
An oil well is a drillhole boring in Earth that is designed to bring petroleum oil hydrocarbons to the surface. Usually some natural gas is released as associated petroleum gas along with the oil. A well that is designed to produce only gas may be termed a gas well. Wells are created by drilling down into an oil or gas reserve that is then mounted with an extraction device such as a pumpjack which allows extraction from the reserve. Creating the wells can be an expensive process, costing at least hundreds of thousands of dollars, and costing much more when in hard to reach areas, e.g., when creating offshore oil platforms. The process of modern drilling for wells first started in the 19th century, but was made more efficient with advances to oil drilling rigs during the 20th century.

In the oil and gas industry, the term wireline usually refers to the use of multi-conductor, single conductor or slickline cable, or "wireline", as a conveyance for the acquisition of subsurface petrophysical and geophysical data and the delivery of well construction services such as pipe recovery, perforating, plug setting and well cleaning and fishing. The subsurface geophysical and petrophysical information results in the description and analysis of subsurface geology, reservoir properties and production characteristics.

A drill string on a drilling rig is a column, or string, of drill pipe that transmits drilling fluid and torque to the drill bit. The term is loosely applied to the assembled collection of the smuggler pool, drill collars, tools and drill bit. The drill string is hollow so that drilling fluid can be pumped down through it and circulated back up the annulus.

Directional drilling is the practice of drilling non-vertical bores. It can be broken down into four main groups: oilfield directional drilling, utility installation directional drilling, directional boring, and surface in seam (SIS), which horizontally intersects a vertical bore target to extract coal bed methane.
In petroleum production, the casing hanger is that portion of a wellhead assembly which provides support for the casing string when it is lowered into the wellbore. It serves to ensure that the casing is properly located. When the casing string has been run into the wellbore it is hung off, or suspended, by a casing hanger, which rests on a landing shoulder inside the casing spool. Casing hangers must be designed to take the full weight of the casing, and provide a seal between the casing hanger and the spool.

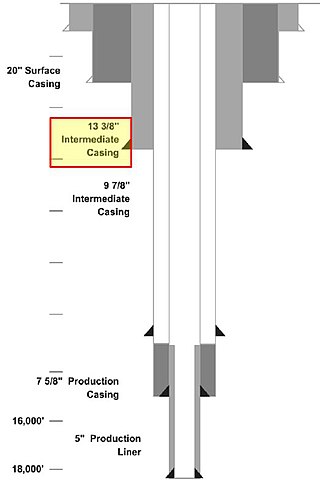
Casing is a large diameter pipe that is assembled and inserted into a recently drilled section of a borehole. Similar to the bones of a spine protecting the spinal cord, casing is set inside the drilled borehole to protect and support the wellstream. The lower portion is typically held in place with cement. Deeper strings usually are not cemented all the way to the surface, so the weight of the pipe must be partially supported by a casing hanger in the wellhead.

A wellhead is the component at the surface of an oil or gas well that provides the structural and pressure-containing interface for the drilling and production equipment.

A blowout preventer (BOP) is a specialized valve or similar mechanical device, used to seal, control and monitor oil and gas wells to prevent blowouts, the uncontrolled release of crude oil or natural gas from a well. They are usually installed in stacks of other valves.
Underbalanced drilling, or UBD, is a procedure used to drill oil and gas wells where the pressure in the wellbore is kept lower than the static pressure of the formation being drilled. As the well is being drilled, formation fluid flows into the wellbore and up to the surface. This is the opposite of the usual situation, where the wellbore is kept at a pressure above the formation to prevent formation fluid entering the well. In such a conventional "overbalanced" well, the invasion of fluid is considered a kick, and if the well is not shut-in it can lead to a blowout, a dangerous situation. In underbalanced drilling, however, there is a "rotating head" at the surface - essentially a seal that diverts produced fluids to a separator while allowing the drill string to continue rotating.

In the oil and gas industry, coiled tubing refers to a long metal pipe, normally 1 to 3.25 in in diameter which is supplied spooled on a large reel. It is used for interventions in oil and gas wells and sometimes as production tubing in depleted gas wells. Coiled tubing is often used to carry out operations similar to wirelining. The main benefits over wireline are the ability to pump chemicals through the coil and the ability to push it into the hole rather than relying on gravity. Pumping can be fairly self-contained, almost a closed system, since the tube is continuous instead of jointed pipe. For offshore operations, the 'footprint' for a coiled tubing operation is generally larger than a wireline spread, which can limit the number of installations where coiled tubing can be performed and make the operation more costly. A coiled tubing operation is normally performed through the drilling derrick on the oil platform, which is used to support the surface equipment, although on platforms with no drilling facilities a self-supporting tower can be used instead. For coiled tubing operations on sub-sea wells a mobile offshore drilling unit (MODU) e.g. semi-submersible, drillship etc. has to be utilized to support all the surface equipment and personnel, whereas wireline can be carried out from a smaller and cheaper intervention vessel. Onshore, they can be run using smaller service rigs, and for light operations a mobile self-contained coiled tubing rig can be used.

A well intervention, or well work, is any operation carried out on an oil or gas well during, or at the end of, its productive life that alters the state of the well or well geometry, provides well diagnostics, or manages the production of the well.
A production packer is a standard component of the completion hardware of oil or gas wells used to provide a seal between the outside of the production tubing and the inside of the casing, liner, or wellbore wall.
Slickline refers to a single strand wire which is used to run a variety of tools down into the wellbore for several purposes. It is used during well drilling operations in the oil and gas industry. In general, it can also describe a niche of the industry that involves using a slickline truck or doing a slickline job. Slickline looks like a long, smooth, unbraided wire, often shiny, silver/chrome in appearance. It comes in varying lengths, according to the depth of wells in the area it is used up to 35,000 feet in length. It is used to lower and raise downhole tools used in oil and gas well maintenance to the appropriate depth of the drilled well.

Snubbing is a type of heavy well intervention performed on oil and gas wells. It involves running the BHA on a pipe string using a hydraulic workover rig. Unlike wireline or coiled tubing, the pipe is not spooled off a drum but made up and broken up while running in and pulling out, much like conventional drill pipe. Due to the large rigup, it is only used for the most demanding of operations when lighter intervention techniques do not offer the strength and durability. The first snubbing unit was primarily designed to work in well control situations to "snub" drill pipe and or casing into, or out of, a well bore when conventional well killing methods could not be used. Unlike conventional drilling and completions operations, snubbing can be performed with the well still under pressure. When done so, it is called hydraulic workover. It can also be performed without having to remove the Christmas tree from the wellhead.

Well completion is the process of making a well ready for production after drilling operations. This principally involves preparing the bottom of the hole to the required specifications, running in the production tubing and its associated down hole tools as well as perforating and stimulating as required. Sometimes, the process of running in and cementing the casing is also included. After a well has been drilled, should the drilling fluids be removed, the well would eventually close in upon itself. Casing ensures that this will not happen while also protecting the wellstream from outside incumbents, like water or sand.
Oilfield terminology refers to the jargon used by those working in fields within and related to the upstream segment of the petroleum industry. It includes words and phrases describing professions, equipment, and procedures specific to the industry. It may also include slang terms used by oilfield workers to describe the same.

Pipe recovery is a specific wireline operation used in the oil and gas industry, when the drill string becomes stuck downhole. Stuck pipe prevents the drill rig from continuing operations. This results in costly downtime, ranging anywhere from $10,000-1,000,000 per day of downtime, therefore it is critical to resolve the problem as quickly as possible. Pipe recovery is the process by which the location of the stuck pipe is identified, and the free pipe is separated from the stuck pipe either by a backoff or a chemical cut. This allows fishing tools to subsequently be run down hole to latch onto and remove the stuck pipe.
Slips is a device used to grip and hold the upper part of a drill string to the drill floor on an oil rig. The slips are constructed as a collection of metal wedges, hinged together to form a circular shape around the drill pipe. On the inside surface, the slips normally has replaceable steel teeth that grips the pipe. The outsides of the slips are tapered and meets a similar taper on the drill floor. Usually the pipe goes through a Rotary table - machinery that makes the pipe rotate.













