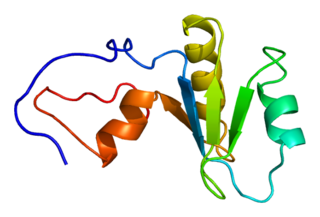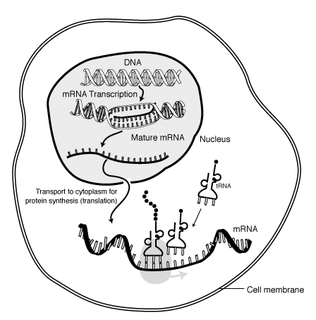
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of synthesizing a protein.

In molecular genetics, the three prime untranslated region (3′-UTR) is the section of messenger RNA (mRNA) that immediately follows the translation termination codon. The 3′-UTR often contains regulatory regions that post-transcriptionally influence gene expression.
In genetics, a transcription terminator is a section of nucleic acid sequence that marks the end of a gene or operon in genomic DNA during transcription. This sequence mediates transcriptional termination by providing signals in the newly synthesized transcript RNA that trigger processes which release the transcript RNA from the transcriptional complex. These processes include the direct interaction of the mRNA secondary structure with the complex and/or the indirect activities of recruited termination factors. Release of the transcriptional complex frees RNA polymerase and related transcriptional machinery to begin transcription of new mRNAs.
Polyadenylation is the addition of a poly(A) tail to an RNA transcript, typically a messenger RNA (mRNA). The poly(A) tail consists of multiple adenosine monophosphates; in other words, it is a stretch of RNA that has only adenine bases. In eukaryotes, polyadenylation is part of the process that produces mature mRNA for translation. In many bacteria, the poly(A) tail promotes degradation of the mRNA. It, therefore, forms part of the larger process of gene expression.
The 5′ untranslated region is the region of a messenger RNA (mRNA) that is directly upstream from the initiation codon. This region is important for the regulation of translation of a transcript by differing mechanisms in viruses, prokaryotes and eukaryotes. While called untranslated, the 5′ UTR or a portion of it is sometimes translated into a protein product. This product can then regulate the translation of the main coding sequence of the mRNA. In many organisms, however, the 5′ UTR is completely untranslated, instead forming complex secondary structure to regulate translation.
RNA-binding proteins are proteins that bind to the double or single stranded RNA in cells and participate in forming ribonucleoprotein complexes. RBPs contain various structural motifs, such as RNA recognition motif (RRM), dsRNA binding domain, zinc finger and others. They are cytoplasmic and nuclear proteins. However, since most mature RNA is exported from the nucleus relatively quickly, most RBPs in the nucleus exist as complexes of protein and pre-mRNA called heterogeneous ribonucleoprotein particles (hnRNPs). RBPs have crucial roles in various cellular processes such as: cellular function, transport and localization. They especially play a major role in post-transcriptional control of RNAs, such as: splicing, polyadenylation, mRNA stabilization, mRNA localization and translation. Eukaryotic cells encode diverse RBPs, approximately 500 genes, with unique RNA-binding activity and protein–protein interaction. During evolution, the diversity of RBPs greatly increased with the increase in the number of introns. Diversity enabled eukaryotic cells to utilize RNA exons in various arrangements, giving rise to a unique RNP (ribonucleoprotein) for each RNA. Although RBPs have a crucial role in post-transcriptional regulation in gene expression, relatively few RBPs have been studied systematically.
Post-transcriptional modification or co-transcriptional modification is a set of biological processes common to most eukaryotic cells by which an RNA primary transcript is chemically altered following transcription from a gene to produce a mature, functional RNA molecule that can then leave the nucleus and perform any of a variety of different functions in the cell. There are many types of post-transcriptional modifications achieved through a diverse class of molecular mechanisms.
Small nuclear RNA (snRNA) is a class of small RNA molecules that are found within the splicing speckles and Cajal bodies of the cell nucleus in eukaryotic cells. The length of an average snRNA is approximately 150 nucleotides. They are transcribed by either RNA polymerase II or RNA polymerase III. Their primary function is in the processing of pre-messenger RNA (hnRNA) in the nucleus. They have also been shown to aid in the regulation of transcription factors or RNA polymerase II, and maintaining the telomeres.

A long terminal repeat (LTR) is a pair of identical sequences of DNA, several hundred base pairs long, which occur in eukaryotic genomes on either end of a series of genes or pseudogenes that form a retrotransposon or an endogenous retrovirus or a retroviral provirus. All retroviral genomes are flanked by LTRs, while there are some retrotransposons without LTRs. Typically, an element flanked by a pair of LTRs will encode a reverse transcriptase and an integrase, allowing the element to be copied and inserted at a different location of the genome. Copies of such an LTR-flanked element can often be found hundreds or thousands of times in a genome. LTR retrotransposons comprise about 8% of the human genome.
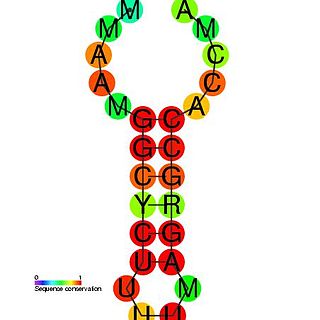
The histone 3′ UTR stem-loop is an RNA element involved in nucleocytoplasmic transport of the histone mRNAs, and in the regulation of stability and of translation efficiency in the cytoplasm. The mRNAs of metazoan histone genes lack polyadenylation and a poly-A tail, instead 3′ end processing occurs at a site between this highly conserved stem-loop and a purine rich region around 20 nucleotides downstream. The stem-loop is bound by a 31 kDa stem-loop binding protein. Together with U7 snRNA binding of the HDE, SLBP binding nucleates the formation of the processing complex.

U1 spliceosomal RNA is the small nuclear RNA (snRNA) component of U1 snRNP, an RNA-protein complex that combines with other snRNPs, unmodified pre-mRNA, and various other proteins to assemble a spliceosome, a large RNA-protein molecular complex upon which splicing of pre-mRNA occurs. Splicing, or the removal of introns, is a major aspect of post-transcriptional modification, and takes place only in the nucleus of eukaryotes.
CPEB, or cytoplasmic polyadenylation element binding protein, is a highly conserved RNA-binding protein that promotes the elongation of the polyadenine tail of messenger RNA. CPEB most commonly activates the target RNA for translation, but can also act as a repressor, dependent on its phosphorylation state. In animals, CPEB is expressed in several alternative splicing isoforms that are specific to particular tissues and functions, including the self-cleaving Mammalian CPEB3 ribozyme. CPEB was first identified in Xenopus oocytes and associated with meiosis; a role has also been identified in the spermatogenesis of Caenorhabditis elegans.
The cytoplasmic polyadenylation element (CPE) is a sequence element found in the 3' untranslated region of messenger RNA. While several sequence elements are known to regulate cytoplasmic polyadenylation, CPE is the best characterized. The most common CPE sequence is UUUUAU, though there are other variations. Binding of CPE binding protein to this region promotes the extension of the existing polyadenine tail and, in general, activation of the mRNA for protein translation. This elongation occurs after the mRNA has been exported from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. A longer poly(A) tail attracts more cytoplasmic polyadenine binding proteins (PABPs) which interact with several other cytoplasmic proteins that encourage the mRNA and the ribosome to associate. The lengthening of the poly(A) tail thus has a role in increasing translational efficiency of the mRNA. The polyadenine tails are extended from approximately 40 bases to 150 bases.

TRAMP complex is a multiprotein, heterotrimeric complex having distributive polyadenylation activity and identifies wide varieties of RNAs produced by polymerases. It was originally discovered in Saccharomycescerevisiae by LaCava et al., Vanacova et al. and Wyers et al. in 2005.

In enzymology, a polynucleotide adenylyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
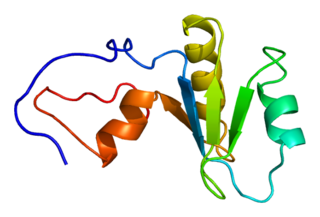
Poly(A)-specific ribonuclease (PARN), also known as polyadenylate-specific ribonuclease or deadenylating nuclease (DAN), is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PARN gene.

U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SNRPA gene.

Poly(A) polymerase alpha is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PAPOLA gene.

Cleavage and polyadenylation specificity factor subunit 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CPSF4 gene.

Cleavage and polyadenylation specificity factor subunit 6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CPSF6 gene.