
The history of Jordan refers to the history of the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan and the background period of the Emirate of Transjordan under British protectorate as well as the general history of the region of Transjordan.

The Emirate of Transjordan, officially known as the Amirate of Trans-Jordan, was a British protectorate established on 11 April 1921, which remained as such until achieving formal independence as the Kingdom of Transjordan in 1946.

Abdullah I bin Al-Hussein was the ruler of Jordan from 11 April 1921 until his assassination in 1951. He was the Emir of Transjordan, a British protectorate, until 25 May 1946, after which he was king of an independent Jordan. As a member of the Hashemite dynasty, the royal family of Jordan since 1921, Abdullah was a 38th-generation direct descendant of Muhammad.

Talal bin Abdullah was King of Jordan from the assassination of his father, King Abdullah I, on 20 July 1951 until his forced abdication on 11 August 1952. As a member of the Hashemite dynasty, the royal family of Jordan since 1921, Talal was a 39th-generation direct descendant of Muhammad.

The coat of arms of Jordan or the emblem of the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan is the arms of dominion for the king of Jordan. The emblem was initially adopted by Abdullah I, the emir of Transjordan, in 1921. The emblem continued to be used after Transjordan emerged as an independent kingdom in 1946.

The Arab Legion was the police force, then regular army, of the Emirate of Transjordan, a British protectorate, in the early part of the 20th century, and then of the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan, an independent state, with a final Arabization of its command taking place in 1956, when British senior officers were replaced by Jordanian ones.

The Jordanian administration of the West Bank officially began on 24 April 1950, and ended with the decision to sever ties on 31 July 1988. The period started during the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, when Jordan occupied and subsequently annexed the portion of Mandatory Palestine that became known as the West Bank, including East Jerusalem. The territory remained under Jordanian control until it was occupied by Israel during the 1967 Six Day War and eventually Jordan renounced its claim to the territory in 1988.
The Arab League was formed in Cairo on 22 March 1945 with six members: Egypt, Iraq, Transjordan, Lebanon, Saudi Arabia, and Syria. Yemen joined on 5 May 1945. Since its formation the Arab League has promoted the Palestinian Arab cause in the Israeli–Palestinian conflict, including by imposing the Arab League boycott of Israel. The Arab League opposed the United Nations Partition Plan for Palestine in 1947. On 15 May 1948, the then seven Arab League members coordinated an invasion of what was by then the former British Mandate, marking the start of the 1948 Arab–Israeli War.

The Hashemite Kingdom of Hejaz was a state in the Hejaz region of Western Asia that included the western portion of the Arabian Peninsula that was ruled by the Hashemite dynasty. It was self-proclaimed as a kingdom in June 1916 during the First World War, to be independent from the Ottoman Empire, on the basis of an alliance with the British Empire to drive the Ottoman Army from the Arabian Peninsula during the Arab Revolt.
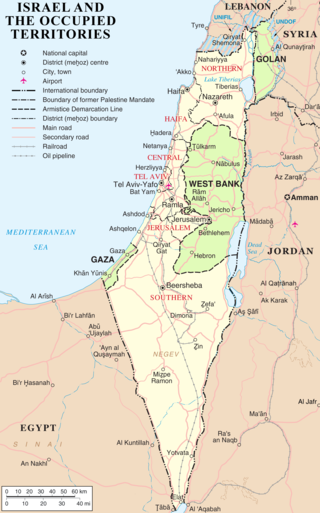
The modern borders of Israel exist as the result both of past wars and of diplomatic agreements between the State of Israel and its neighbours, as well as an effect of the agreements among colonial powers ruling in the region before Israel's creation. Only two of Israel's five total potential land borders are internationally recognized and uncontested, while the other three remain disputed; the majority of its border disputes are rooted in territorial changes that came about as a result of the 1967 Arab–Israeli War, which saw Israel occupy large swathes of territory from its rivals. Israel's two formally recognized and confirmed borders exist with Egypt and Jordan since the 1979 Egypt–Israel peace treaty and the 1994 Israel–Jordan peace treaty, while its borders with Syria, Lebanon and the Palestinian territories remain internationally defined as contested.
The history of the Jews in Jordan can be traced back to Biblical times. Presently, there are no legal restrictions on Jews in Jordan, and they are permitted to own property and conduct business in the country, but in 2006 there were reported to be no Jewish citizens of Jordan, nor any synagogues or other Jewish institutions.

The Trans-Jordan Frontier Force was formed on 1 April 1926, to replace the disbanded British Gendarmerie. It was a creation of the British High Commissioner for Palestine whose intention was that the Force should defend Trans-Jordan's northern and southern borders. The TJFF was also an Imperial Service regiment whose Imperial Service soldiers agreed to serve wherever required and not just within the borders of their own colony, protectorate or, in the case of the Transjordan, mandate. This was in contrast to the Arab Legion, which was seen more as an internal security militia, deriving from the troops of the Arab Revolt and closely associated with the Hashemite cause. The Amir Abdullah was an Honorary Colonel of the Trans-Jordan Frontier Force from its inception. However, the local commanders thought it unnecessary to form an additional force, believing that the expansion of The Arab Legion would be a better action.

This is a survey of the postage stamps and postal history of Jordan, formerly Transjordan.
This is a timeline of major events in the history of the modern state of Jordan.

The Mandate for Palestine was a League of Nations mandate for British administration of the territories of Palestine and Transjordan – which had been part of the Ottoman Empire for four centuries – following the defeat of the Ottoman Empire in World War I. The mandate was assigned to Britain by the San Remo conference in April 1920, after France's concession in the 1918 Clemenceau–Lloyd George Agreement of the previously agreed "international administration" of Palestine under the Sykes–Picot Agreement. Transjordan was added to the mandate after the Arab Kingdom in Damascus was toppled by the French in the Franco-Syrian War. Civil administration began in Palestine and Transjordan in July 1920 and April 1921, respectively, and the mandate was in force from 29 September 1923 to 15 May 1948 and to 25 May 1946 respectively.

Jordanian nationalism is a nationalistic ideology that considers the Jordanian people a separate nation and strives to maintain Jordan as an independent nation-state. It emerged as one of three nationalist currents in the 1920s, and was opposed to both Palestinian nationalism present in the region, as well as the Hashemite Arab nationalism promoted by Abdullah I, the first ruler of the Emirate of Transjordan.
Jordan–United Kingdom relations, or Anglo-Jordanian relations, refers to the relationship between the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.

Independence Day is an event in Jordan marking its 1946 independence from the United Kingdom.

The Occupation of Ma'an was the post-World War I occupation of the Sanjak of Ma'an, which straddled the regions of Syria and Arabia, by members of the Hashemite family, who came to power in various regions of the Near East and Arabia; they were King Hussein in the Kingdom of Hejaz, Emir Faisal representing the Arab government in Damascus and Abdullah, who was to become Emir of Transjordan. The region includes the governorates of Ma'an and Aqaba, today in Jordan, as well as the area which was to become a large part of the Israeli Southern District, including the city of Eilat.
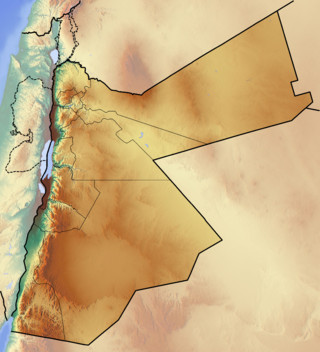
The Jordan–Saudi Arabia border is 731 km (454 mi) in length and runs from the Gulf of Aqaba in the south-west to the tripoint with Iraq in the north-east.

















