Related Research Articles

Dressage is a form of horse riding performed in exhibition and competition, as well as an art sometimes pursued solely for the sake of mastery. As an equestrian sport defined by the International Equestrian Federation, dressage is described as "the highest expression of horse training" where "horse and rider are expected to perform from memory a series of predetermined movements.".

Horses can use various gaits during locomotion across solid ground, either naturally or as a result of specialized training by humans.

Collection occurs when a horse's center of gravity is shifted backwards. Energy is directed in a more horizontal trajectory with less forward movement. Biomechanical markers include: increased flexion in the lumbo-sacral joint, stifle, and hocks of the horse; increased engagement of the thoracic sling muscles resulting in the withers rising relative to the horse's scapula; and reduced ranges of limb protraction–retraction.

Equitation is the art or practice of horse riding or horsemanship.

The piaffe is a dressage movement where the horse is in a highly collected and cadenced trot, in place or nearly in place. The center of gravity of the horse should be more towards the hind end, with the hindquarters slightly lowered and great bending of the joints in the hind legs. The front end of the horse is highly mobile, free, and light, with great flexion in the joints of the front legs, and the horse remains light in the hand. The horse should retain a clear and even rhythm, show great impulsion, and ideally should have a moment of suspension between the foot falls. As in all dressage, the horse should perform in a calm manner and remain on the bit with a round back.

The trot is a two-beat diagonal horse gait where the diagonal pairs of legs move forward at the same time with a moment of suspension between each beat. It has a wide variation in possible speeds, but averages about 13 kilometres per hour (8.1 mph). A very slow trot is sometimes referred to as a jog. An extremely fast trot has no special name, but in harness racing, the trot of a Standardbred is faster than the gallop of the average non-racehorse, and has been clocked at over 30 miles per hour (48 km/h).

The canter and gallop are variations on the fastest gait that can be performed by a horse or other equine. The canter is a controlled three-beat gait, while the gallop is a faster, four-beat variation of the same gait. It is a natural gait possessed by all horses, faster than most horses' trot, or ambling gaits. The gallop is the fastest gait of the horse, averaging about 40 to 48 kilometres per hour. The speed of the canter varies between 16 and 27 kilometres per hour depending on the length of the horse's stride. A variation of the canter, seen in western riding, is called a lope, and is generally quite slow, no more than 13–19 kilometres per hour (8–12 mph).

The half-pass is a lateral movement seen in dressage, in which the horse moves forward and sideways at the same time. Unlike the easier leg-yield, the horse is bent in the direction of travel, slightly around the rider's inside leg. The outside hind and forelegs should cross over the inside legs, with the horse's body parallel to the arena wall and his forehand leading. The horse should remain forward, balanced, and bent, moving with cadence. The inside hind leg remains engaged throughout the half-pass, and the horse should not lose its rhythm.

A Pirouette is a French word for the Ballet reference, "to whirl about."
Turn on the forehand is a lateral movement in equestrian schooling that involves moving the horse's hindquarters around his front legs. Although a basic movement, it is an important training tool for both horse and rider.

A "baucher" is also a type of bit, named after the man.

Riding figures are prescribed paths a horse is ridden on in a riding arena, usually for training purposes. Figures may also be performed out in a field or other open area, but a riding arena provides markers that can help indicate the correctness in the size or shape of a figure.
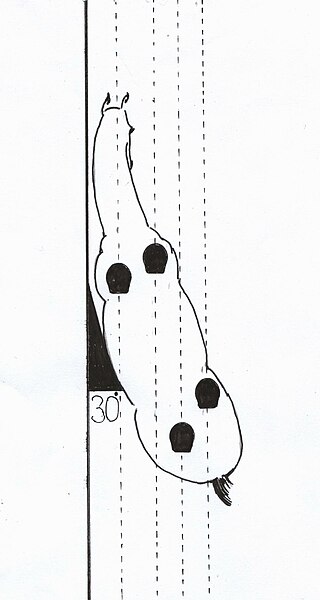
The leg-yield is a lateral movement in which a horse travels both forward and sideways at the same time. The horse is fairly straight through his body in the leg-yield, although he may have a slight bend opposite to the direction of travel. It is one of the "three initial movements leading up to true lateral work", the others being the turn on the forehand and the shoulder-fore.

Riding aids are the cues a rider gives to a horse to communicate what they want the animal to do. Riding aids are broken into the natural aids and the artificial aids.
Lateral movements or lateral flexions within equestrianism, have a specific meaning, used to refer to movements made by a horse where the animal is moving in a direction other than straight forward. They are used both in training and in competition, vary in difficulty, and are used in a progressive manner, according to the training and physical limitations of the animal.

Impulsion is the movement of a horse when it is going forward with controlled power. Related to the concept of collection, impulsion helps a horse effectively use the power in its hindquarters. To achieve impulsion, a horse is not using speed, but muscular control; the horse exhibits a relaxed spinal column, which allows its hindquarters to come well under its body and "engage" so that they can be used in the most effective manner to move the horse forward at any speed.
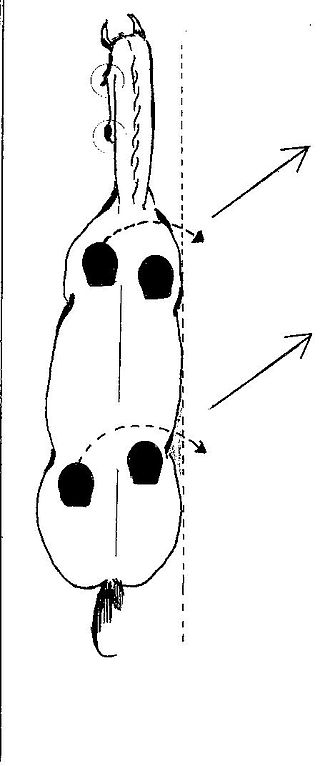
Haunches-in, also called travers or tête au mur, is a lateral movement used in the dressage discipline of horse training. It has a close cousin, haunches-out, renvers, or croupe au mur, that is slightly more difficult. Both movements are four-track, meaning they produce four lines of hoof prints in the sand, as opposed to the usual two seen if the horse is straight and to the three-track shoulder-in.
The shoulder-in is a lateral movement in dressage used to supple and balance the horse and encourage use of its hindquarters. It is performed on three tracks, where the horse is bent around the rider's inside leg so that the horse's inside hind leg and outside foreleg travel on the same line. For some authors it is a "key lesson" of dressage, performed on a daily basis.
The half-halt is a specific riding aid given by an equestrian to his horse, in which the driving aids and restraining aids are applied in quick succession. It is sometimes thought of as an "almost halt," asking the horse to prepare to halt in balance, before pushing it onward to continue in its gait.

Lead refers to which set of legs, left or right, leads or advances forward to a greater extent when a quadruped animal is cantering, galloping, or leaping. The feet on the leading side touch the ground forward of its partner. On the "left lead", the animal's left legs lead. The choice of lead is of special interest in horse riding.
References
- ↑ "Turn On the Haunches". 9 March 2015. Retrieved 2022-06-13.
- ↑ Foley, Cynthia (2012-12-29). "Turns On The Forehand And The Haunches". EquiSearch. Retrieved 2022-06-13.