USS Monadnock may refer to:
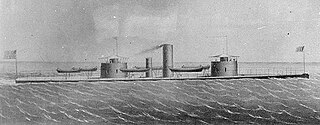
- USS Monadnock (1864), was a double-turret monitor commissioned in October 1864 and decommissioned June 1866
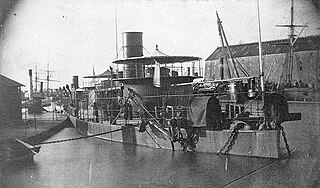
- USS Monadnock (BM-3), was an Amphitrite-class monitor commissioned in September 1883 and decommissioned March 1919
- USS Monadnock (ACM-10), was acquired by the US Navy in June 1941 and sold in 1949
- USS Monadnock (ACM-14), was acquired by the US Navy in March 1951 and removed from the Navy List in July 1960