
Giovanni Boccaccio was an Italian writer, poet, correspondent of Petrarch, and an important Renaissance humanist. Born in the town of Certaldo, he became so well known as a writer that he was sometimes simply known as "the Certaldese" and one of the most important figures in the European literary panorama of the fourteenth century. Some scholars define him as the greatest European prose writer of his time, a versatile writer who amalgamated different literary trends and genres, making them converge in original works, thanks to a creative activity exercised under the banner of experimentalism.

The Book of the City of Ladies, or Le Livre de la Cité des Dames, is a book written by Christine de Pizan believed to have been finished by 1405. Perhaps Pizan's most famous literary work, it is her second work of lengthy prose. Pizan uses the vernacular French language to compose the book, but she often uses Latin-style syntax and conventions within her French prose. The book serves as her formal response to Jean de Meun's popular Roman de la Rose. Pizan combats Meun's statements about women by creating an allegorical city of ladies. She defends women by collecting a wide array of famous women throughout history. These women are "housed" in the City of Ladies, which is actually the book. As Pizan builds her city, she uses each famous woman as a building block for not only the walls and houses of the city, but also as building blocks for her thesis. Each woman introduced to the city adds to Pizan's argument towards women as valued participants in society. She also advocates in favour of education for women.
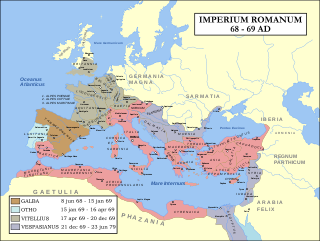
AD 69 (LXIX) was a common year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar. In the Roman Empire, it was known as the Year of the consulship of Galba and Vinius. The denomination AD 69 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Antonia Minor was the younger of two surviving daughters of Mark Antony and Octavia Minor. She was a niece of the Emperor Augustus, sister-in-law of the Emperor Tiberius, paternal grandmother of the Emperor Caligula and Empress Agrippina the Younger, mother of the Emperor Claudius, and maternal great-grandmother of the Emperor Nero. She outlived her husband Drusus, her oldest son, her daughter, and several of her grandchildren.

In Greek mythology, Argia or Argea was a daughter of King Adrastus of Argos, and of Amphithea, daughter of Pronax. She was married to Polynices, the exiled king of Thebes, and bore him three sons: Thersander, Adrastus, and Timeas.

In ancient Roman religion and myth, Carmenta was a goddess of childbirth and prophecy, associated with technological innovation as well as the protection of mothers and children and a patron of midwives. She was also said to have invented the Latin alphabet.

The gens Julia was one of the most prominent patrician families in ancient Rome. Members of the gens attained the highest dignities of the state in the earliest times of the Republic. The first of the family to obtain the consulship was Gaius Julius Iulus in 489 BC. The gens is perhaps best known, however, for Gaius Julius Caesar, the dictator and grand uncle of the emperor Augustus, through whom the name was passed to the so-called Julio-Claudian dynasty of the first century AD. The nomen Julius became very common in imperial times, as the descendants of persons enrolled as citizens under the early emperors began to make their mark in history.
Gaius Sallustius Passienus Crispus was a prominent figure in the Roman Empire during the first century. He held the consulship twice, and was stepfather of the future emperor Nero.

De Mulieribus Claris or De Claris Mulieribus is a collection of biographies of historical and mythological women by the Florentine author Giovanni Boccaccio, composed in Latin prose in 1361–1362. It is notable as the first collection devoted exclusively to biographies of women in post-ancient Western literature. At the same time as he was writing On Famous Women, Boccaccio also compiled a collection of biographies of famous men, De Casibus Virorum Illustrium.

Pompeia Paulina was the wife of the statesman, philosopher, and orator Lucius Annaeus Seneca, and she was part of a circle of educated Romans who sought to lead a principled life under the emperor Nero. She was likely the daughter of Pompeius Paulinus, an eques from Arelate in Gaul. Seneca was the emperor's tutor and later became his political adviser and minister. In 65 AD Nero demanded that Seneca commit suicide, having accused Seneca of taking part in the Pisonian conspiracy against him. Paulina attempted to die with her husband, but survived the suicide attempt.
Epicharis was an Ancient Roman freedwoman and a leading member of the Pisonian conspiracy against the emperor Nero.
Titus Flavius T. f. T. n. Sabinus was a Roman politician and soldier. A native of Reate, he was the elder son of Titus Flavius Sabinus and Vespasia Polla, and brother of the Emperor Vespasian.
Cornelius Fuscus was a Roman general who fought campaigns under the Emperors of the Flavian dynasty. He first distinguished himself as one of Vespasian's most ardent supporters during the civil war of 69 AD, known as the Year of the Four Emperors. Vespasian's son Domitian employed Fuscus as prefect of the Praetorian Guard, a post he held from 81 until his death.

De casibus virorum illustrium is a work of 56 biographies in Latin prose composed by the Florentine poet Giovanni Boccaccio of Certaldo in the form of moral stories of the falls of famous people, similar to his work of 106 biographies De Mulieribus Claris.

Sulpicia was the wife of Quintus Fulvius Flaccus and earned everlasting fame when she was determined to be the most chaste of all the Roman matrons.
There are several figures in Greek mythology named Manto, the most prominent being the daughter of Tiresias. The name Manto derives from Ancient Greek Mantis, "seer, prophet".
The gens Paccia, occasionally written Pactia, was a minor plebeian family at ancient Rome. Only a few members of this gens achieved distinction in the Roman state, of whom the most illustrious was Gaius Paccius Africanus, consul in AD 67.

Lucius Calpurnius Piso was a Roman senator active in the first century AD. During the Year of Four Emperors he was governor of Africa and supported Vitellius. After the death of Vitellius he was killed by supporters of Vespasian.

Vitellia was a Roman noblewoman, who was the daughter of the emperor Aulus Vitellius and was married to the Roman senator Decimus Valerius Asiaticus. A fictionalised Vitellia is a central character in the opera La clemenza di Tito by Mozart.

The gens Triaria was an obscure plebeian family at ancient Rome. Only a few members of this gens are mentioned by Roman writers, but two of them attained the consulship in imperial times. Other Triarii are known from inscriptions.















