Related Research Articles

Human rights are moral principles, or norms, for certain standards of human behaviour and are regularly protected as substantive rights in substantive law, municipal and international law. They are commonly understood as inalienable, fundamental rights "to which a person is inherently entitled simply because she or he is a human being" and which are "inherent in all human beings", regardless of their age, ethnic origin, location, language, religion, ethnicity, or any other status. They are applicable everywhere and at every time in the sense of being universal, and they are egalitarian in the sense of being the same for everyone. They are regarded as requiring empathy and the rule of law, and imposing an obligation on persons to respect the human rights of others; it is generally considered that they should not be taken away except as a result of due process based on specific circumstances.
International human rights instruments are the treaties and other international texts that serve as legal sources for international human rights law and the protection of human rights in general. There are many varying types, but most can be classified into two broad categories: declarations, adopted by bodies such as the United Nations General Assembly, which are by nature declaratory, so not legally-binding although they may be politically authoritative and very well-respected soft law;, and often express guiding principles; and conventions that are multi-party treaties that are designed to become legally binding, usually include prescriptive and very specific language, and usually are concluded by a long procedure that frequently requires ratification by each states' legislature. Lesser known are some "recommendations" which are similar to conventions in being multilaterally agreed, yet cannot be ratified, and serve to set common standards. There may also be administrative guidelines that are agreed multilaterally by states, as well as the statutes of tribunals or other institutions. A specific prescription or principle from any of these various international instruments can, over time, attain the status of customary international law whether it is specifically accepted by a state or not, just because it is well-recognized and followed over a sufficiently long time.

Self-determination refers to a people's right to form its own political entity, and internal self-determination is the right to representative government with full suffrage.
Civil and political rights are a class of rights that protect individuals' freedom from infringement by governments, social organizations, and private individuals. They ensure one's entitlement to participate in the civil and political life of society and the state.

The International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR) is a multilateral treaty that commits nations to respect the civil and political rights of individuals, including the right to life, freedom of religion, freedom of speech, freedom of assembly, electoral rights and rights to due process and a fair trial. It was adopted by United Nations General Assembly Resolution 2200A (XXI) on 16 December 1966 and entered into force on 23 March 1976 after its thirty-fifth ratification or accession. As of June 2022, the Covenant has 173 parties and six more signatories without ratification, most notably the People's Republic of China and Cuba; North Korea is the only state that has tried to withdraw.
The division of human rights into three generations was initially proposed in 1979 by the Czech jurist Karel Vasak at the International Institute of Human Rights in Strasbourg. He used the term at least as early as November 1977. Vasak's theories have primarily taken root in European law.
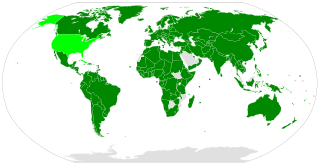
The International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights (ICESCR) is a multilateral treaty adopted by the United Nations General Assembly (GA) on 16 December 1966 through GA. Resolution 2200A (XXI), and came into force on 3 January 1976. It commits its parties to work toward the granting of economic, social, and cultural rights (ESCR) to all individuals including those living in Non-Self-Governing and Trust Territories. The rights include labour rights, the right to health, the right to education, and the right to an adequate standard of living. As of February 2024, the Covenant has 172 parties. A further four countries, including the United States, have signed but not ratified the Covenant.
A stateless nation is an ethnic group or nation that does not possess its own sovereign state. Use of the term implies that the nation has the right to self-determination, to establish an independent nation-state with its own government. Members of stateless nations may be citizens of the country in which they live, or they may be denied citizenship by that country. Stateless nations are usually not represented in international sports or in international organisations such as the United Nations. Nations without a state are classified as fourth-world nations. Some stateless nations have a history of statehood, while some were always stateless.
Fundamental rights are a group of rights that have been recognized by a high degree of protection from encroachment. These rights are specifically identified in a constitution, or have been found under due process of law. The United Nations' Sustainable Development Goal 17, established in 2015, underscores the link between promoting human rights and sustaining peace.
Section 35 of the Constitution Act, 1982 provides constitutional protection to the indigenous and treaty rights of indigenous peoples in Canada. The section, while within the Constitution of Canada, falls outside the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms. The section does not define the term "aboriginal rights" or provide a closed list; some examples of the rights that section 35 has been found to protect are fishing, logging, hunting, the right to land and the right to enforcement of treaties. There remains a debate over whether the right to indigenous self-government is included within section 35. As of 2006 the Supreme Court of Canada has made no ruling on the matter. However, since 1995 the Government of Canada has had a policy recognizing the inherent right of self-government under section 35.
Minority rights are the normal individual rights as applied to members of racial, ethnic, class, religious, linguistic or gender and sexual minorities, and also the collective rights accorded to any minority group.
The right to property, or the right to own property, is often classified as a human right for natural persons regarding their possessions. A general recognition of a right to private property is found more rarely and is typically heavily constrained insofar as property is owned by legal persons and where it is used for production rather than consumption. The Fourth Amendment to the United States Constitution is credited as a significant precedent for the legal protection of individual property rights.

The right to education has been recognized as a human right in a number of international conventions, including the International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights which recognizes a right to free, primary education for all, an obligation to develop secondary education accessible to all with the progressive introduction of free secondary education, as well as an obligation to develop equitable access to higher education, ideally by the progressive introduction of free higher education. In 2021, 171 states were parties to the Covenant.
Linguistic rights are the human and civil rights concerning the individual and collective right to choose the language or languages for communication in a private or public atmosphere. Other parameters for analyzing linguistic rights include the degree of territoriality, amount of positivity, orientation in terms of assimilation or maintenance, and overtness.

The Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples is a legally non-binding resolution passed by the United Nations in 2007. It delineates and defines the individual and collective rights of indigenous peoples, including their ownership rights to cultural and ceremonial expression, identity, language, employment, health, education, and other issues. Their ownership also extends to the protection of their intellectual and cultural property. The declaration "emphasizes the rights of Indigenous peoples to maintain and strengthen their own institutions, cultures and traditions, and to pursue their development in keeping with their own needs and aspirations." It "prohibits discrimination against indigenous peoples," and it "promotes their full and effective participation in all matters that concern them and their right to remain distinct and to pursue their own visions of economic and social development".

The Minority Treaties[a] are treaties, League of Nations mandates, and unilateral declarations made by countries applying for membership in the League of Nations that conferred basic rights on all the inhabitants of the country without distinction of birth, nationality, language, race or religion. The country concerned had to acknowledge the clauses of the treaty as fundamental laws of state and as obligations of international concern placed under the guarantee of the League of Nations. Most of the treaties entered into force after the Paris Peace Conference.

Indigenous intellectual property is a term used in national and international forums to describe intellectual property that is "collectively owned" by various Indigenous peoples, and by extension, their legal rights to protect specific such property. This property includes cultural knowledge of their groups and many aspects of their cultural heritage and knowledge, including that held in oral history. In Australia, the term Indigenous cultural and intellectual property, abbreviated as ICIP, is commonly used.
Indigenous rights are those rights that exist in recognition of the specific condition of the indigenous peoples. This includes not only the most basic human rights of physical survival and integrity, but also the rights over their land, language, religion, and other elements of cultural heritage that are a part of their existence and identity as a people. This can be used as an expression for advocacy of social organizations, or form a part of the national law in establishing the relation between a government and the right of self-determination among its indigenous people, or in international law as a protection against violation of indigenous rights by actions of governments or groups of private interests.
The Permanent Peoples' Tribunal (PPT) is an international human rights organization founded in Bologna, Italy, on June 24, 1979, at the initiative of Senator Lelio Basso. It was established during the final session of the Russell Tribunal with the aim of condemning Latin American dictatorships. The court is composed of a president, four vice-presidents, a secretary-general and 66 international members. Since its establishment, the Tribunal conducted held 46 sessions.

Development is a human right that belongs to everyone, individually and collectively. Everyone is “entitled to participate in, contribute to, and enjoy economic, social, cultural and political development, in which all human rights and fundamental freedoms can be fully realized,” states the groundbreaking UN Declaration on the Right to Development, proclaimed in 1986.
References
- ↑ "Algiers Charter". Fondazionebasso. Retrieved 18 March 2022.
- ↑ Richard Falk; Samuel S. Kim; Saul H. Mendlovitz, eds. (1982). "Universal Declaration of the Rights of Peoples". Toward a Just World Order. pp. 432–434. doi:10.4324/9780429269400-35. ISBN 978-0-429-26940-0.