This article needs additional citations for verification .(February 2023) |
utmp, wtmp, btmp and variants such as utmpx, wtmpx and btmpx are files on Unix-like systems that keep track of all logins and logouts to the system. [1]
This article needs additional citations for verification .(February 2023) |
utmp, wtmp, btmp and variants such as utmpx, wtmpx and btmpx are files on Unix-like systems that keep track of all logins and logouts to the system. [1]
These files are not regular text files, but rather a binary format which needs to be edited by specially crafted programs. The implementation and the fields present in the file differ depending on the system or the libc version, and are defined in the utmp.h header file. The wtmp and btmp format are exactly like utmp except that a null value for "username" indicates a logout on the associated terminal (the actual user name is located by finding the preceding login on that terminal). Furthermore, the value "~" as a terminal name with username "shutdown" or "reboot" indicates a system shutdown or reboot (respectively). [2]
These files are not set by any given PAM module (such as pam_unix.so or pam_sss.so) but are set by the application performing the operation (e.g. mingetty, /bin/login, or sshd). As such it is the obligation of the program itself to record the utmp information.
Utmpx and wtmpx are extensions to the original utmp and wtmp, originating from Sun Microsystems. Utmpx is specified in POSIX. [3] The utmp, wtmp and btmp files were never a part of any official Unix standard, such as Single UNIX Specification, while utmpx and corresponding APIs are part of it. [4] [5] While some systems create different newer files for the utmpx variants and have deprecated/obsoleted former formats, this is not always the case. Linux for example uses the utmpx structure in the place of the older file structure.
Depending on the system, those files may commonly be found in different places (non-exhaustive list) :
/etc/utmp /var/adm/wtmp
/var/run/utmp /var/log/wtmp /var/log/btmp
/var/adm/utmp (deprecated), /var/adm/utmpx /var/adm/wtmp (deprecated), /var/adm/wtmpx
/etc/utmp (deprecated), /etc/utmpx /var/adm/wtmp (deprecated), /var/adm/wtmpx /var/adm/btmp (deprecated), /var/adm/btmpx
FreeBSD 9.0 introduced new files while adding support for utmpx: [8]
/var/run/utx.active (replaces utmp) /var/log/utx.lastlogin (replaces lastlog) /var/log/utx.log (replaces wtmp)
Different commands allow users to consult the information stored in those files. This includes programs who (which show current system users), last (which shows the last logged in users) and lastb (which shows the last failed login attempts; Linux-specific).

The system utility fsck is a tool for checking the consistency of a file system in Unix and Unix-like operating systems, such as Linux, macOS, and FreeBSD. The equivalent programs on MS-DOS and Microsoft Windows are CHKDSK, SFC, and SCANDISK.

A man page is a form of software documentation usually found on a Unix or Unix-like operating system. Topics covered include computer programs, formal standards and conventions, and even abstract concepts. A user may invoke a man page by issuing the man command.

In computing, ls is a command to list computer files and directories in Unix and Unix-like operating systems. It is specified by POSIX and the Single UNIX Specification.
A home directory is a file system directory on a multi-user operating system containing files for a given user of the system. The specifics of the home directory are defined by the operating system involved; for example, Linux / BSD (FHS) systems use /home/⟨username⟩ or /usr/home/⟨username⟩ and Windows systems since Windows Vista use \Users\⟨username⟩.
The Unix command su, which stands for 'substitute user', is used by a computer user to execute commands with the privileges of another user account. When executed it invokes a shell without changing the current working directory or the user environment.

passwd is a command on Unix, Plan 9, Inferno, and most Unix-like operating systems used to change a user's password. The password entered by the user is run through a key derivation function to create a hashed version of the new password, which is saved. Only the hashed version is stored; the entered password is not saved for security reasons.
fortune is a program that displays a pseudorandom message from a database of quotations. Early versions of the program appeared in Version 7 Unix in 1979. The most common version on modern systems is the BSD fortune, originally written by Ken Arnold. Distributions of fortune are usually bundled with a collection of themed files, containing sayings like those found on fortune cookies, quotations from famous people, jokes, or poetry.
The Berkeley r-commands are a suite of computer programs designed to enable users of one Unix system to log in or issue commands to another Unix computer via TCP/IP computer network. The r-commands were developed in 1982 by the Computer Systems Research Group at the University of California, Berkeley, based on an early implementation of TCP/IP.
fstab is a system file commonly found in the directory /etc on Unix and Unix-like computer systems. In Linux, it is part of the util-linux package. The fstab file typically lists all available disk partitions and other types of file systems and data sources that may not necessarily be disk-based, and indicates how they are to be initialized or otherwise integrated into the larger file system structure.
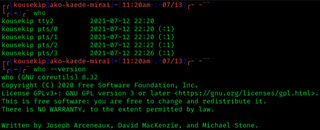
The standard Unix command who displays a list of users who are currently logged into the computer.

In the X Window System, an X display manager is a graphical login manager which starts a login session on an X server from the same or another computer.
tail is a program available on Unix, Unix-like systems, FreeDOS and MSX-DOS used to display the tail end of a text file or piped data.

lsof is a command meaning "list open files", which is used in many Unix-like systems to report a list of all open files and the processes that opened them. This open source utility was developed and supported by Victor A. Abell, the retired Associate Director of the Purdue University Computing Center. It works in and supports several Unix flavors.
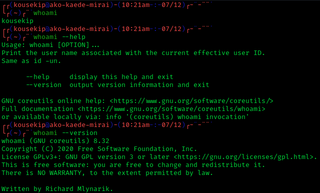
In computing, whoami is a command found on most Unix-like operating systems, Intel iRMX 86, every Microsoft Windows operating system since Windows Server 2003, and on ReactOS. It is a concatenation of the words "Who am I?" and prints the effective username of the current user when invoked.
getty, short for "get tty", is a Unix program running on a host computer that manages physical or virtual terminals (TTYs). When it detects a connection, it prompts for a username and runs the 'login' program to authenticate the user.
chsh is a command on Unix-like operating systems that is used to change a login shell. Users can either supply the pathname of the shell that they wish to change to on the command line, or supply no arguments, in which case chsh allows the user to change the shell interactively.
lastlog is a program available on most Linux distributions. It formats and prints the contents of the last login log file, /var/log/lastlog, including the login name, port, and last login date and time. It is similar in functionality to the BSD program last, also included in Linux distributions; however, last parses a different binary database file.

System Activity Report (sar) is a Unix System V-derived system monitor command used to report on various system loads, including CPU activity, memory/paging, interrupts, device load, network and swap space utilization. Sar uses /proc filesystem for gathering information.
The script command is a Unix utility that records a terminal session. It dates back to the 1979 3.0 Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD).

ProFTPD is an FTP server. ProFTPD is Free and open-source software, compatible with Unix-like systems and Microsoft Windows . Along with vsftpd and Pure-FTPd, ProFTPD is among the most popular FTP servers in Unix-like environments today. Compared to those, which focus e.g. on simplicity, speed or security, ProFTPD's primary design goal is to be a highly feature rich FTP server, exposing a large amount of configuration options to the user.