
In human anatomy, the arm refers to the upper limb in common usage, although academically the term specifically means the upper arm between the glenohumeral joint and the elbow joint. The distal part of the upper limb between the elbow and the radiocarpal joint is known as the forearm or "lower" arm, and the extremity beyond the wrist is the hand.

Coronary artery bypass surgery, also known as coronary artery bypass graft is a surgical procedure to treat coronary artery disease (CAD), the buildup of plaques in the arteries of the heart. It can relieve chest pain caused by CAD, slow the progression of CAD, and increase life expectancy. It aims to bypass narrowings in heart arteries by using arteries or veins harvested from other parts of the body, thus restoring adequate blood supply to the previously ischemic heart.
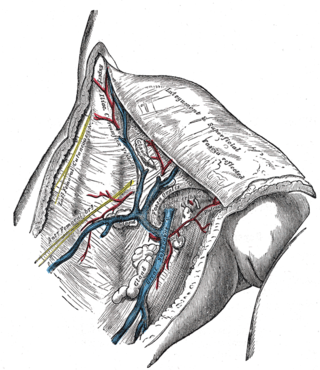
The great saphenous vein is a large, subcutaneous, superficial vein of the leg. It is the longest vein in the body, running along the length of the lower limb, returning blood from the foot, leg and thigh to the deep femoral vein at the femoral triangle.
Graft or grafting may refer to:

The scalp is the anatomical area bordered by the human face at the front, and by the neck at the sides and back.

The umbilical vein is a vein present during fetal development that carries oxygenated blood from the placenta into the growing fetus. The umbilical vein provides convenient access to the central circulation of a neonate for restoration of blood volume and for administration of glucose and drugs.

In human anatomy, the radial artery is the main artery of the lateral aspect of the forearm.
Grafting refers to a surgical procedure to move tissue from one site to another on the body, or from another creature, without bringing its own blood supply with it. Instead, a new blood supply grows in after it is placed. A similar technique where tissue is transferred with the blood supply intact is called a flap. In some instances, a graft can be an artificially manufactured device. Examples of this are a tube to carry blood flow across a defect or from an artery to a vein for use in hemodialysis.

In human anatomy, the internal thoracic artery (ITA), previously commonly known as the internal mammary artery, is an artery that supplies the anterior chest wall and the breasts. It is a paired artery, with one running along each side of the sternum, to continue after its bifurcation as the superior epigastric and musculophrenic arteries.

An arteriovenous fistula is an abnormal connection or passageway between an artery and a vein. It may be congenital, surgically created for hemodialysis treatments, or acquired due to pathologic process, such as trauma or erosion of an arterial aneurysm.
A vascular bypass is a surgical procedure performed to redirect blood flow from one area to another by reconnecting blood vessels. Often, this is done to bypass around a diseased artery, from an area of normal blood flow to another relatively normal area. It is commonly performed due to inadequate blood flow (ischemia) caused by atherosclerosis, as a part of organ transplantation, or for vascular access in hemodialysis. In general, someone's own vein (autograft) is the preferred graft material for a vascular bypass, but other types of grafts such as polytetrafluoroethylene (Teflon), polyethylene terephthalate (Dacron), or a different person's vein (allograft) are also commonly used. Arteries can also serve as vascular grafts. A surgeon sews the graft to the source and target vessels by hand using surgical suture, creating a surgical anastomosis.

The posterior auricular vein is a vein of the head. It begins from a plexus with the occipital vein and the superficial temporal vein, descends behind the auricle, and drains into the external jugular vein.
Vascular access refers to a rapid, direct method of introducing or removing devices or chemicals from the bloodstream. In hemodialysis, vascular access is used to remove the patient's blood so that it can be filtered through the dialyzer. Three primary methods are used to gain access to the blood: an intravenous catheter, an arteriovenous fistula (AV) or a synthetic graft. In the latter two, needles are used to puncture the graft or fistula each time dialysis is performed.

VGF or VGF nerve growth factor inducible is a secreted protein and neuropeptide precursor that may play a role in regulating energy homeostasis, metabolism and synaptic plasticity. The protein was first discovered in 1985 by Levi et al. in an experiment with PC12 cells and its name is non-acronymic. VGF gene encodes a precursor which is divided by proteolysis to polypeptides of different mass, which have a variety of functions, the best studied of which are the roles of TLQP-21 in the control of appetite and inflammation, and TLQP-62 as well as AQEE-30 in regulating depression-like behaviors and memory. The expression of VGF and VGF-derived peptides is detected in a subset of neurons in the central and peripheral nervous systems and specific populations of endocrine cells in the adenohypophysis, adrenal medulla, gastrointestinal tract, and pancreas. VGF expression is induced by NGF, CREB and BDNF and regulated by neurotrophin-3. Physical exercise significantly increases VGF expression in mice hippocampal tissue and upregulates a neurotrophic signaling cascade thought to underlie the action of antidepressants.
Artivion, Inc. is a distributor of cryogenically preserved human tissues for cardiac and vascular transplant applications and develops medical devices. Among its products are human heart valves, which are treated to remove excess cellular material and antigens, and BioGlue surgical adhesive.
Endoscopic vessel harvesting (EVH) is a surgical technique that may be used in conjunction with coronary artery bypass surgery. For patients with coronary artery disease, a physician may recommend a bypass to reroute blood around blocked arteries to restore and improve blood flow and oxygen to the heart. To create the bypass graft, a surgeon will remove or "harvest" healthy blood vessels from another part of the body, often from the patient's leg or arm. This vessel becomes a graft, with one end attaching to a blood source above and the other end below the blocked area, creating a "conduit" channel or new blood flow connection across the heart.

Ude Desh ka Aam Naagrik, known by its acronym UDAN is a regional airport development program of the Government of India and part of the Regional Connectivity Scheme (RCS) of upgrading under-serviced air routes. Its goal is to make air travel affordable and improve economic development in India. At the beginning of the scheme, out of total 486 airports, 406 were under-serviced airports, 27 were well-served airports, out of 97 non-RCS airports only 12 were operational airports, out of 18 participating airports under-served regional operational airports with regular fixed-wing scheduled flights. UDAN scheme will add to this number by expediting the development and operationalisation of India's potential-target of nearly 425 unserved, under-served, and mostly underdeveloped regional airports with regular scheduled flights. However, there are several issues and criticisms such as poor infrastructure, dominance by larger airlines and degradation of regional airlines, slow implementation that plague this scheme.
In medicine, vein graft failure (VGF) is a condition in which vein grafts, which are used as alternative conduits in bypass surgeries, get occluded.

In cardiac surgery and vascular surgery, external support is a type of scaffold made of metal or plastic material that is inserted over the outside of the vein graft in order to decrease the intermediate and late vein graft failure after bypass surgery.
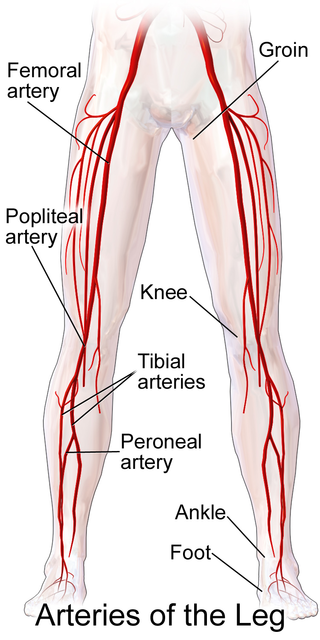
Popliteal bypass surgery, more commonly known as femoropopliteal bypass or more generally as lower extremity bypass surgery, is a surgical procedure used to treat diseased leg arteries above or below the knee. It is used as a medical intervention to salvage limbs that are at risk of amputation and to improve walking ability in people with severe intermittent claudication and ischemic rest pain.












