
The Blockade of Africa began in 1808 after the United Kingdom outlawed the Atlantic slave trade, making it illegal for British ships to transport slaves. The Royal Navy immediately established a presence off Africa to enforce the ban, called the West Africa Squadron. Although the ban initially applied only to British ships, Britain negotiated treaties with other countries to give the Royal Navy the right to intercept and search their ships for slaves. A notable exception was the United States, which refused such permission. The 1807 Act Prohibiting Importation of Slaves technically abolished the intercontinental slave trade in the United States but the ban was not widely enforced and many of the slave ships which escaped the blockade were destined for the southern United States.

USS Crusader (1858) was a screw steamer of the United States Navy that served prior to, and during, the American Civil War.
Three ships of the United States Navy have borne the name USS Scourge:
USS Gallatin (1807) was a post-Revolutionary War sailing vessel that the U.S. Department of the Treasury purchased at Norfolk, Virginia, for the United States Revenue-Marine in December 1807. An explosion on board destroyed her in 1813.

The first USS Wanderer was a high-speed schooner originally built for pleasure. It was used in 1858 to illegally import slaves from Africa. It was seized for service with the United States Navy during the American Civil War. In U.S. Navy service from 1861 to 1865, and under outright U.S. Navy ownership from 1863 to 1865, she was used by the Union Navy as a gunboat, as a tender, and as a hospital ship. She was decommissioned, put into merchant use, and lost off Cuba in 1871.
USS Herald was built at Newburyport, Massachusetts, possibly in 1797. The US Navy purchased her from Edward Davis on 15 June 1798, and sold her in 1801. She became the French 20-gun privateer corvette Africaine. In 1804 a British privateer seized her on 4 May 1804 at Charleston, South Carolina. The seizure gave rise to a case in the U.S. courts that defined the limits of U.S. territorial waters. The U.S. courts ruled that the privateer had seized Africaine outside U.S. jurisdiction. Africaine then became a Liverpool-based slave ship that made two voyages carrying slaves from West Africa to the West Indies. After the abolition of the slave trade in 1807 she became a West Indiaman that two French privateers captured in late 1807 or early 1808.
The Confederate privateers were privately owned ships that were authorized by the government of the Confederate States of America to attack the shipping of the United States. Although the appeal was to profit by capturing merchant vessels and seizing their cargoes, the government was most interested in diverting the efforts of the Union Navy away from the blockade of Southern ports, and perhaps to encourage European intervention in the conflict.
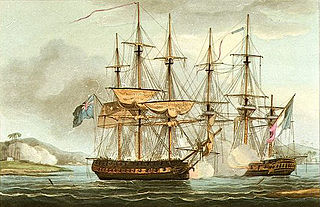
Sibylle was a 38-gun Hébé-class frigate of the French Navy. She was launched in 1791 at the dockyards in Toulon and placed in service in 1792. After the 50-gun fourth rate HMS Romney captured her in 1794, the British took her into service as HMS Sybille. She served in the Royal Navy until disposed of in 1833. While in British service Sybille participated in three notable single ship actions, in each case capturing a French vessel. On anti-slavery duties off West Africa from July 1827 to June 1830, Sybille captured numerous slavers and freed some 3,500 slaves. She was finally sold in 1833 in Portsmouth.

HMS Favourite was a 16-gun Cormorant-class sloop of the Royal Navy, launched in 1794 at Rotherhithe. The French captured her in 1806 and renamed her Favorite. However, the British recaptured her in 1807 and renamed her HMS Goree. She became a prison ship in 1810 and was broken up in Bermuda in 1817.

African Slave Trade Patrol was part of the suppression of the Atlantic slave trade between 1819 and the beginning of the American Civil War in 1861. Due to the abolitionist movement in the United States, a squadron of U.S. Navy warships were assigned to catch slave traders in and around Africa. The operations were largely ineffective as after 42 years only about 100 suspected slave ships were captured.
The British Royal Navy purchased HMS Shark on the stocks in 1775. She was launched in 1776, and in 1778 converted to a fireship and renamed HMS Salamander. The Navy sold her in 1783. She then became the mercantile Salamander. In the 1780s she was in the Greenland whale fisheries. In 1791 she transported convicts to Australia. She then became a whaling ship in the South Seas whale fisheries for a number of years, before becoming a general transport and then a slave ship. In 1804 the French captured her, but the Royal Navy recaptured her. Although she is last listed in 1811, she does not appear in Lloyd's List (LL) ship arrival and departure (SAD) data after 1804.
Numerous ships have sailed under the name Antelope. Notable ones include:
Several vessels have borne the name Kitty, a diminutive for the name "Catherine", and a name in its own right:
Several ships have been named Mariner:
Vanguard was launched in Liverpool in 1799. She made four voyages as a slave ship. After the outlawing of the British slave trade she became a West Indiaman. A French privateer captured her in March 1809.
Several ships have been named Swallow for the bird Swallow:
Several vessels have been named Africaine:
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.





