
USS Bunker Hill was one of 24 Essex-class aircraft carriers built during World War II for the United States Navy. The ship was named for the Battle of Bunker Hill in the American Revolutionary War. Commissioned in May 1943 and sent to the Pacific Theater of Operations, the ship participated in battles in the Southwest Pacific, Central Pacific and the drive toward Japan through Iwo Jima, Okinawa, and air raids on the Japanese homeland.

VFA-31 or Strike Fighter Squadron 31 is known as the Tomcatters, callsign "Felix", a United States Navy strike fighter squadron stationed at Naval Air Station Oceana flying the F/A-18E Super Hornet. The Tomcatters are the second oldest Navy Fighter Attack squadron operating today.

Fighter Squadron 61 (VF-61), the Jolly Rogers, was a fighter squadron of the United States Navy. Originally established as VF-17 on 1 January 1943, it was redesignated as VF-5B on 15 November 1946, redesignated as VF-61 on 28 July 1948 it was disestablished on 15 April 1959. It was the first navy squadron to be designated VF-17.
Fighter Squadron 11 or VF-11 was an aviation unit of the United States Navy. It was originally established as VF-5 on 1 February 1927, redesignated as VF-5S on 1 July 1927, redesignated as VF-5B in January 1928, redesignated VB-1B on 1 July 1928, redesignated VF-5B on 1 July 1930, redesignated VF-5S in July 1932, redesignated VF-5B in April 1933, redesignated VF-4 on 1 July 1937, redesignated VF-41 on 15 March 1941, redesignated VF-4 on 4 August 1943, redesignated VF-1A on 15 November 1946, redesignated VF-11 on 2 August 1948 and disestablished on 15 February 1959. It was the second US Navy squadron to be designated VF-11.

Fighter Squadron 111 (VF-111), also known as the Sundowners, was a fighter squadron of the United States Navy. Originally established as Fighter Squadron 11 (VF-11) on 10 October 1942, it was redesignated as VF-11A on 15 November 1946, redesignated as VF-111 on 15 July 1948 and disestablished on 19 January 1959. On 20 January, another squadron, VF-111 (1956-95) then assumed the designation until its de-establishment in 1995. In November 2006, VFC-13 Detachment Key West was redesignated as VFC-111, taking on the Sundowner insignia and callsign.

Fighting Squadron 10 (VF-10), also known as the "Grim Reapers", was an aviation unit of the United States Navy, established on 3 June 1942 and disestablished on 26 November 1945.

Fighter Squadron 12 or VF-12 was an aviation unit of the United States Navy. Originally established on 9 January 1943, it was disestablished on 17 September 1945. It was the first US Navy squadron to be designated as VF-12.
Fighter Squadron 13 or VF-13 was an aviation unit of the United States Navy. Established on 2 November 1943, it was disestablished on 20 October 1945. It was the first US Navy squadron to be designated as VF-13.
Fighter Squadron 33, or VF-33, was an aviation unit of the United States Navy. Originally established as Escort-Scouting Squadron 16 or VGS-16 on 6 August 1942, it was redesignated as Composite Squadron 16 or VC-16 on 1 March 1943, redesignated as VF-33 on 15 August 1943, and disestablished on 19 November 1945. It was the first US Navy squadron to be designated as VF-33.
Fighter Squadron 2 or VF-2 was an aviation unit of the United States Navy. Established on 1 June 1943, it was disestablished on 9 November 1945. It was the third US Navy squadron to be designated as VF-2.
Fighting Squadron 16 or VF-16 was an aviation unit of the United States Navy during World War II. Originally established in 1943, it was disestablished on 16 November 1945.
Fighter Squadron 15 or VF-15 was an aviation unit of the United States Navy. Originally established on 1 September 1943, it was disestablished on 20 October 1945. During six months of combat in 1944 the squadron destroyed more enemy planes than any other squadron in the Pacific War. Twenty-six of the squadron’s pilots became aces.
Fighter Squadron 8 or VF-8 was an aviation unit of the U.S. Navy, originally established on 1 June 1943, it was disestablished on 23 November 1945. It was the second US Navy squadron to be designated VF-8.
Fighting Squadron 72 or VF-72 was an aviation unit of the U.S. Navy, originally established as VF-7 on 1 July 1939, it was redesignated as VF-72 on 19 November 1940 and disestablished on 29 March 1943.
Fighter Squadron 7 or VF-7 was an aviation unit of the U.S. Navy, originally established on 3 January 1944, it was disestablished on 8 June 1946. It was the second US Navy squadron to be designated VF-7.
Fighting Squadron 9 or VF-9 was an aviation unit of the U.S. Navy, originally established on 1 March 1942, it was disestablished on 28 September 1945.
Fighter Squadron 38 or VF-38 was an aviation unit of the United States Navy. Originally established on 20 June 1943, it was disestablished on 31 January 1946. It was the only US Navy squadron to be designated as VF-38.

Ira Cassius Kepford was an American flying ace of World War II who served with a land-based unit of the United States Navy. In 76 days of combat flying with the VF-17 "Jolly Rogers," he was credited with shooting down 16 enemy aircraft. At the close of his combat service in April 1944, Kepford was the Navy's leading ace.

Commander Hamilton McWhorter III was a United States Navy aviator and a flying ace of World War II, credited with shooting down twelve Japanese aircraft. He was the first Hellcat ace, first USN carrier-based double ace, and the first Grumman F6F Hellcat pilot to achieve double ace status. He flew 89 combat missions during World War II while flying with the VF-9 and VF-12 units. On May 23, 2014, he was also posthumously awarded the American Fighter Aces Congressional Gold Medal, when the United States Congress collectively awarded the gold medal to all flying aces: a navy pilot is depicted on the medal in the upper right.
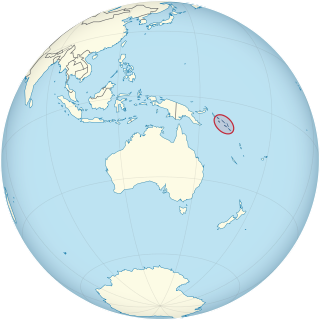
US Naval Base Solomons was a number of United States Navy bases in the Solomon Islands in the Pacific Ocean. Most were built by the US Navy Seabees, Naval Construction Battalions, during World War II as part of the Pacific War. In August 1942 the United States Armed Forces took the Guadalcanal in the Solomon, in the Battle of Guadalcanal. US Navy Seabees built a new base at Guadalcanal, Naval Base Guadalcanal and then on other islands in the Solomons.









