Related Research Articles

A stock market crash is a sudden dramatic decline of stock prices across a major cross-section of a stock market, resulting in a significant loss of paper wealth. Crashes are driven by panic selling and underlying economic factors. They often follow speculation and economic bubbles.

In finance, being short in an asset means investing in such a way that the investor will profit if the market value of the asset falls. This is the opposite of the more common long position, where the investor will profit if the market value of the asset rises. An investor that sells an asset short is, as to that asset, a short seller.

William Avery Rockefeller Jr. was an American businessman and financier. Rockefeller was a co-founder of Standard Oil along with his elder brother John Davison Rockefeller. He was also a part owner of Anaconda Copper, which was the fourth-largest company in the world by the late 1920s. Rockefeller started his business career as a clerk at 16. In 1867, he joined his brother's company, Rockefeller, Andrews & Flagler, which later became Standard Oil. The company was eventually split up by the Supreme Court in 1911. Rockefeller also had a significant involvement in the copper industry. In 1899, Rockefeller and Standard Oil principal Henry H. Rogers joined with Anaconda Company founder Marcus Daly to create the Amalgamated Copper Mining Company, which later returned to the name Anaconda Copper.

In the stock market, a short squeeze is a rapid increase in the price of a stock owing primarily to an excess of short selling of a stock rather than underlying fundamentals. A short squeeze occurs when demand has increased relative to supply because short sellers have to buy stock to cover their short positions.

The Panic of 1907, also known as the 1907 Bankers' Panic or Knickerbocker Crisis, was a financial crisis that took place in the United States over a three-week period starting in mid-October, when the New York Stock Exchange suddenly fell almost 50% from its peak the previous year. The panic occurred during a time of economic recession, and there were numerous runs affecting banks and trust companies. The 1907 panic eventually spread throughout the nation when many state and local banks and businesses entered bankruptcy. The primary causes of the run included a retraction of market liquidity by a number of New York City banks and a loss of confidence among depositors, exacerbated by unregulated side bets at bucket shops.

The Anaconda Copper Mine was a large copper mine in Butte, Montana that closed operations in 1947 and was eventually consumed by the Berkeley Pit, a vast open-pit mine. Originally a silver mine, it was bought for $30,000 in 1881 by an Irish immigrant named Marcus Daly from Michael Hickey, a Civil War veteran, and co-owner Charles X. Larabie. From this beginning Daly, along with partners George Hearst, James Ben Ali Haggin and Lloyd Tevis, created the Anaconda Copper Mining Company, which ultimately became a global mining enterprise that would go on to mine 18 billion pounds of copper over 100 years. At the height of The Anaconda Copper Mining Company, it consisted of the Anaconda and other Butte mines, a smelter at Anaconda, Montana, processing plants in Great Falls, Montana, the American Brass Company, and many other properties spanning multiple countries.

The Copper Kings were industrialists Marcus Daly, William A. Clark, James Andrew Murray and F. Augustus Heinze. They were known for the epic battles fought in Butte, Montana, and the surrounding region, during the Gilded Age, over control of the local copper mining industry, the fight that had ramifications for not only Montana, but the United States as a whole.

The Knickerbocker Trust was a bank based in New York City that was, at one time, among the largest banks in the United States. It was a central player in the Panic of 1907.

Frederick "Fritz" Augustus Heinze was an American businessman, known as one of the three Copper Kings of Butte, Montana, along with William Andrews Clark and Marcus Daly. Contemporary assessments variously described him as an intelligent, charismatic but also devious character. To some people in Montana, he was seen as a hero for standing up to the Amalgamated Copper Company, but he also eventually sold his Butte interests to Amalgamated for a reported $12 million. Thereafter, he played a significant role in the Panic of 1907, for which he was indicted but eventually exonerated. Ultimately, Heinze's flamboyant, hard-drinking lifestyle resulted in a hemorrhage of the stomach thought to be caused by cirrhosis of the liver, and he died in November 1914, aged 44.
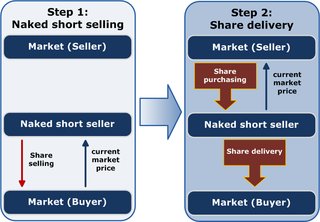
Naked short selling, or naked shorting, is the practice of short-selling a tradable asset of any kind without first borrowing the asset from someone else or ensuring that it can be borrowed. When the seller does not obtain the asset and deliver it to the buyer within the required time frame, the result is known as a "failure to deliver" (FTD). The transaction generally remains open until the asset is acquired and delivered by the seller, or the seller's broker settles the trade on their behalf.
The Anaconda Copper Mining Company, known as the Amalgamated Copper Company from 1899 to 1915, was an American mining company headquartered in Butte, Montana. It was one of the largest trusts of the early 20th century and one of the largest mining companies in the world for much of the 20th century.

The Panic of 1901 was the first stock market crash on the New York Stock Exchange, caused in part by struggles between E. H. Harriman, Jacob Schiff, and J. P. Morgan/James J. Hill for the financial control of the Northern Pacific Railway. The stock cornering was orchestrated by James Stillman and William Rockefeller's First National City Bank financed with Standard Oil money. After reaching a compromise, the moguls formed the Northern Securities Company. As a result of the panic, thousands of small investors were ruined.

Thomas William Lawson was an American businessman and writer. A highly controversial Boston stock promoter, he is known for both his efforts to promote reforms in the stock markets and the fortune he amassed for himself through highly dubious stock manipulations.

Charles Tracy Barney was an American banker who was the president of the Knickerbocker Trust Company, the collapse of which shortly before Barney's death sparked the Panic of 1907.

Charles Wyman Morse was an American businessman and speculator who committed frauds and engaged in corrupt business practices. At one time he controlled 13 banks. Known as the "Ice King" early in his career out of New York City, through Tammany Hall corruption he established a monopoly in New York's ice business, before buying several shipping companies and moving into high finance. His attempt to manipulate the price of copper-shares set off a wave of selling that developed into the Panic of 1907. Jailed for violating federal banking laws, he faked serious illness and was released. Later he was indicted for war profiteering and fraud.

John Denis Ryan was an American industrialist and copper mining magnate. He served as President of the Anaconda Copper Mining Company and was a founder of the Montana Power Company.

Colonel William Cornell Greene was an American businessman who was famous for discovering rich copper reserves in Cananea, Mexico, and for founding the Greene Consolidated Copper Company in 1899. By 1905, Greene was one of the wealthiest businessmen in the world.

The phrase curbstone broker, curb-stone broker or curb broker refers to a broker who conducts trading on the literal curbs of a financial district. Such brokers were prevalent in the 1800s and early 1900s, and the most famous curb market existed on Broad Street in the financial district of Manhattan. Curbstone brokers often traded stocks that were speculative in nature, as well as stocks in small industrial companies such as iron, textiles and chemicals. Efforts to organize and standardize the market started early in the 20th century under notable curb-stone brokers such as Emanuel S. Mendels.
The Boston and Montana Consolidated Copper and Silver Mining Company was a mining, smelting, and refining company which operated primarily in the state of Montana in the United States. It was established in 1887 and merged with the Amalgamated Copper Company in 1901. The Amalgamated Copper Company changed its name to Anaconda Copper in 1910, and became one of America's largest corporations. Historian Michael P. Malone has written, "Well financed and well managed, the Boston and Montana came to rank among the world's greatest copper companies."
Edward Mahon (1862–1937) was born in Rawmarsh, England to Sir William Vesey Ross Mahon (1813–1893), who became Fourth Baronet in 1852, but chose not to abandon his Yorkshire parish in favour of Castlegar, the ancestral Mahon family residence in County Galway, Ireland.
References
- 1 2 3 "The United Copper Company Incorporated" (PDF). The New York Times . April 29, 1902. Retrieved on September 16, 2008.
- ↑ "Copper Merger May Get the Rich Clark Mines" (PDF). The New York Times . February 18, 1906. Retrieved on September 16, 2008.
- ↑ "F.A. Heinze Indicted for Overcertifying" (PDF). The New York Times . January 8, 1908. Retrieved on September 16, 2008.
- ↑ "United Copper Co. Passes to Receivers" (PDF). The New York Times . February 11, 1913. Retrieved on September 16, 2008.
- ↑ "Heinze Asks $30 Million; Arthur P. Is Suing Amalgamated and Others for This Amount" (PDF). The New York Times . March 4, 1913. Retrieved on September 16, 2008.