
The United States Postal Service (USPS), also known as the Post Office, U.S. Mail, or Postal Service, is an independent agency of the executive branch of the United States federal government responsible for providing postal service in the United States, its insular areas, and its associated states. It is one of the few government agencies explicitly authorized by the Constitution of the United States. As of 2023, the USPS has 525,469 career employees and 114,623 non-career employees.

The mail or post is a system for physically transporting postcards, letters, and parcels. A postal service can be private or public, though many governments place restrictions on private systems. Since the mid-19th century, national postal systems have generally been established as a government monopoly, with a fee on the article prepaid. Proof of payment is usually in the form of an adhesive postage stamp, but a postage meter is also used for bulk mailing.

A ZIP Code is a system of postal codes used by the United States Postal Service (USPS). The term ZIP was chosen to suggest that the mail travels more efficiently and quickly when senders use the code in the postal address.
A voicemail system is a computer-based system that allows people to leave a recorded message when the recipient is unable to answer the phone. The caller is prompted to leave a message and the recipient can retrieve said message at a later time.

A Canadian postal code is a six-character string that forms part of a postal address in Canada. Like British, Irish and Dutch postcodes, Canada's postal codes are alphanumeric. They are in the format A1A 1A1, where A is a letter and 1 is a digit, with a space separating the third and fourth characters. As of October 2019, there were 876,445 postal codes using Forward Sortation Areas from A0A in Newfoundland to Y1A in Yukon.

The British Forces Post Office (BFPO) provides a postal service to HM Forces separate from that provided by Royal Mail in the United Kingdom. BFPO addresses are used for the delivery of mail in the UK and around the world. BFPO moved from its original base at Inglis Barracks, Mill Hill to its current base at RAF Northolt in west London in 2007.
Email filtering is the processing of email to organize it according to specified criteria. The term can apply to the intervention of human intelligence, but most often refers to the automatic processing of messages at an SMTP server, possibly applying anti-spam techniques. Filtering can be applied to incoming emails as well as to outgoing ones.
Variable data printing (VDP) is a form of digital printing, including on-demand printing, in which elements such as text, graphics and images may be changed from one printed piece to the next, without stopping or slowing down the printing process and using information from a database or external file. For example, a set of personalized letters, each with the same basic layout, can be printed with a different name and address on each letter. Variable data printing is mainly used for direct marketing, customer relationship management, advertising, invoicing and applying addressing on selfmailers, brochures or postcard campaigns.
Pitney Bowes Inc. is an American technology company most known for its postage meters and other mailing equipment and services, and with expansions into e-commerce, software, and other technologies. The company was founded by Arthur Pitney, who invented the first commercially available postage meter, and Walter Bowes as the Pitney Bowes Postage Meter Company on April 23, 1920.

A postal address in Ireland is a place of delivery defined by Irish Standard (IS) EN 14142-1:2011 and serviced by the universal service provider, An Post. Its addressing guides comply with the guidelines of the Universal Postal Union (UPU), the United Nations-affiliated body responsible for promoting standards in the postal industry, across the world.
A multiline optical-character reader, or MLOCR, is a type of mail sorting machine that uses optical character recognition (OCR) technology to determine how to route mail through the postal system.
An optional information line is a line above the postal address on mail in the United States. The lines are usually seen on bulk mail to indicate the sorting and separation that allows the mail to have a lower postal rate.

Postcodes in Australia are used to more efficiently sort and route mail within the Australian postal system. Postcodes in Australia have four digits and are placed at the end of the Australian address, before the country. Postcodes were introduced in Australia in 1967 by the Postmaster-General's Department and are now managed by Australia Post, Australia's national postal service. Postcodes are published in booklets available from post offices or online from the Australia Post website.

Heathrow Worldwide Distribution Centre (HWDC) is a sorting office for inbound and outbound international mail operated by Royal Mail. Located close to Heathrow Airport, the HWDC is situated in the town of Langley, Berkshire, near Slough, and began operations in 2003. The centre is often referred to by its abbreviation, Langley HWDC, or as 'GBLALA' in mail tracking information.

Mail sorting refers to the methods by which postal systems determine how and where to route mail for delivery. Once accomplished by hand, mail sorting is now largely automated through the aid of specialized machines. The first widely adopted mail sorting machine was the Transorma, first made operational in Rotterdam in 1930.
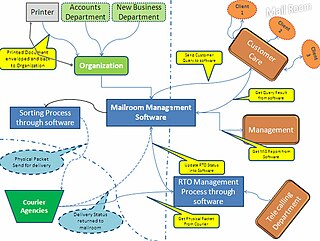
Digital mailroom is the automation of incoming mail processes. Using document scanning and document capture technologies, companies can digitise incoming mail and automate the classification and distribution of mail within the organization. Both paper and electronic mail (email) can be managed through the same process allowing companies to standardize their internal mail distribution procedures and adhere to company compliance policies.
STD-4C or STANDARD-4C refers to a set of standards and regulations set by the United States Postal Service regarding the specifications of cluster mailbox units used in new construction. All multi unit constructions building plans submitted after October 6, 2006 are required to use STD-4C compliant mailboxes
The Queen's Award for Enterprise: Innovation (Technology) (2001) was awarded on 20 April.
The Center of Excellence for Document Analysis and Recognition (CEDAR) is a research laboratory at the University at Buffalo, State University of New York. The center was established with funding from the United States Postal Service and National Institute of Justice. CEDAR was formalized by the United States Postal Service by Postmaster General Anthony Frank in 1991.The primary goal of CEDAR was to conduct research and development for developing software useful for the automation of postal sorting equipment. Work at CEDAR, with Sargur Srihari as principal investigator, led to the first handwritten address interpretation system in the world. CEDAR-FOX, the first system for automatic comparison of handwriting for the purpose of forensic analysis, was developed at CEDAR.

Package tracking or package logging is the process of localizing shipping containers, mail and parcel post at different points of time during sorting, warehousing, and package delivery to verify their provenance and to predict and aid delivery.











