Related Research Articles
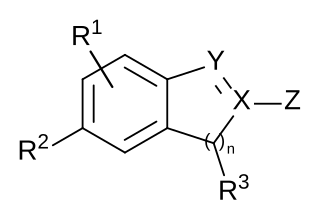
A chemical patent, pharmaceutical patent or drug patent is a patent for an invention in the chemical or pharmaceuticals industry. Strictly speaking, in most jurisdictions, there are essentially no differences between the legal requirements to obtain a patent for an invention in the chemical or pharmaceutical fields, in comparison to obtaining a patent in the other fields, such as in the mechanical field. A chemical patent or a pharmaceutical patent is therefore not a sui generis right, i.e. a special legal type of patent.

A generic drug is a pharmaceutical drug that contains the same chemical substance as a drug that was originally protected by chemical patents. Generic drugs are allowed for sale after the patents on the original drugs expire. Because the active chemical substance is the same, the medical profile of generics is equivalent in performance compared to their performance at the time when they were patented drugs. A generic drug has the same active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) as the original, but it may differ in some characteristics such as the manufacturing process, formulation, excipients, color, taste, and packaging.
Prescription drug list prices in the United States continually rank among the highest in the world. The high cost of prescription drugs became a major topic of discussion in the 21st century, leading up to the American health care reform debate of 2009, and received renewed attention in 2015. One major reason for high prescription drug prices in the United States relative to other countries is the inability of government-granted monopolies in the American health care sector to use their bargaining power to negotiate lower prices, and the American payer ends up subsidizing the world's R&D spending on drugs.
An orphan drug is a pharmaceutical agent that is developed to treat certain rare medical conditions. An orphan drug would not be profitable to produce without government assistance, due to the small population of patients affected by the conditions. The conditions that orphan drugs are used to treat are referred to as orphan diseases. The assignment of orphan status to a disease and to drugs developed to treat it is a matter of public policy that depends on the legislation of the country.

The pharmaceutical industry discovers, develops, produces, and markets pharmaceutical drugs for the use as medications to be administered to patients, with the aim to cure and prevent diseases, or alleviate symptoms. Pharmaceutical companies may deal in generic or brand medications and medical devices. They are subject to a variety of laws and regulations that govern the patenting, testing, safety, efficacy using drug testing and marketing of drugs. The global pharmaceuticals market produced treatments worth $1,228.45 billion in 2020 and showed a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 1.8%.

Medical research, also known as experimental medicine, encompasses a wide array of research, extending from "basic research", – involving fundamental scientific principles that may apply to a preclinical understanding – to clinical research, which involves studies of people who may be subjects in clinical trials. Within this spectrum is applied research, or translational research, conducted to expand knowledge in the field of medicine.
The pharmaceutical industry is one of the leading industries in the People's Republic of China, covering synthetic chemicals and drugs, prepared Chinese medicines, medical devices, apparatus and instruments, hygiene materials, packing materials, and pharmaceutical machinery. China has the second-largest pharmaceutical market in the world as of 2017 which is worth US$110 billion. China accounts for 20% of the world's population but only a small fraction of the global drug market. China's changing health-care environment is designed to extend basic health insurance to a larger portion of the population and give individuals greater access to products and services. Following the period of change, the pharmaceutical industry is expected to continue its expansion.

Drug development is the process of bringing a new pharmaceutical drug to the market once a lead compound has been identified through the process of drug discovery. It includes preclinical research on microorganisms and animals, filing for regulatory status, such as via the United States Food and Drug Administration for an investigational new drug to initiate clinical trials on humans, and may include the step of obtaining regulatory approval with a new drug application to market the drug. The entire process – from concept through preclinical testing in the laboratory to clinical trial development, including Phase I–III trials – to approved vaccine or drug typically takes more than a decade.
The pharmaceutical industry in India was valued at an estimated US$42 billion in 2021 and is estimated to reach $130 billion by 2030. India is the world's largest provider of generic medicines by volume, with a 20% share of total global pharmaceutical exports. It is also the largest vaccine supplier in the world by volume, accounting for more than 60% of all vaccines manufactured in the world. Indian pharmaceutical products are exported to various regulated markets including the US, UK, European Union and Canada.

The Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP), or Trans-Pacific Partnership Agreement, was a proposed trade agreement between 12 Pacific Rim economies: Australia, Brunei, Canada, Chile, Japan, Malaysia, Mexico, New Zealand, Peru, Singapore, Vietnam, and the United States. In the United States, the proposal was signed on 4 February 2016 but not ratified, being opposed by many Democrats and Republicans, including both major-party presidential nominees, Donald Trump and Hillary Clinton. After taking office, the newly elected President Donald Trump formally withdrew the United States from TPP in January 2017, therefore the TPP could not be ratified as required and did not enter into force. The remaining countries negotiated a new trade agreement called Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership, which incorporates most of the provisions of the TPP and which entered into force on 30 December 2018.
Pharmacoeconomics refers to the scientific discipline that compares the value of one pharmaceutical drug or drug therapy to another. It is a sub-discipline of health economics. A pharmacoeconomic study evaluates the cost and effects of a pharmaceutical product. Pharmacoeconomic studies serve to guide optimal healthcare resource allocation, in a standardized and scientifically grounded manner.
Legal scholars, economists, activists, policymakers, industries, and trade organizations have held differing views on patents and engaged in contentious debates on the subject. Critical perspectives emerged in the nineteenth century that were especially based on the principles of free trade. Contemporary criticisms have echoed those arguments, claiming that patents block innovation and waste resources that could otherwise be used productively, and also block access to an increasingly important "commons" of enabling technologies, apply a "one size fits all" model to industries with differing needs, that is especially unproductive for industries other than chemicals and pharmaceuticals and especially unproductive for the software industry. Enforcement by patent trolls of poor quality patents has led to criticism of the patent office as well as the system itself. Patents on pharmaceuticals have also been a particular focus of criticism, as the high prices they enable puts life-saving drugs out of reach of many people. Alternatives to patents have been proposed, such Joseph Stiglitz's suggestion of providing "prize money" as a substitute for the lost profits associated with abstaining from the monopoly given by a patent.
Medication costs, also known as drug costs are a common health care cost for many people and health care systems. Prescription costs are the costs to the end consumer. Medication costs are influenced by multiple factors such as patents, stakeholder influence, and marketing expenses. A number of countries including Canada, parts of Europe, and Brazil use external reference pricing as a means to compare drug prices and to determine a base price for a particular medication. Other countries use pharmacoeconomics, which looks at the cost/benefit of a product in terms of quality of life, alternative treatments, and cost reduction or avoidance in other parts of the health care system. Structures like the UK's National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence and to a lesser extent Canada's Common Drug Review evaluate products in this way.
Healthcare in the United States is largely provided by private sector healthcare facilities, and paid for by a combination of public programs, private insurance, and out-of-pocket payments. The U.S. is the only developed country without a system of universal healthcare, and a significant proportion of its population lacks health insurance.
The pharmaceutical industry in the United Kingdom directly employs around 73,000 people and in 2007 contributed £8.4 billion to the UK's GDP and invested a total of £3.9 billion in research and development. In 2007 exports of pharmaceutical products from the UK totalled £14.6 billion, creating a trade surplus in pharmaceutical products of £4.3 billion.
Some authors advocating patent reform have proposed the use of prizes as an alternative to patents. Critics of the current patent system, such as Joseph E. Stiglitz, say that patents fail to provide incentives for innovations which are not commercially marketable. Stiglitz provides the idea of prizes instead of patents to be awarded in order to further advance solutions to global problems such as AIDS.
Pharmaceutical innovations are currently guided by a patent system, the patent system protects the innovator of medicines for a period of time. The patent system does not currently stimulate innovation or pricing that provides access to medicine for those who need it the most, It provides for profitable innovation. As of 2014 about $140 Billion is spent on research and development of pharmaceuticals which produces 25–35 new drugs annually. Technology, which is transforming science, medicine, and research tools has increased the speed at which we can analyze data but we currently still must test the products which is a lengthy process. Differences in the performance of medical care may be due to variation in the introduction and circulation of pharmaceutical innovations.
The US carries out 46% of global research and development (R&D) in the life sciences, making it the world leader in medical research.
The cost of drug development is the full cost of bringing a new drug to market from drug discovery through clinical trials to approval. Typically, companies spend tens to hundreds of millions of U.S. dollars on drug development. One element of the complexity is that the much-publicized final numbers often not only include the out-of-pocket expenses for conducting a series of Phase I-III clinical trials, but also the capital costs of the long period during which the company must cover out-of-pocket costs for preclinical drug discovery. Additionally, companies often do not report whether a given figure includes the capitalized cost or comprises only out-of-pocket expenses, or both.

Vaccine development and production is economically complex and prone to market failure. Many of the diseases most demanding a vaccine, including HIV, malaria and tuberculosis, exist principally in poor countries. Pharmaceutical firms and biotechnology companies have little incentive to develop vaccines for these diseases because there is little revenue potential. Even in more affluent countries, financial returns are usually minimal and the financial and other risks are great.
References
- ↑ "History". Tufts Center for the Study of Drug Development.
- ↑ "Financial Disclosure". Tufts Center for the Study of Drug Development.
- 1 2 Silverman, Ed (20 November 2014). "What Does It Cost to Develop a New Drug? Latest Study Says $2.6 Billion". Wall Street Journal. Retrieved 21 November 2014.
- ↑ "Databases". Tufts Center for the Study of Drug Development.
- ↑ "Research Platforms and Current Research Agenda". Tufts Center for the Study of Drug Development.
- ↑ Pear, Robert (1 December 2001). "Research Cost For New Drugs Said to Soar". New York Times. Retrieved 21 November 2014.
- ↑ Pierson, Ransdell (18 November 2014). "CORRECTED-Tufts says average new drug costs $2.6 bln to develop, critics wary". Reuters. Retrieved 21 November 2014.
- ↑ Carroll, Aaron (19 November 2014). "$2.6 Billion to Develop a Drug? New Estimate Makes Questionable Assumptions". New York Times. Retrieved 25 November 2014.
- ↑ Joseph A. DiMasi; Henry G. Grabowski; Ronald W. Hansen (2016). "Innovation in the pharmaceutical industry: New estimates of R&D costs" (PDF). Journal of Health Economics . 47: 20–33. doi:10.1016/j.jhealeco.2016.01.012. hdl: 10161/12742 . PMID 26928437.