The House of Ascania is a dynasty of German rulers. It is also known as the House of Anhalt, which refers to its longest-held possession, Anhalt.

Saxony-Anhalt is a state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony, Thuringia and Lower Saxony. It covers an area of 20,447.7 square kilometres (7,894.9 sq mi) and has a population of 2.19 million inhabitants, making it the 8th-largest state in Germany by area and the 11th-largest by population. Its capital is Magdeburg and its largest city is Halle (Saale).

The Duchy of Anhalt was a historical German duchy. The duchy was located between the Harz Mountains in the west and the river Elbe and beyond to the Fläming Heath in the east. The territory was once ruled by the House of Ascania, and is now part of the federal state of Saxony-Anhalt.

Anhalt-Zerbst was a district in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. It is bounded by the districts Potsdam-Mittelmark (Brandenburg) and Wittenberg, the city of Dessau and the districts of Köthen, Schönebeck and Jerichower Land.

The Mulde is a river in Saxony and Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. It is a left tributary of the Elbe and is 124 kilometres (77 mi) long.
Wittenberg is a district in the east of Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. Neighboring districts are Anhalt-Bitterfeld, the district-free city of Dessau-Roßlau, the districts of Potsdam-Mittelmark, Teltow-Fläming and Elbe-Elster in Brandenburg, and the district of Nordsachsen in the Free State of Saxony. Capital and largest city is Wittenberg, a UNESCO world heritage.

The Province of Saxony, also known as Prussian Saxony was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia and later the Free State of Prussia from 1816 until 1944. Its capital was Magdeburg.

The Aland is a river in the German states of Lower Saxony and Saxony-Anhalt, left tributary of the Elbe. It is the continuation of the river Biese, which is the continuation of the river Milde. The Aland is 27 kilometres (17 mi) long, whereas the total Milde-Biese-Aland system is 97 kilometres (60 mi) long. The Aland flows into the Elbe in Schnackenburg.

The Principality of Anhalt was a State of the Holy Roman Empire, located in Central Germany, in what is today part of the federal state of Saxony-Anhalt.
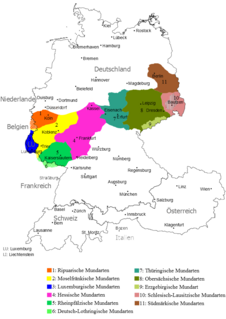
Thuringian is an East Central German dialect group spoken in much of the modern German Free State of Thuringia north of the Rennsteig ridge, southwestern Saxony-Anhalt and adjacent territories of Hesse and Bavaria. It is close to Upper Saxon spoken mainly in the state of Saxony, therefore both are also regarded as one Thuringian-Upper Saxon dialect group. Thuringian dialects are among the Central German dialects with the highest number of speakers.

The Königsberg is a neighbouring peak of the Brocken and, at 1033.5 m above sea level the third highest elevation in the Harz mountains. It lies on a long ridge that runs from southeast to northwest about 1.5 km south of the Brocken's summit. Near its summit on the northwest side is the rock formation of Hirschhörner. To the east the land descends to the Schwarze Schluftwasser, a small tributary of the Kalte Bode which flows south of the mountain. To the east on the far side of the Schwarzer Schluftwasser is the Heinrichshöhe, another subpeak of the Brocken.

The Wolfsklippen, also called the Wolfsklippe, is a granite mountain in the Harz mountains in Central Germany with an observation platform on the summit. Its height is frequently given as about 723 m above sea level (NN), but occasionally also as only around 710 m above NN.

The Ottofels, named after Prince Otto of Stolberg-Wernigerode, is a tor and natural monument near Wernigerode in the Harz mountains of central Germany.
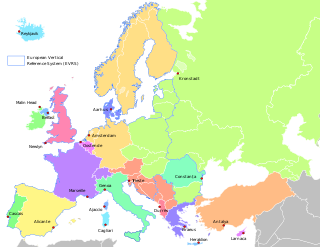
Normalhöhennull or NHN is a vertical datum used in Germany.

The Trudenstein is a rock formation and popular hiker's destination in the Harz Mountains of central Germany. It is located in the federal state of Saxony-Anhalt.
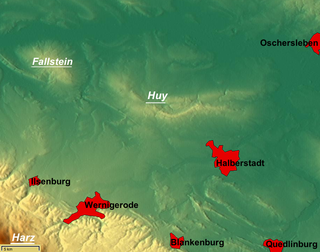
The Huy or Huywald is a ridge, up to 314.8 metres high, in western Saxony-Anhalt in Germany. It lies in the northern part of the district of Harz, about 10 kilometres northwest of Halberstadt and a few kilometres west of Schwanebeck. It is chiefly composed of bunter sandstone and muschelkalk and has been designated a protected area. Towards the north and northwest the terrain falls away into the Großes Bruch. Towards the east the Huy transitions to the Magdeburg Börde; to the south and southwest it is adjoined by the Harz Foreland and the Harz Mountains.
The Biese is a river in the German state of Saxony-Anhalt, source river of the Aland. It is the continuation of the river Milde, downstream from Beese. The Biese is 33 kilometres (21 mi) long, whereas the total Milde-Biese-Aland system is 97 kilometres (60 mi) long. The Biese flows into the Aland in Seehausen.
The Milde is a river in the German state of Saxony-Anhalt, source river of the Biese. It is 36 kilometres (22 mi) long, whereas the total Milde-Biese-Aland system is 97 kilometres (60 mi) long. The Milde flows into the Biese near Meßdorf.














