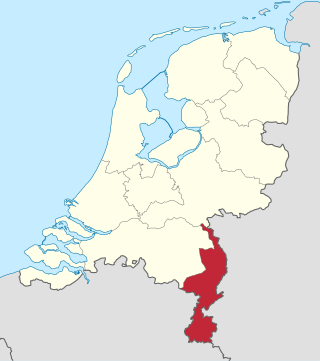
Limburg, also known as Dutch Limburg, is the southernmost of the twelve provinces of the Netherlands. It is bordered by Gelderland to the north and by North Brabant to its west. Its long eastern boundary forms the international border with the state of North Rhine-Westphalia in Germany. To the west is the international border with the similarly named Belgian province of Limburg, part of which is delineated by the river Meuse. To the south, Limburg is bordered by the Belgian province of Liège. The Vaalserberg is on the extreme southeastern point, marking the tripoint of the Netherlands, Germany and Belgium.

The Meuse or Maas is a major European river, rising in France and flowing through Belgium and the Netherlands before draining into the North Sea from the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta. It has a total length of 925 km.

Limburg, also known as Belgian Limburg, is a province in Belgium. It is the easternmost of the five Dutch-speaking provinces that together form the Region of Flanders, which is one of the three main political and cultural sub-divisions of modern-day Belgium. As of January 2024, Limburg had a population of 0.9 million.

The Scheldt is a 435-kilometre-long (270 mi) river that flows through northern France, western Belgium, and the southwestern part of the Netherlands, with its mouth at the North Sea. Its name is derived from an adjective corresponding to Old English sċeald ("shallow"), Modern English shoal, Low German schol, West Frisian skol, and obsolete Swedish skäll ("thin").

Zonhoven is a municipality located in the middle of the Belgian province of Limburg located north of Hasselt and also borders Houthalen-Helechteren, Genk and Heusden-Zolder. It’s an urbanized municipality, in the edge area of Hasselt. The municipality belongs to the On January 1, 2019, Zonhoven had a total population of 21,237. The total area is 39.34 km2 which gives a population density of 506 inhabitants per km2.

The Southern Netherlands, also called the Catholic Netherlands, were the parts of the Low Countries belonging to the Holy Roman Empire which were at first largely controlled by Habsburg Spain and later by the Austrian Habsburgs until occupied and annexed by Revolutionary France (1794–1815).
The Treaty of London of 1839, was signed on 19 April 1839 between the major European powers, the United Kingdom of the Netherlands, and the Kingdom of Belgium. It was a direct follow-up to the 1831 Treaty of the XVIII Articles, which the Netherlands had refused to sign, and the result of negotiations at the London Conference of 1838–1839 which sought to maintain the Concert of Europe.

The Spanish Netherlands was the Habsburg Netherlands ruled by the Spanish branch of the Habsburgs from 1556 to 1714. They were a collection of States of the Holy Roman Empire in the Low Countries held in personal union by the Spanish Crown. This region comprised most of the modern states of Belgium and Luxembourg, as well as parts of northern France, the southern Netherlands, and western Germany, with the capital being Brussels. The Army of Flanders was given the task of defending the territory.

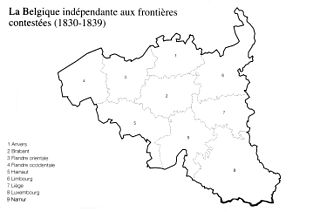
Limburg was one of the provinces of the United Kingdom of the Netherlands and later Belgium. The province existed for the duration of the United Kingdom, from 1815 to 1830, and for the first years after Belgian independence, from 1830 to 1839. When King William I signed the Treaty of London in 1839, the province was split into a Belgian part and a Dutch part, the latter being a new Duchy of Limburg.

François Auguste, Baron Lambermont, was a Belgian statesman. He came of a family of small farmer proprietors, who had held land during three centuries. He was intended for the priesthood and entered the seminary of Floreffe, but his energies claimed a more active sphere.

The ten days' campaign was a failed military expedition by the United Kingdom of the Netherlands against the secessionist Kingdom of Belgium between 2 and 12 August 1831. The campaign was an attempt by the Dutch King William I to halt the course of the Belgian Revolution which had broken out in August 1830.
The Eight Articles of London, also known as the London Protocol of 21 June 1814, were a secret convention between the Great Powers: the United Kingdom, the Kingdom of Prussia, the Austrian Empire, and the Russian Empire to award the territory of current Belgium and The Netherlands to William I of the Netherlands, then "Sovereign Prince" of the United Netherlands. He accepted this award on 21 July 1814.

The history of Flanders concerns not only the modern Dutch-speaking part of Belgium, which is now called "Flanders", but also several neighbouring territories and populations. Its historical core territory was in western Belgium between the coast and the Scheldt river.

The Belgian province of Limburg in Flanders is a region which has had many names and border changes over its long recorded history. Its modern name is a name shared with the neighbouring province of the Netherlands, with which it was for a while politically united. The two provinces received their modern name after 1815, based upon the name of the medieval Duchy of Limburg, which had actually been in what is now neighbouring Wallonia, centred upon the town of Limbourg on the Vesdre.

The Sovereign Principality of the United Netherlands was a short-lived sovereign principality and the precursor of the United Kingdom of the Netherlands, in which it was reunited with the Southern Netherlands in 1815. The principality was proclaimed in 1813 when the victors of the Napoleonic Wars established a political reorganisation of Europe, which would eventually be defined by the Congress of Vienna.

The Belgium–Netherlands border separates Belgium and the Netherlands and is 450 km (280 mi) long.
Events in the year 1833 in Belgium.

Events in the year 1863 in Belgium.
Events in the year 1851 in Belgium.
The Kingdom of Hanover and the United States began relations with mutual recognition in 1830 but never formulated diplomatic ties. All ties came to an abrupt halt when Hanover was defeated during the Austro-Prussian War of 1866 and subsequently merged directly into the Kingdom of Prussia. From this point, Hanover had relations with the United States as a part of the Kingdom of Prussia.















