In chemistry, amines are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia, wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such as an alkyl or aryl group. Important amines include amino acids, biogenic amines, trimethylamine, and aniline. Inorganic derivatives of ammonia are also called amines, such as monochloramine.
Demethylation is the chemical process resulting in the removal of a methyl group (CH3) from a molecule. A common way of demethylation is the replacement of a methyl group by a hydrogen atom, resulting in a net loss of one carbon and two hydrogen atoms.

In organic chemistry, nitration is a general class of chemical processes for the introduction of a nitro group into an organic compound. The term also is applied incorrectly to the different process of forming nitrate esters between alcohols and nitric acid. The difference between the resulting molecular structures of nitro compounds and nitrates is that the nitrogen atom in nitro compounds is directly bonded to a non-oxygen atom, whereas in nitrate esters, the nitrogen is bonded to an oxygen atom that in turn usually is bonded to a carbon atom.
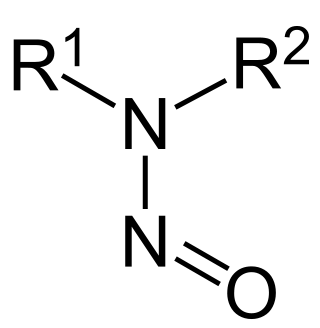
In organic chemistry, nitrosamines are organic compounds with the chemical structure R2N−N=O, where R is usually an alkyl group. They feature a nitroso group bonded to a deprotonated amine. Most nitrosamines are carcinogenic in nonhuman animals. A 2006 systematic review supports a "positive association between nitrite and nitrosamine intake and gastric cancer, between meat and processed meat intake and gastric cancer and oesophageal cancer, and between preserved fish, vegetable and smoked food intake and gastric cancer, but is not conclusive".
The Suzuki reaction is an organic reaction, classified as a cross-coupling reaction, where the coupling partners are a boronic acid and an organohalide and the catalyst is a palladium(0) complex. It was first published in 1979 by Akira Suzuki, and he shared the 2010 Nobel Prize in Chemistry with Richard F. Heck and Ei-ichi Negishi for their contribution to the discovery and development of palladium-catalyzed cross-couplings in organic synthesis. This reaction is also known as the Suzuki–Miyaura reaction or simply as the Suzuki coupling. It is widely used to synthesize polyolefins, styrenes, and substituted biphenyls. Several reviews have been published describing advancements and the development of the Suzuki reaction. The general scheme for the Suzuki reaction is shown below, where a carbon-carbon single bond is formed by coupling a halide (R1-X) with an organoboron species (R2-BY2) using a palladium catalyst and a base. The organoboron species is usually synthesized by hydroboration or carboboration, allowing for rapid generation of molecular complexity.

In organic chemistry, sulfonic acid refers to a member of the class of organosulfur compounds with the general formula R−S(=O)2−OH, where R is an organic alkyl or aryl group and the S(=O)2(OH) group a sulfonyl hydroxide. As a substituent, it is known as a sulfo group. A sulfonic acid can be thought of as sulfuric acid with one hydroxyl group replaced by an organic substituent. The parent compound is the parent sulfonic acid, HS(=O)2(OH), a tautomer of sulfurous acid, S(=O)(OH)2. Salts or esters of sulfonic acids are called sulfonates.
In organic chemistry, the Ugi reaction is a multi-component reaction involving a ketone or aldehyde, an amine, an isocyanide and a carboxylic acid to form a bis-amide. The reaction is named after Ivar Karl Ugi, who first reported this reaction in 1959.
The Sandmeyer reaction is a chemical reaction used to synthesize aryl halides from aryl diazonium salts using copper salts as reagents or catalysts. It is an example of a radical-nucleophilic aromatic substitution. The Sandmeyer reaction provides a method through which one can perform unique transformations on benzene, such as halogenation, cyanation, trifluoromethylation, and hydroxylation.

The Baeyer–Villiger oxidation is an organic reaction that forms an ester from a ketone or a lactone from a cyclic ketone, using peroxyacids or peroxides as the oxidant. The reaction is named after Adolf von Baeyer and Victor Villiger who first reported the reaction in 1899.
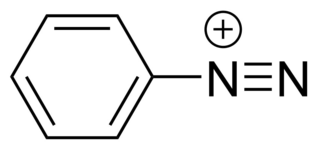
Diazonium compounds or diazonium salts are a group of organic compounds sharing a common functional group [R−N+≡N]X− where R can be any organic group, such as an alkyl or an aryl, and X is an inorganic or organic anion, such as a halide.

Photosensitizers are light absorbers that alter the course of a photochemical reaction. They usually are catalysts. They can function by many mechanisms, sometimes they donate an electron to the substrate, sometimes they abstract a hydrogen atom from the substrate. At the end of this process, the photosensitizer returns to its ground state, where it remains chemically intact, poised to absorb more light. One branch of chemistry which frequently utilizes photosensitizers is polymer chemistry, using photosensitizers in reactions such as photopolymerization, photocrosslinking, and photodegradation. Photosensitizers are also used to generate prolonged excited electronic states in organic molecules with uses in photocatalysis, photon upconversion and photodynamic therapy. Generally, photosensitizers absorb electromagnetic radiation consisting of infrared radiation, visible light radiation, and ultraviolet radiation and transfer absorbed energy into neighboring molecules. This absorption of light is made possible by photosensitizers' large de-localized π-systems, which lowers the energy of HOMO and LUMO orbitals to promote photoexcitation. While many photosensitizers are organic or organometallic compounds, there are also examples of using semiconductor quantum dots as photosensitizers.
The Negishi coupling is a widely employed transition metal catalyzed cross-coupling reaction. The reaction couples organic halides or triflates with organozinc compounds, forming carbon-carbon bonds (C-C) in the process. A palladium (0) species is generally utilized as the metal catalyst, though nickel is sometimes used. A variety of nickel catalysts in either Ni0 or NiII oxidation state can be employed in Negishi cross couplings such as Ni(PPh3)4, Ni(acac)2, Ni(COD)2 etc.
In organic chemistry, the Buchwald–Hartwig amination is a chemical reaction for the synthesis of carbon–nitrogen bonds via the palladium-catalyzed coupling reactions of amines with aryl halides. Although Pd-catalyzed C–N couplings were reported as early as 1983, Stephen L. Buchwald and John F. Hartwig have been credited, whose publications between 1994 and the late 2000s established the scope of the transformation. The reaction's synthetic utility stems primarily from the shortcomings of typical methods for the synthesis of aromatic C−N bonds, with most methods suffering from limited substrate scope and functional group tolerance. The development of the Buchwald–Hartwig reaction allowed for the facile synthesis of aryl amines, replacing to an extent harsher methods while significantly expanding the repertoire of possible C−N bond formations.
The Wurtz–Fittig reaction is the chemical reaction of an aryl halide, alkyl halides, and sodium metal to give substituted aromatic compounds. Following the work of Charles Adolphe Wurtz on the sodium-induced coupling of alkyl halides, Wilhelm Rudolph Fittig extended the approach to the coupling of an alkyl halide with an aryl halide. This modification of the Wurtz reaction is considered a separate process and is named for both scientists.
In organic chemistry, the Kumada coupling is a type of cross coupling reaction, useful for generating carbon–carbon bonds by the reaction of a Grignard reagent and an organic halide. The procedure uses transition metal catalysts, typically nickel or palladium, to couple a combination of two alkyl, aryl or vinyl groups. The groups of Robert Corriu and Makoto Kumada reported the reaction independently in 1972.

Richard Frederick Heck was an American chemist noted for the discovery and development of the Heck reaction, which uses palladium to catalyze organic chemical reactions that couple aryl halides with alkenes. The analgesic naproxen is an example of a compound that is prepared industrially using the Heck reaction.
In organic chemistry, a cross-coupling reaction is a reaction where two different fragments are joined. Cross-couplings are a subset of the more general coupling reactions. Often cross-coupling reactions require metal catalysts. One important reaction type is this:
Trifluoromethylation in organic chemistry describes any organic reaction that introduces a trifluoromethyl group in an organic compound. Trifluoromethylated compounds are of some importance in pharmaceutical industry and agrochemicals. Several notable pharmaceutical compounds have a trifluoromethyl group incorporated: fluoxetine, mefloquine, Leflunomide, nulitamide, dutasteride, bicalutamide, aprepitant, celecoxib, fipronil, fluazinam, penthiopyrad, picoxystrobin, fluridone, norflurazon, sorafenib and triflurazin. A relevant agrochemical is trifluralin. The development of synthetic methods for adding trifluoromethyl groups to chemical compounds is actively pursued in academic research.
Photoredox catalysis is a branch of photochemistry that uses single-electron transfer. Photoredox catalysts are generally drawn from three classes of materials: transition-metal complexes, organic dyes, and semiconductors. While organic photoredox catalysts were dominant throughout the 1990s and early 2000s, soluble transition-metal complexes are more commonly used today.

Bis(cyclopentadienyl)titanium(III) chloride, also known as the Nugent–RajanBabu reagent, is the organotitanium compound which exists as a dimer with the formula [(C5H5)2TiCl]2. It is an air sensitive green solid. The complex finds specialized use in synthetic organic chemistry as a single electron reductant.









