
This article concerns the 200 BC decade, that lasted from 209 BC to 200 BC.
This article concerns the period 219 BC – 210 BC.
This article concerns the period 199 BC – 190 BC.
Year 205 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Scipio and Dives. The denomination 205 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Philip V was king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon from 221 to 179 BC. Philip's reign was principally marked by the Social War in Greece and a struggle with the emerging power of the Roman Republic. He would lead Macedon against Rome in the First and Second Macedonian Wars. While he lost the latter, Philip later allied with Rome against Antiochus III in the Roman-Seleucid War. He died in 179 BC from illness after efforts to recover the military and economic condition of Macedonia and passed the throne onto his elder son, Perseus of Macedon.
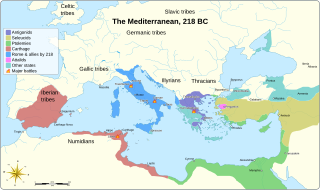
The First Macedonian War was fought by Rome, allied with the Aetolian League and Attalus I of Pergamon, against Philip V of Macedon, contemporaneously with the Second Punic War against Carthage. There were no decisive engagements, and the war ended in a stalemate.
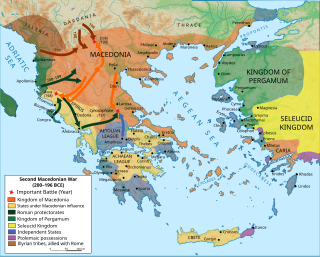
The Second Macedonian War was fought between Macedon, led by Philip V of Macedon, and Rome, allied with Pergamon and Rhodes. Philip was defeated and was forced to abandon all possessions in southern Greece, Thrace and Asia Minor. During their intervention, although the Romans declared the "freedom of the Greeks" against the rule from the Macedonian kingdom, the war marked a significant stage in increasing Roman intervention in the affairs of the eastern Mediterranean, which would eventually lead to Rome's conquest of the entire region.

The Battle of Magnesia took place in either December 190 or January 189 BC. It was fought as part of the Roman–Seleucid War, pitting forces of the Roman Republic led by the consul Lucius Cornelius Scipio Asiaticus and the allied Kingdom of Pergamon under Eumenes II against a Seleucid army of Antiochus III the Great. The two armies initially camped northeast of Magnesia ad Sipylum in Asia Minor, attempting to provoke each other into a battle on favorable terrain for several days.

Hellenistic Greece is the historical period of the country following Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the annexation of the classical Greek Achaean League heartlands by the Roman Republic. This culminated at the Battle of Corinth in 146 BC, a crushing Roman victory in the Peloponnese that led to the destruction of Corinth and ushered in the period of Roman Greece. Hellenistic Greece's definitive end was with the Battle of Actium in 31 BC, when the future emperor Augustus defeated Greek Ptolemaic queen Cleopatra VII and Mark Antony, the next year taking over Alexandria, the last great center of Hellenistic Greece.

The AetolianLeague was a confederation of tribal communities and cities in ancient Greece centered in Aetolia in Central Greece. It was probably established during the early Hellenistic era, in opposition to Macedon and the Achaean League. Two annual meetings were held at Thermon and Panaetolika. The league occupied Delphi from 290 BC and steadily gained territory until, by the end of the 3rd century BC, it controlled the whole of central Greece with the exception of Attica and Boeotia. At its peak, the league's territory included Locris, Malis, Dolopes, parts of Thessaly, Phocis, and Acarnania. In the latter part of its power, certain Greek city-states joined the Aetolian League such as the Arcadian cities of Mantineia, Tegea, Phigalia and Kydonia on Crete.

The Macedonian Wars were a series of conflicts fought by the Roman Republic and its Greek allies in the eastern Mediterranean against several different major Greek kingdoms. They resulted in Roman control or influence over Greece and the rest of the eastern Mediterranean basin, in addition to their hegemony in the western Mediterranean after the Punic Wars. Traditionally, the "Macedonian Wars" include the four wars with Macedonia, in addition to one war with the Seleucid Empire, and a final minor war with the Achaean League. The most significant war was fought with the Seleucid Empire, while the war with Macedonia was the second, and both of these wars effectively marked the end of these empires as major world powers, even though neither of them led immediately to overt Roman domination. Four separate wars were fought against the weaker power, Macedonia, due to its geographic proximity to Rome, though the last two of these wars were against haphazard insurrections rather than powerful armies. Roman influence gradually dissolved Macedonian independence and digested it into what was becoming a leading empire. The outcome of the war with the now-deteriorating Seleucid Empire was ultimately fatal to it as well, though the growing influence of Parthia and Pontus prevented any additional conflicts between it and Rome.
The Illyro-Roman Wars were a series of wars fought between the Roman Republic and the Illyrian kingdom of the Ardiaei. In the First Illyrian War, which lasted from 229 BC to 228 BC, Rome's concern was that the trade across the Adriatic Sea increased after the First Punic War at a time when Ardiaei power increased under queen Teuta. Attacks on trading vessels of Rome's Italic allies by Illyrian pirates and the death of a Roman envoy named Coruncanius on Teuta's orders, prompted the Roman senate to dispatch a Roman army under the command of the consuls Lucius Postumius Albinus and Gnaeus Fulvius Centumalus. Rome expelled Illyrian garrisons from a number of Greek cities including Epidamnus, Apollonia, Corcyra, Pharos and established a protectorate over these Greek towns. The Romans also set up Demetrius of Pharos as a power in Illyria to counterbalance the power of Teuta.

Philopoemen was a skilled Greek general and statesman, who was Achaean strategos on eight occasions.
Demetrius of Pharos was a ruler of Pharos involved in the First Illyrian War, after which he ruled a portion of the Illyrian Adriatic coast on behalf of the Romans, as a client king.
Scerdilaidas or Skerdilaid was an Illyrian ruler of the Illyrian kingdom under the Labeatan dynasty. Before taking the throne, Scerdilaidas was commander of the Illyrian armies and played a major role in the Illyrian Wars against the Romans.

Attalus I, surnamed Soter, was the ruler of the Ionian Greek polis of Pergamon and the larger Pergamene Kingdom from 241 BC to 197 BC. He was the adopted son of King Eumenes I, whom he succeeded, and was the first of the Attalid dynasty to assume the title of king, sometime around 240 to 235 BC. He was the son of Attalus and his wife Antiochis.

The Cretan War was fought by King Philip V of Macedon, the Aetolian League, many Cretan cities and Spartan pirates against the forces of Rhodes and later Attalus I of Pergamum, Byzantium, Cyzicus, Athens, and Knossos.

The Roman–Seleucid war (192–188 BC), also called the Aetolian war, Antiochene war, Syrian war, and Syrian-Aetolian war was a military conflict between two coalitions, one led by the Roman Republic and the other led by the Seleucid king Antiochus III. The fighting took place in modern-day southern Greece, the Aegean Sea, and Asia Minor.
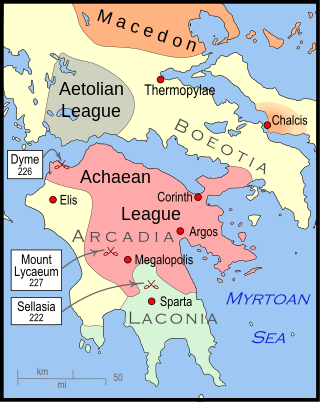
The Social War, also War of the Allies and the Aetolian War, was fought from 220 BC to 217 BC between the Hellenic League under Philip V of Macedon and the Aetolian League, Sparta and Elis. It was ended with the Peace of Naupactus.

The kingdom of Macedonia was an ancient state in what is now the Macedonian region of northern Greece, founded in the mid-7th century BC during the period of Archaic Greece and lasting until the mid-2nd century BC. Led first by the Argead dynasty of kings, Macedonia became a vassal state of the Achaemenid Empire of ancient Persia during the reigns of Amyntas I of Macedon and his son Alexander I of Macedon. The period of Achaemenid Macedonia came to an end in roughly 479 BC with the ultimate Greek victory against the second Persian invasion of Greece led by Xerxes I and the withdrawal of Persian forces from the European mainland.











