Related Research Articles

The 1810s was a decade of the Gregorian calendar that began on January 1, 1810, and ended on December 31, 1819.

The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of conflicts fought between the French First Republic (1803–1804) and First French Empire (1804–1815) under the First Consul and Emperor of the French Napoleon Bonaparte and a fluctuating array of European coalitions. The wars originated in political forces arising from the French Revolution (1789–1799) and from the French Revolutionary Wars (1792–1802) and produced a period of French domination over Continental Europe. The wars are categorised as seven conflicts, five named after the coalitions that fought Napoleon, plus two named for their respective theatres: the War of the Third Coalition, War of the Fourth Coalition, War of the Fifth Coalition, War of the Sixth Coalition, War of the Seventh Coalition, the Peninsular War, and the French invasion of Russia.
The Treaty of Paris, signed on 30 May 1814, ended the war between France and the Sixth Coalition, part of the Napoleonic Wars, following an armistice signed on 23 April between Charles, Count of Artois, and the allies. The treaty set the borders for France under the House of Bourbon and restored territories to other nations. It is sometimes called the First Peace of Paris, as another one followed in 1815.

The Hundred Days, also known as the War of the Seventh Coalition, marked the period between Napoleon's return from eleven months of exile on the island of Elba to Paris on 20 March 1815 and the second restoration of King Louis XVIII on 8 July 1815. This period saw the War of the Seventh Coalition, and includes the Waterloo Campaign and the Neapolitan War as well as several other minor campaigns. The phrase les Cent Jours was first used by the prefect of Paris, Gaspard, comte de Chabrol, in his speech welcoming the king back to Paris on 8 July.

In the War of the Sixth Coalition, sometimes known in Germany as the Wars of Liberation, a coalition of Austria, Prussia, Russia, Spain, the United Kingdom, Portugal, Sweden, Sardinia, and a number of German States defeated France and drove Napoleon into exile on Elba. After the disastrous French invasion of Russia of 1812 in which they had been forced to support France, Prussia and Austria joined Russia, the United Kingdom, Sweden, and Portugal, and the rebels in Spain who were already at war with France.

The War of the Second Coalition was the second war targeting revolutionary France by many European monarchies, led by Britain, Austria, and Russia and including the Ottoman Empire, Portugal, Naples and various German monarchies. Prussia did not join the coalition, while Spain supported France.

The Treaty of Kiel or Peace of Kiel was concluded between the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and the Kingdom of Sweden on one side and the Kingdoms of Denmark and Norway on the other side on 14 January 1814 in Kiel. It ended the hostilities between the parties in the ongoing Napoleonic Wars, where the United Kingdom and Sweden were part of the anti-French camp while Denmark–Norway was allied to the French Empire.
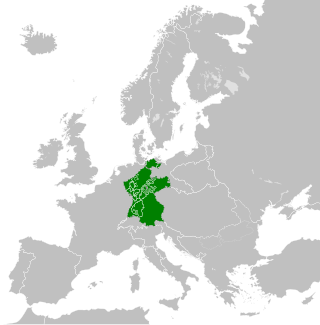
The Confederated States of the Rhine, simply known as the Confederation of the Rhine or Rhine Confederation, was a confederation of German client states established at the behest of Napoleon some months after he defeated Austria and Russia at the Battle of Austerlitz. Its creation brought about the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire shortly afterward. The Confederation of the Rhine lasted for only seven years, from 1806 to 1813, dissolving after Napoleon's defeat in the War of the Sixth Coalition.

The War of the Fourth Coalition was a war spanning 1806–1807 that saw a multinational coalition fight against Napoleon's French Empire, subsequently being defeated. The main coalition partners were Prussia and Russia with Saxony, Sweden, and Great Britain also contributing. Excluding Prussia, some members of the coalition had previously been fighting France as part of the Third Coalition, and there was no intervening period of general peace. On 9 October 1806, Prussia declared war on France and joined a renewed coalition, fearing the rise in French power after the defeat of Austria and establishment of the French-sponsored Confederation of the Rhine in addition to having learned of French plans to cede Prussian-desired Hanover to Britain in exchange for peace. Prussia and Russia mobilized for a fresh campaign with France, massing troops in Saxony.

The Battle of Sehested was fought on 10 December 1813 during the Dano-Swedish War of 1813–1814 between a Dano-Norwegian army under Prince Frederik of Hesse and a Coalition force led by Ludwig von Wallmoden-Gimborn. Near Sehested, Holstein, Frederik's troops defeated the Coalition army, inflicting over 1,100 casualties on von Wallmoden-Gimborn's force while suffering only 500. However, this victory did not prevent the Coalition from emerging victorious in the conflict in 1814.

The Swedish–Norwegian War, also known as the Campaign against Norway, War with Sweden 1814, also called the War of Cats or the Norwegian War of Independence, was a war fought between Sweden and Norway in the summer of 1814. According to the Treaty of Kiel, Norway would enter a union with Sweden under Charles XIII of Sweden. The war resulted in Norway being forced into the United Kingdoms of Sweden and Norway, but with its own constitution and parliament. The war marked the last time Sweden participated in an armed conflict with another nation, and its conclusion signalled the beginning of the country's long period of military neutrality.

The Polish Legions were several Polish military units that served with the French Army in the Napoleonic era, mainly from 1797 to 1803, although some units continued to serve until 1815.
The Treaties of Reichenbach were a series of agreements signed in Reichenbach between Great Britain, Prussia, Russia, and Austria. These accords served to establish and strengthen a united coalition force against Napoleon I of France.
The Treaty of Töplitz was signed in Töplitz on 9 September 1813, between Russia, Austria, and Prussia. The purpose of the agreement was to establish and strengthen a united coalition force against Napoleon I of France. Based on the terms of the accord, all signatories agreed to support each other with 60,000 troops. Another Treaty of Töplitz was signed between Great Britain and Austria.

The Russian–German Legion was a military formation of the Imperial Russian Army raised in 1812 by Peter I, Grand Duke of Oldenburg after being instigated by Alexander I of Russia.

The First French Empire or French Empire, also known as Napoleonic France, was the empire ruled by Napoleon Bonaparte, who established French hegemony over much of continental Europe at the beginning of the 19th century. It lasted from 18 May 1804 to 4 April 1814 and again briefly from 20 March 1815 to 7 July 1815, when Napoleon was exiled to St. Helena.

Alexander I, nicknamed "the Blessed", was Emperor of Russia from 1801, the first king of Congress Poland from 1815, and the grand duke of Finland from 1809 to his death in 1825. He ruled Russia during the chaotic period of the Napoleonic Wars.

The French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars, sometimes called the Great French War, were a series of conflicts between the French and several European monarchies between 1792 and 1815. They encompass first the French Revolutionary Wars against the newly declared French Republic and from 1803 onwards the Napoleonic Wars against First Consul and later Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte. They include the Coalition Wars as a subset: seven wars waged by various military alliances of European powers, known as Coalitions, against Revolutionary France – later the First French Empire – and its allies between 1792 and 1815:
References
- ↑ Clare, p. 2707. The following were the treaties constituting the new Coalition against Napoleon: ... 4. The Treaty of Peterswaldau between Great Britain and Russia, July 6, 1813, by which the former agreed to support a German legion of ten thousand men in the Russian service.