A turbine engine is a machine using a turbine and may refer to:
Compound may refer to:

A jet engine is a type of reaction engine, discharging a fast-moving jet of heated gas that generates thrust by jet propulsion. While this broad definition may include rocket, water jet, and hybrid propulsion, the term jet engine typically refers to an internal combustion air-breathing jet engine such as a turbojet, turbofan, ramjet, pulse jet, or scramjet. In general, jet engines are internal combustion engines.

A turbine is a rotary mechanical device that extracts energy from a fluid flow and converts it into useful work. The work produced can be used for generating electrical power when combined with a generator. A turbine is a turbomachine with at least one moving part called a rotor assembly, which is a shaft or drum with blades attached. Moving fluid acts on the blades so that they move and impart rotational energy to the rotor. Early turbine examples are windmills and waterwheels.

A turboprop is a turbine engine that drives an aircraft propeller.
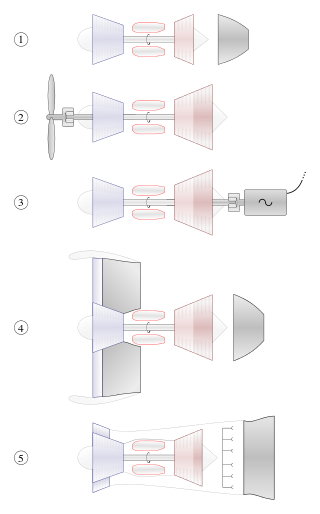
A gas turbine, gas turbine engine, or also known by its old name internal combustion turbine, is a type of continuous flow internal combustion engine. The main parts common to all gas turbine engines form the power-producing part and are, in the direction of flow:

A boiler is a closed vessel in which fluid is heated. The fluid does not necessarily boil. The heated or vaporized fluid exits the boiler for use in various processes or heating applications, including water heating, central heating, boiler-based power generation, cooking, and sanitation.

A stationary engine is an engine whose framework does not move. They are used to drive immobile equipment, such as pumps, generators, mills or factory machinery, or cable cars. The term usually refers to large immobile reciprocating engines, principally stationary steam engines and, to some extent, stationary internal combustion engines. Other large immobile power sources, such as steam turbines, gas turbines, and large electric motors, are categorized separately.

The bypass ratio (BPR) of a turbofan engine is the ratio between the mass flow rate of the bypass stream to the mass flow rate entering the core. A 10:1 bypass ratio, for example, means that 10 kg of air passes through the bypass duct for every 1 kg of air passing through the core.
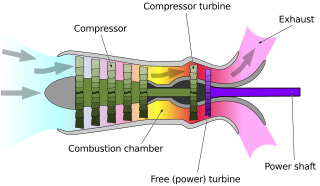
A turboshaft engine is a form of gas turbine that is optimized to produce shaft horsepower rather than jet thrust. In concept, turboshaft engines are very similar to turbojets, with additional turbine expansion to extract heat energy from the exhaust and convert it into output shaft power. They are even more similar to turboprops, with only minor differences, and a single engine is often sold in both forms.

Cogeneration or combined heat and power (CHP) is the use of a heat engine or power station to generate electricity and useful heat at the same time.

Turbomachinery, in mechanical engineering, describes machines that transfer energy between a rotor and a fluid, including both turbines and compressors. While a turbine transfers energy from a fluid to a rotor, a compressor transfers energy from a rotor to a fluid. It is an important application of fluid mechanics.

A thermal power station is a type of power station in which heat energy is converted to electrical energy. In a steam-generating cycle heat is used to boil water in a large pressure vessel to produce high-pressure steam, which drives a steam turbine connected to an electrical generator. The low-pressure exhaust from the turbine enters a steam condenser where it is cooled to produce hot condensate which is recycled to the heating process to generate more high pressure steam. This is known as a Rankine cycle.

The steam-electric power station is a power station in which the electric generator is steam driven. Water is heated, turns into steam and spins a steam turbine which drives an electrical generator. After it passes through the turbine, the steam is condensed in a condenser. The greatest variation in the design of steam-electric power plants is due to the different fuel sources.
A swing-piston engine is a type of internal combustion engine in which the pistons move in a circular motion inside a ring-shaped "cylinder", moving closer and further from each other to provide compression and expansion. Generally two sets of pistons are used, geared to move in a fixed relationship as they rotate around the cylinder. In some versions the pistons oscillate around a fixed center, as opposed to rotating around the entire engine. The design has also been referred to as a oscillating piston engine, vibratory engine when the pistons oscillate instead of rotate, or toroidal engine based on the shape of the "cylinder".

This timeline of heat engine technology describes how heat engines have been known since antiquity but have been made into increasingly useful devices since the 17th century as a better understanding of the processes involved was gained. A heat engine is any system that converts heat to mechanical energy, which can then be used to do mechanical work.They continue to be developed today.

Marine propulsion is the mechanism or system used to generate thrust to move a watercraft through water. While paddles and sails are still used on some smaller boats, most modern ships are propelled by mechanical systems consisting of an electric motor or internal combustion engine driving a propeller, or less frequently, in pump-jets, an impeller. Marine engineering is the discipline concerned with the engineering design process of marine propulsion systems.
The Fiat 4700 was an Italian turbo-generator developed by Fiat Aviazione under contract to the Italian Defence Ministry and used to power the experimental Fiat 7002 tip jet helicopter.

The Steamexfire refers to a high flow inert gas generator, or any inert gas generator that produces an inert gas consisting of nitrogen and CO2, steam and water vapour. Such generators reduce environmental oxygen enough to extinguish fires in settings like tunnels, mining, or shipping.

The accessory drive is a gearbox that forms part of a gas turbine engine. Although not part of the engine's core, it drives the accessories – such as generators, pumps for fuel and lubrication oil, air compressors, hydraulic pumps and engine starters – that are otherwise essential for the operation of the engine or the aircraft on which it is mounted. Accessory drives on large engines handle between 400–500 hp.

An internal combustion engine is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal combustion engine, the expansion of the high-temperature and high-pressure gases produced by combustion applies direct force to some component of the engine. The force is typically applied to pistons, turbine blades, a rotor, or a nozzle. This force moves the component over a distance, transforming chemical energy into kinetic energy which is used to propel, move or power whatever the engine is attached to.