The Neptune Range is a mountain range, 70 nautical miles long, lying west-southwest of Forrestal Range in the central part of the Pensacola Mountains, Antarctica. The range comprises Washington Escarpment with its associated ridges, valleys and peaks, the Iroquois Plateau, the Schmidt and the Williams Hills.
The Reedy Glacier is a major glacier in Antarctica, over 100 nautical miles long and 6 to 12 nautical miles wide, descending from the polar plateau to the Ross Ice Shelf between the Michigan Plateau and Wisconsin Range in the Transantarctic Mountains. It marks the limits of the Queen Maud Mountains on the west and the Horlick Mountains on the east.

Shackleton Glacier is a major Antarctic glacier, over 60 nautical miles long and from 5 to 10 nautical miles wide, descending from the Antarctic Plateau from the vicinity of Roberts Massif and flowing north through the Queen Maud Mountains to enter the Ross Ice Shelf between Mount Speed and Waldron Spurs. Discovered by the United States Antarctic Service (USAS) (1939–41) and named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) for Sir Ernest Shackleton, British Antarctic explorer.
Irvine Glacier is a glacier, 40 miles (64 km) long, draining southeast between the Guettard Range and the Rare Range into the northern part of Gardner Inlet, Antarctica. It was discovered by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition (RARE), 1947–48, under Finn Ronne, who named it for George J. Irvine, of the Engineer Depot at Fort Belvoir, Virginia, who outlined the RARE photographic program.

Leonardo Glacier is a glacier flowing into Wilhelmina Bay between Sadler Point and Café Point, on the west coast of Graham Land, Antarctica. It was charted by the Belgian Antarctic Expedition under Gerlache, 1897–99, and was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1960 for Leonardo da Vinci, artist, musician, architect and the first aeronautical scientist.

Marzales is a municipality located in the province of Valladolid, Castile and León, Spain. According to the 2004 census (INE), the municipality has a population of 64 inhabitants.
Lady Newnes Bay is a bay about 60 nautical miles long in the western Ross Sea, extending along the coast of Victoria Land from Cape Sibbald to Coulman Island.
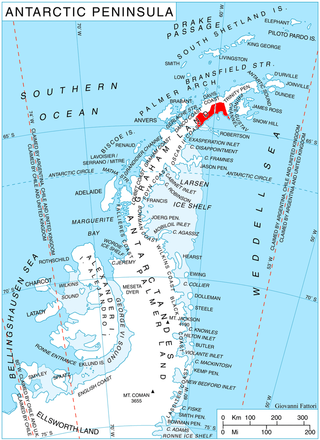
Albone Glacier is a deeply entrenched narrow glacier on the east side of Wolseley Buttress flowing southward from Detroit Plateau on Nordenskjöld Coast in Graham Land, Antarctica.
Niemur River, a perennial stream of the Murray catchment and part of the Murray–Darling basin, is located in the western Riverina region of south western New South Wales, Australia.
The Porthos Range is the second range south in the Prince Charles Mountains of Antarctica, extending for about 30 miles in an east-to-west direction between Scylla Glacier and Charybdis Glacier. First visited in December 1956 by the Australian National Antarctic Research Expeditions (ANARE) southern party under W.G. Bewsher (1956-57) and named after Porthos, a character in Alexandre Dumas, père's novel The Three Musketeers, the most popular book read on the southern journey.
Rancul is a town in La Pampa Province in Argentina.
Clodomira is a municipality and village in Santiago del Estero in Argentina.
Nilsen Plateau is a rugged, ice-covered plateau in Antarctica. When including Fram Mesa, the plateau is about 30 nautical miles long and 1 to 12 nautical miles wide, rising to 3,940 metres (12,930 ft) high between the upper reaches of the Amundsen and Scott glaciers, in the Queen Maud Mountains. Discovered in November 1911 by the Norwegian expedition under Roald Amundsen, and named by him for Captain Thorvald Nilsen, commander of the ship Fram.

Walker Point is a point on the southwest side of the entrance to Gurkovska Cove which lies 6 km (3.7 mi) south-west of Cape Valentine, near the eastern end of Elephant Island in the South Shetland Islands of Antarctica. The name appears on Powell's map of 1822 based upon the joint cruise of Captain Nathaniel B. Palmer, in the sloop James Monroe with Captain George Powell, in the sloop Dove, in December 1821. It was probably named for Captain John Walker, whose assistance in the construction of the map was acknowledged by Powell.
Watson Escarpment is a major escarpment in the Queen Maud Mountains, trending northward along the east margin of Scott Glacier, then eastward to Reedy Glacier where it turns southward along the glacier's west side. Somewhat arcuate, the escarpment is nearly 100 nautical miles long, rises 3,550 metres (11,650 ft) above sea level, and 1,000 to 1,500 metres above the adjacent terrain.

Weir Glacier is a glacier 8 nautical miles (15 km) long, flowing north into the south part of Barilari Bay between Prestoy Point and Byaga Point, on the west coast of Graham Land. First sighted and roughly charted in 1909 by the French Antarctic Expedition under Charcot. It was surveyed in 1935-36 by the British Graham Land Expedition (BGLE) under Rymill and later named for William D. Weir, 1st Viscount Weir of Eastwood, and his son, the Hon. James K. Weir, who contributed toward the cost of the BGLE, 1934–37.
Gregory Glacier is a glacier flowing into Cierva Cove north of Breguet Glacier, on the west coast of Graham Land, Antarctica. It was shown on an Argentine government chart of 1957. The glacier was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1960 for Hollingsworth Franklin Gregory, an American pioneer in the development and use of helicopters.

Henryk Glacier is a glacier on Arctowski Peninsula, on the Danco Coast of Antarctica, with a noteworthy cirque at the head; it flows southwest between Wild Spur and Hubl Peak into Errera Channel. The glacier was named in association with the peninsula after Henryk Arctowski, by the Polish Antarctic Expedition, in about 1993.

Luke Glacier is a glacier at least 15 nautical miles (28 km) long, flowing northwest into the head of Leroux Bay on the west coast of Graham Land, Antarctica. It is surmounted by Mount Chevreux on the south, Mount Perchot on the southwest and Mount Radotina on the northeast. The glacier was first sighted and roughly surveyed in 1909 by the Fourth French Antarctic Expedition. It was resurveyed in 1935–36 by the British Graham Land Expedition and later named for George Lawson Johnston, 1st Baron Luke of Pavenham, Chairman of Bovril Ltd, who contributed toward the cost of the expedition.






