribbon is a decoration of the United States Navy which was established in May 1986. The ribbon is authorized to any member of the U.S. Navy or United States Marine Corps for service above the Arctic Circle. Like the Antarctica Service Medal, it may also be awarded to civilians and members of other U.S. services.
A "V" device is a metal 1⁄4-inch (6.4 mm) capital letter "V" with serifs which, when worn on certain decorations awarded by the United States Armed Forces, distinguishes a decoration awarded for combat valor or heroism from the same decoration being awarded for a member's actions under circumstances other than combat.

A service star is a miniature bronze or silver five-pointed star 3⁄16 inch (4.8 mm) in diameter that is authorized to be worn by members of the eight uniformed services of the United States on medals and ribbons to denote an additional award or service period. The service star may also be referred to as a campaign star or battle star depending on which award the star is authorized for and the manner in which the device is used for the award. "Battle star" is also the term used to refer to decorations issued by the United States Navy during World War II and the Korean War to individual ships, recognizing a vessel's participation in a particular battle or operation.
The Secretary of Transportation Outstanding Unit Award is a U.S. government unit decoration which was established in 1994. The Presidential Unit Citation and Joint Meritorious Unit Award are considered senior to the Secretary of Transportation Outstanding Unit Award. Additional awards of the decoration were denoted by gold award stars.
An Overseas Service Ribbon is a service military award of the United States military which recognizes those service members who have performed military tours outside the borders of the United States of America. There are different versions of the Overseas Service Ribbons for the U.S. Army, U.S. Navy, U.S. Air Force, U.S. Space Force, and the U.S. Coast Guard. Both the U.S. Navy and the U.S. Marines receive the Navy and Marine Corps Overseas Service Ribbon.
The Coast Guard Unit Commendation is the highest peacetime unit award that may be awarded to military commands of the United States Coast Guard. The decoration was first created in 1963 and is presented to members of any Coast Guard unit that distinguishes itself by valorous or extremely meritorious service, not involving combat, but in support of Coast Guard operations.
The American Defense Service Medal was a military award of the United States Armed Forces, established by Executive Order 8808, by President Franklin D. Roosevelt, on June 28, 1941. The medal was intended to recognize those military service members who had served on active duty between September 8, 1939, and December 7, 1941.

The Global War on Terrorism Service Medal (GWOT-SM) is a military award of the United States Armed Forces which was created through Executive Order 13289 on 12 March 2003, by President George W. Bush. The medal recognizes those military service members who have supported operations to counter terrorism in the War on Terror from 11 September 2001, to a date yet to be determined.

The Armed Forces Reserve Medal (AFRM) is a service medal of the United States Armed Forces that has existed since 1958. The medal recognizes service performed by members of the reserve components and is awarded to both officers and enlisted personnel. The medal is considered a successor award to the Naval Reserve Medal and the Marine Corps Reserve Ribbon, which were discontinued in 1958 and 1965, respectively.

The Cold War Victory Medal is not an official medal of the United States federal government, but is a state National Guard medal in Louisiana and Texas, and in ribbon form only by the State of Alaska, for those who served in their positions honorably during the years of the Cold War, defined as lasting from September 2, 1945 to December 26, 1991. In the medal's unofficial capacity it can be purchased, but not worn in uniform.

The Transportation 9-11 Medal is a special decoration of the U.S. Department of Transportation which was first created in 2002. The decoration recognizes those civilians and members of the military who performed heroic deeds and valorous accomplishments in the immediate aftermath of the September 11, 2001 attacks on the United States of America.
Awards and decorations of the United States Coast Guard are military medals and ribbons of the United States Coast Guard which are currently issued under the authority of the Department of Homeland Security.
Awards and decorations of the United States government are civilian awards of the U.S. federal government which are typically issued for sustained meritorious service, in a civilian capacity, while serving in the U.S. federal government. Certain U.S. government awards may also be issued to military personnel of the United States Armed Forces and be worn in conjunction with awards and decorations of the United States military. In order of precedence, those U.S. non-military awards and decorations authorized for wear are worn after U.S. military personal decorations and unit awards and before U.S. military campaign and service awards.
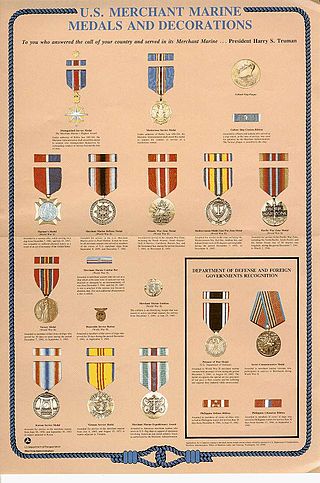
Awards and decorations of the United States Merchant Marine are civilian decorations of the United States which are issued to the members of the United States Merchant Marine for a variety of duties both in peace and war. Originally authorized to be issued by the War Shipping Administration of the World War II era, these awards were later issued by the Maritime Commission and are currently issued by the Department of Transportation's Martitime Administration.
The Guardian Medal or Department of Transportation Guardian Medal is an award of the United States Department of Transportation which was established by Secretary of Transportation Norman Y. Mineta following the terrorist attacks on September 11, 2001.







