Related Research Articles

Indian Territory and the Indian Territories are terms that generally described an evolving land area set aside by the United States government for the relocation of Native Americans who held original Indian title to their land as an independent. The concept of an Indian territory was an outcome of the U.S. federal government's 18th- and 19th-century policy of Indian removal. After the American Civil War (1861–1865), the policy of the U.S. government was one of assimilation.

The Treaty of Greenville, also known to Americans as the Treaty with the Wyandots, etc., but formally titled A treaty of peace between the United States of America, and the tribes of Indians called the Wyandots, Delawares, Shawanees, Ottawas, Chippewas, Pattawatimas, Miamis, Eel Rivers, Weas, Kickapoos, Piankeshaws, and Kaskaskias was a 1795 treaty between the United States and indigenous nations of the Northwest Territory, including the Wyandot and Delaware peoples, that redefined the boundary between indigenous peoples' lands and territory for European American community settlement.
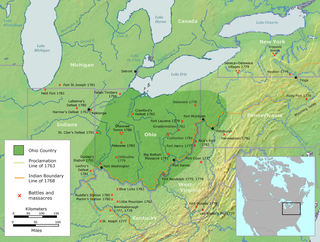
The Ohio Country was a name used for a loosely defined region of colonial North America west of the Appalachian Mountains and south of Lake Erie.

The Shawnee are a Native American people of the Northeastern Woodlands. Their language, Shawnee, is an Algonquian language.
Cherokee Nation v. Georgia (1831), 30 U.S. 1 (1831), was a landmark United States Supreme Court case. The Cherokee Nation asked the Court to stop Georgia from enforcing state laws that took away their rights within the Cherokee territory. However, the Supreme Court declined to rule on the cases's merits, stating that it lacked the original jurisdiction, or authority, to decide in a matter between a U.S. state and the Cherokee Nation. Chief Justice John Marshall explained that the Cherokee Nation was not a "foreign nation" but a "domestic dependent nation," comparing their relationship with the United States to that of a "ward to its guardian."

Tenskwatawa was a Native American religious and political leader of the Shawnee tribe, known as the Prophet or the Shawnee Prophet. He was a younger brother of Tecumseh, a leader of the Shawnee. In his early years Tenskwatawa was given the name Lalawethika, but he changed it around 1805 and transformed himself from a hapless, alcoholic youth into an influential spiritual leader. Tenskwatawa denounced the Americans, calling them the offspring of the Evil Spirit, and led a purification movement that promoted unity among the Indigenous peoples of North America, rejected acculturation to the American way of life, and encouraged his followers to pursue traditional ways.

The Treaty of St. Mary's may refer to one of six treaties concluded in fall of 1818 between the United States and Natives of central Indiana regarding purchase of Native land. The treaties were
The Shawnee Tribe is a federally recognized Native American tribe in Oklahoma. Formerly known as the Loyal Shawnee, they are one of three federally recognized Shawnee tribes. The others are the Absentee-Shawnee Tribe of Indians of Oklahoma and the Eastern Shawnee Tribe of Oklahoma.
On August 3, 1829, members of the Shawnee Indians and the Seneca Indians signed the Treaty of Lewistown with the United States. In this treaty, Senecas and Shawnees living at Lewistown, Ohio, relinquished their claim to the land and joined the rest of the Ohio Senecas already living on a reservation west of the Mississippi River.

The Treaty of Fort Meigs, also called the Treaty of the Maumee Rapids, formally titled, "Treaty with the Wyandots, etc., 1817", was the most significant Indian treaty by the United States in Ohio since the Treaty of Greenville in 1795. It resulted in cession by bands of several tribes of nearly all their remaining Indian lands in northwestern Ohio. It was the largest wholesale purchase by the United States of Indian land in the Ohio area. It was also the penultimate one; a small area below the St. Mary's River and north of the Greenville Treaty Line was ceded in the Treaty of St. Mary's in 1818.
Snake was the English language name of two Shawnee leaders prominent in the history of the Ohio Country: Peteusha and Shemanetoo. They were both commonly referred to as "Snake" in historical records, or by variations such as "Black Snake" or "Captain Snake," so it is often difficult to determine which individual was being referred to. On a number of occasions, the two Snakes both signed a letter or appeared together, so it is clear they were two different people. There may have been additional Shawnees called "Snake," further complicating the matter. According to historian John Sugden, "it is unlikely if the biographies of these chiefs will ever be completely disentangled."

The Choctaw Trail of Tears was the attempted ethnic cleansing and relocation by the United States government of the Choctaw Nation from their country, referred to now as the Deep South, to lands west of the Mississippi River in Indian Territory in the 1830s by the United States government. A Choctaw Miko (chief) was quoted by the Arkansas Gazette as saying that the removal was a "trail of tears and death." Since removal, the Choctaw have developed since the 20th century as three federally recognized tribes: the largest, the Choctaw Nation of Oklahoma; the Mississippi Band of Choctaw Indians, and the Jena Band of Choctaw Indians in Louisiana.
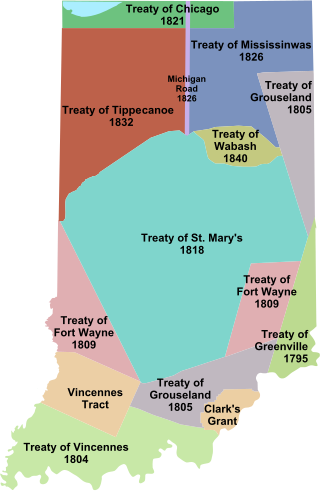
Indian removals in Indiana followed a series of the land cession treaties made between 1795 and 1846 that led to the removal of most of the native tribes from Indiana. Some of the removals occurred prior to 1830, but most took place between 1830 and 1846. The Lenape (Delaware), Piankashaw, Kickapoo, Wea, and Shawnee were removed in the 1820s and 1830s, but the Potawatomi and Miami removals in the 1830s and 1840s were more gradual and incomplete, and not all of Indiana's Native Americans voluntarily left the state. The most well-known resistance effort in Indiana was the forced removal of Chief Menominee and his Yellow River band of Potawatomi in what became known as the Potawatomi Trail of Death in 1838, in which 859 Potawatomi were removed to Kansas and at least forty died on the journey west. The Miami were the last to be removed from Indiana, but tribal leaders delayed the process until 1846. Many of the Miami were permitted to remain on land allotments guaranteed to them under the Treaty of St. Mary's (1818) and subsequent treaties.
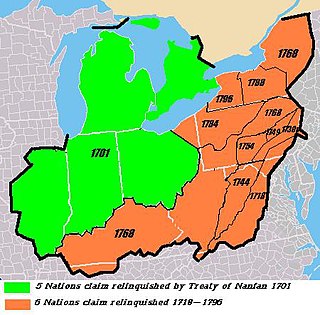
The Six Nations land cessions were a series of land cessions by the Haudenosaunee and Lenape which ceded large amounts of land, including both recently conquered territories acquired from other indigenous peoples in the Beaver Wars, and ancestral lands to the Thirteen Colonies and the United States. The land ceded covered, partially or in the entire, the U.S. states of New York, Pennsylvania, Maryland, Virginia, West Virginia, Kentucky, Ohio, Tennessee and North Carolina. They were bordered to the west by the Algonquian lands in the Ohio Country, Cherokee lands to the south, and Muscogee and Choctaw lands to the southeast.
The Eastern Shawnee Tribe of Oklahoma is one of three federally recognized Shawnee tribes. They are located in Oklahoma and Missouri.

The Cherokee Nation was a legal, autonomous, tribal government in North America recognized from 1794 to 1907. It was often referred to simply as "The Nation" by its inhabitants. The government was effectively disbanded in 1907, after its land rights had been extinguished, prior to the admission of Oklahoma as a state. During the late 20th century, the Cherokee people reorganized, instituting a government with sovereign jurisdiction known as the Cherokee Nation. On July 9, 2020, the United States Supreme Court ruled that the Muscogee (Creek) Nation had never been disestablished in the years before allotment and Oklahoma Statehood.
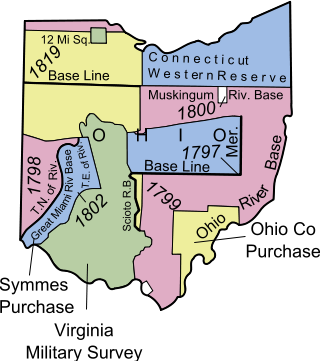
Indian Land Grants were land tracts granted to various Indians by Treaty or by United States Congressional action in the Nineteenth century in northwestern Ohio.
On the eve of the American Civil War in 1861, a significant number of Indigenous peoples of the Americas had been relocated from the Southeastern United States to Indian Territory, west of the Mississippi. The inhabitants of the eastern part of the Indian Territory, the Five Civilized Tribes, were suzerain nations with established tribal governments, well established cultures, and legal systems that allowed for slavery. Before European Contact these tribes were generally matriarchial societies, with agriculture being the primary economic pursuit. The bulk of the tribes lived in towns with planned streets, residential and public areas. The people were ruled by complex hereditary chiefdoms of varying size and complexity with high levels of military organization.

Quatawapea or John Lewis, also known as Captain Lewis and Colonel Lewis and ‘’’Captain Johnny’’’, was a Shawnee leader for whom Lewistown, Ohio, is named.
References
- Ohio Historical Society, 2005, "Treaty of Wapakoneta (1831)", Ohio History Central: An Online Encyclopedia of Ohio History.
- Full text of the Treaty of Wapakoneta