Advanced power management (APM) is an API developed by Intel and Microsoft and released in 1992 which enables an operating system running an IBM-compatible personal computer to work with the BIOS to achieve power management.

In computing, BIOS is firmware used to provide runtime services for operating systems and programs and to perform hardware initialization during the booting process. The BIOS firmware comes pre-installed on an IBM PC or IBM PC compatible's system board and exists in some UEFI-based systems to maintain compatibility with operating systems that do not support UEFI native operation. The name originates from the Basic Input/Output System used in the CP/M operating system in 1975. The BIOS originally proprietary to the IBM PC has been reverse engineered by some companies looking to create compatible systems. The interface of that original system serves as a de facto standard.

Wake-on-LAN is an Ethernet or Token Ring computer networking standard that allows a computer to be turned on or awakened by a network message.

In computing, the Preboot eXecution Environment, PXE specification describes a standardized client–server environment that boots a software assembly, retrieved from a network, on PXE-enabled clients. On the client side it requires only a PXE-capable network interface controller (NIC), and uses a small set of industry-standard network protocols such as DHCP and TFTP.

UEFI is a set of specifications written by the UEFI Forum. They define the architecture of the platform firmware used for booting and its interface for interaction with the operating system. Examples of firmware that implement these specifications are AMI Aptio, Phoenix SecureCore, TianoCore EDK II and InsydeH2O.

AMI is an international hardware and software company, specializing in PC hardware and firmware. The company was founded in 1985 by Pat Sarma and Subramonian Shankar. It is headquartered in Building 800 at 3095 Satellite Boulevard in unincorporated Gwinnett County, Georgia, United States, near the city of Duluth, and in the Atlanta metropolitan area.
In computing, the System Management BIOS (SMBIOS) specification defines data structures that can be used to read management information produced by the BIOS of a computer. This eliminates the need for the operating system to probe hardware directly to discover what devices are present in the computer. The SMBIOS specification is produced by the Distributed Management Task Force (DMTF), a non-profit standards development organization. The DMTF estimates that two billion client and server systems implement SMBIOS.
The Intelligent Platform Management Interface (IPMI) is a set of computer interface specifications for an autonomous computer subsystem that provides management and monitoring capabilities independently of the host system's CPU, firmware and operating system. IPMI defines a set of interfaces used by system administrators for out-of-band management of computer systems and monitoring of their operation. For example, IPMI provides a way to manage a computer that may be powered off or otherwise unresponsive by using a network connection to the hardware rather than to an operating system or login shell. Another use case may be installing a custom operating system remotely. Without IPMI, installing a custom operating system may require an administrator to be physically present near the computer, insert a DVD or a USB flash drive containing the OS installer and complete the installation process using a monitor and a keyboard. Using IPMI, an administrator can mount an ISO image, simulate an installer DVD, and perform the installation remotely.

Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI) is an open standard that operating systems can use to discover and configure computer hardware components, to perform power management, auto configuration, and status monitoring. First released in December 1996, ACPI aims to replace Advanced Power Management (APM), the MultiProcessor Specification, and the Plug and Play BIOS (PnP) Specification. ACPI brings power management under the control of the operating system, as opposed to the previous BIOS-centric system that relied on platform-specific firmware to determine power management and configuration policies. The specification is central to the Operating System-directed configuration and Power Management (OSPM) system. ACPI defines hardware abstraction interfaces between the device's firmware, the computer hardware components, and the operating systems.

The GUID Partition Table (GPT) is a standard for the layout of partition tables of a physical computer storage device, such as a hard disk drive or solid-state drive, using universally unique identifiers, which are also known as globally unique identifiers (GUIDs). Forming a part of the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) standard, it is nevertheless also used for some BIOS systems, because of the limitations of master boot record (MBR) partition tables, which use 32 bits for logical block addressing (LBA) of traditional 512-byte disk sectors.
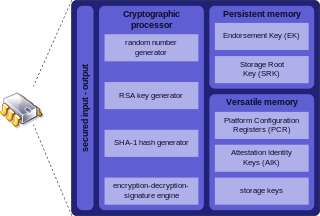
Trusted Platform Module is an international standard for a secure cryptoprocessor, a dedicated microcontroller designed to secure hardware through integrated cryptographic keys. The term can also refer to a chip conforming to the standard.
System Management Mode is an operating mode of x86 central processor units (CPUs) in which all normal execution, including the operating system, is suspended. An alternate software system which usually resides in the computer's firmware, or a hardware-assisted debugger, is then executed with high privileges.

The Apple–Intel architecture, or Mactel, is an unofficial name used for Macintosh personal computers developed and manufactured by Apple Inc. that use Intel x86 processors, rather than the PowerPC and Motorola 68000 ("68k") series processors used in their predecessors or the ARM-based Apple silicon SoCs used in their successors. With the change in architecture, a change in firmware became necessary; Apple selected the Intel-designed Extensible Firmware Interface (EFI) as its comparable component to the Open Firmware used on its PowerPC architectures, and as the firmware-based replacement for the PC BIOS from Intel. With the change in processor architecture to x86, Macs gained the ability to boot into x86-native operating systems, while Intel VT-x brought near-native virtualization with macOS as the host OS.
Insyde Software is a company that specializes in UEFI system firmware and engineering support services, primarily for OEM and ODM computer and component device manufacturers. They are listed on the Gre Tai Market of Taiwan and headquartered in Taipei, with offices in Westborough, Massachusetts, and Portland, Oregon. The company's market capitalization of the company's common shares is currently around $115M.
Intel vPro technology is an umbrella marketing term used by Intel for a large collection of computer hardware technologies, including VT-x, VT-d, Trusted Execution Technology (TXT), and Intel Active Management Technology (AMT). When the vPro brand was launched, it was identified primarily with AMT, thus some journalists still consider AMT to be the essence of vPro.

The EFIsystem partition or ESP is a partition on a data storage device that is used by computers having the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI). When a computer is booted, UEFI firmware loads files stored on the ESP to start installing operating systems and various utilities.

The term Legacy Plug and Play, also shortened to Legacy PnP, describes a series of specifications and Microsoft Windows features geared towards operating system configuration of devices, and some device IDs are assigned by UEFI Forum. The standards were primarily aimed at the IBM PC standard bus, later dubbed Industry Standard Architecture (ISA). Related specifications are also defined for the common external or specialist buses commonly attached via ISA at the time of development, including RS-232 and parallel port devices.
The Platform Initialization Specification is a specification published by the Unified EFI Forum that describes the internal interfaces between different parts of computer platform firmware. This allows for more interoperability between firmware components from different sources. This specification is normally, but not by requirement, used in conjunction with the UEFI specification.
InstantGo or InstantOn or Modern Standby is a Microsoft specification for Windows 8 hardware and software that aims to bring smartphone-type power management capabilities to the PC platform, as well as increasing physical security.
Management Component Transport Protocol (MCTP) is a protocol designed by the Distributed Management Task Force (DMTF) to support communications between different intelligent hardware components that make up a platform management subsystem, providing monitoring and control functions inside a managed computer system. This protocol is independent of the underlying physical bus properties, as well as the data link layer messaging used on the bus. The MCTP communication model includes a message format, transport description, message exchange patterns, and operational endpoint characteristics.











