Tsonga may refer to:
- Tsonga language, a Bantu language spoken in southern Africa
- Tsonga people, a large group of people living mainly in southern Mozambique and South Africa.
- Jo-Wilfried Tsonga (born 1985), French tennis player
Tsonga may refer to:
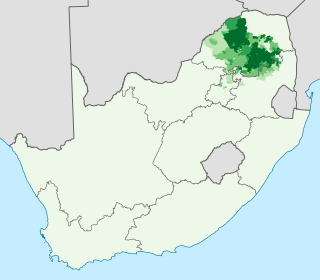
Northern Sotho, or Sesotho sa Leboa as an endonym, is a Sotho-Tswana language spoken in the northeastern provinces of South Africa. It is sometimes referred to as Sepedi or Pedi, its main dialect, through synecdoche.
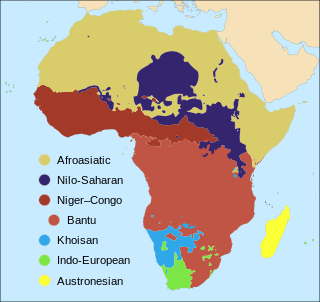
The languages of Africa are divided into several major language families:
Sotho or SesothoSouthern Sotho is a Southern Bantu language of the Sotho–Tswana ("S.30") group, spoken in Lesotho, where it is the national and official language; South Africa, where it is one of the 11 official languages; and in Zimbabwe where it is one of 16 official languages.

Tsonga or Xitsonga as an endonym, is a Bantu language spoken by the Tsonga people of southern Africa. It is mutually intelligible with Tswa and Ronga and the name "Tsonga" is often used as a cover term for all three, also sometimes referred to as Tswa-Ronga. The Xitsonga language has been standardised for both academic and home use. Tsonga is an official language of South Africa, and under the name "Shangani" it is recognised as an official language in the Constitution of Zimbabwe. All Tswa-Ronga languages are recognised in Mozambique. It is not official in Eswatini.

iSimangaliso Wetland Park is situated on the east coast of KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa, about 235 kilometres north of Durban by road. It is South Africa's third-largest protected area, spanning 280 km of coastline, from the Mozambican border in the north to Mapelane south of the Lake St. Lucia estuary, and made up of around 3,280 km2 of natural ecosystems, managed by the iSimangaliso Authority. The park includes:
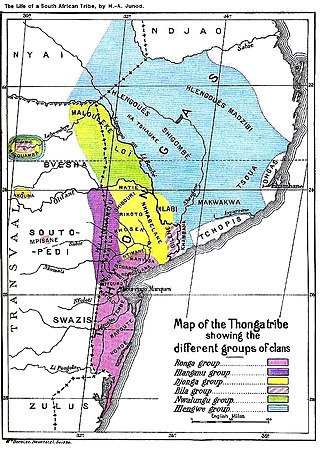
The Tsonga people are a Bantu ethnic group primarily native to Southern Mozambique and South Africa. They speak Xitsonga, a Southern Bantu language. A very small number of Tsonga people are also found in Zimbabwe and Northern Eswatini. The Tsonga people of South Africa share some history with the Tsonga people of Southern Mozambique, and have similar cultural practices; however they differ on the dialects spoken.

Hazyview is a sub-tropical farming town in Mpumalanga, South Africa, renowned for its large banana and macadamia nut industries, contributing about 20% of South Africa's bananas and 30% of macadamia output. Bordering the Kruger National Park, the town's name is derived from the shimmering haze that occurs during the heat of summer. Most of the province of Mpumalanga's private game reserves are found just east of Hazyview.
Elandspark is a suburb of Johannesburg, South Africa. It is located in Region 9.
Sandown is an affluent suburb of Johannesburg, South Africa, in Sandton. It is located in Region E of the City of Johannesburg Metropolitan Municipality. Sandown is both a residential and commercial area and is home to the offices of many major national and international corporations as well as the Johannesburg Stock Exchange in the area known as Sandton Central. The Gautrain rapid rail system's Sandton Station is located in Sandown, linking Sandton to O.R. Tambo International Airport, Johannesburg Central and the Capital City, Pretoria.

Munghana Lonene FM is an SABC radio station broadcasting in Tsonga language in South Africa. In Tsonga, "Munghana Lonene" means "a true friend." Munghana Lonene FM is geared to listeners who understand Xitsonga. Munghana Lonene FM is branded as an "infotainment" radio station with a 50% split of music and talk. It offers an environment interactive with its listeners, providing a mixture of news, music, current affairs, talk shows, education, sport, weather and traffic. The music repertoire consists of Jazz, R&B, Kwaito, House, Gospel music and African music.

Vhembe is one of the 5 districts of Limpopo province of South Africa. It is the northernmost district of the country and shares its northern border with Beitbridge district in Zimbabwe and on the east with Gaza Province in Mozambique. Vhembe consist of all territories that were part of the former Venda Bantustan, however, two large densely populated districts of the former Tsonga homeland of Gazankulu, in particular, Hlanganani and Malamulele were also incorporated into Vhembe, hence the ethnic diversity of the District. The seat of Vhembe is Thohoyandou, the capital of the former Venda Bantustan. According to 2011 census, the majority of Vhembe residents, about 800,000, speak TshiVenda as their mother language, while 400,000 speak Xitsonga as their home language. However, the Tsonga people are in majority south of Levubu River and they constitute more than 85% of the population in the south of the historic river Levubu, while the Venda are the minority south of Levubu, at 15%. The Northern Sotho speakers number 27,000. The district code is DC34.

South African Bantu-speaking peoples are the majority of black South Africans. Occasionally grouped as Bantu, the term itself is derived from the word for "people" common to many of the Bantu languages. The Oxford Dictionary of South African English describes its contemporary usage in a racial context as "obsolescent and offensive" because of its strong association with white minority rule with their apartheid system. However, Bantu is used without pejorative connotations in other parts of Africa and is still used in South Africa as the group term for the language family.
The Chopi are an ethnic group of Mozambique. They have lived primarily in the Zavala region of southern Mozambique, in the Inhambane Province. They traditionally lived a life of subsistence agriculture, traditionally living a rural existence, although many were displaced or killed in the civil war that followed Mozambique's liberation from Portuguese colonial rule in 1975. In addition, drought forced many away from their homeland and into the nation's cities.

The Tonga people of Zambia and Zimbabwe are a Bantu ethnic group of southern Zambia and neighbouring northern Zimbabwe, and to a lesser extent, in Mozambique. They are related to the Batoka who are part of the Tokaleya people in the same area, but not to the Tonga people of Malawi. In southern Zambia they are patrons of the Kafue Twa. They differ culturally and linguistically from the Tsonga people of South Africa and southern Mozambique.
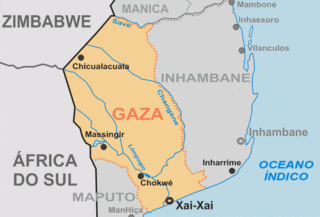
The Gaza Empire (1824–1895) was an African empire established by general Soshangane and was located in southeastern Africa in the area of southern Mozambique and southeastern Zimbabwe. The Gaza Empire, at its height in the 1860s, covered all of Mozambique between the Zambezi and Limpopo rivers, known as Gazaland.
Tswa (Xitswa) is a South-Eastern Bantu language in Southern Mozambique. Its closest relatives are Ronga and Tsonga, the three forming the Tswa–Ronga family of languages.
The Tswa–Ronga languages are a group of closely related Southern Bantu languages spoken in Southern Africa chiefly in southern Mozambique, northeastern South Africa and southeastern Zimbabwe.
Eswatini is home to several languages. Native languages are SiSwati, Zulu, Tsonga, Afrikaans, and English. Recent immigrant languages include Chichewa and Southern Sotho.
Hlanganani, also known as Spelonken, is an amalgamation of various large villages which are situated in the north western portion of the former Tsonga homeland of Gazankulu, South Africa. Hlanganani is situated alongside the R578 road to Giyani and Elim.
Valdezia is a sprawling rural settlement situated at the foothills of the Soutpansberg mountain range in Louis Trichardt, Limpopo Province, South Africa. It was formerly known as Albasini before Swiss Missionaries renamed it Valdezia in 1875. The village itself was formally established in 1820 by Tsonga refugees who were fleeing despotic rule from Soshangane. It is roughly 10 km east of Elim Hospital in the Hlanganani district in the former Gazankulu homeland, South Africa. It was the site of a Swiss mission station, and it was named after the Swiss canton of Vaud. Valdezia's population, according to the official census of 2011, currently stands at between 7,600 and 8,000 people. It is considered the birthplace of the written Tsonga language in South Africa.