A substance is anhydrous if it contains no water. Many processes in chemistry can be impeded by the presence of water; therefore, it is important that water-free reagents and techniques are used. In practice, however, it is very difficult to achieve perfect dryness; anhydrous compounds gradually absorb water from the atmosphere so they must be stored carefully.

Benzophenone is a naturally occurring organic compound with the formula (C6H5)2CO, generally abbreviated Ph2CO. Benzophenone has been found in some fungi, fruits and plants, including grapes. It is a white solid with a low melting point and rose-like odor that is soluble in organic solvents. Benzophenone is the simplest diaromatic ketone. It is a widely used building block in organic chemistry, being the parent diarylketone.
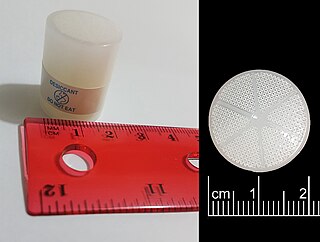
A desiccant is a hygroscopic substance that is used to induce or sustain a state of dryness (desiccation) in its vicinity; it is the opposite of a humectant. Commonly encountered pre-packaged desiccants are solids that absorb water. Desiccants for specialized purposes may be in forms other than solid, and may work through other principles, such as chemical bonding of water molecules. They are commonly encountered in foods to retain crispness. Industrially, desiccants are widely used to control the level of water in gas streams.

Acetylacetone is an organic compound with the chemical formula CH3−C(=O)−CH2−C(=O)−CH3. It is classified as a 1,3-diketone. It exists in equilibrium with a tautomer CH3−C(=O)−CH=C(−OH)−CH3. The mixture is a colorless liquid. These tautomers interconvert so rapidly under most conditions that they are treated as a single compound in most applications. Acetylacetone is a building block for the synthesis of many coordination complexes as well as heterocyclic compounds.

A molecular sieve is a material with pores of uniform size. These pore diameters are similar in size to small molecules, and thus large molecules cannot enter or be adsorbed, while smaller molecules can. As a mixture of molecules migrates through the stationary bed of porous, semi-solid substance referred to as a sieve, the components of the highest molecular weight leave the bed first, followed by successively smaller molecules. Some molecular sieves are used in size-exclusion chromatography, a separation technique that sorts molecules based on their size. Another important use is as a desiccant. Most of molecular sieves are aluminosilicate zeolites with Si/Al molar ratio less than 2, but there are also examples of activated charcoal and silica gel.
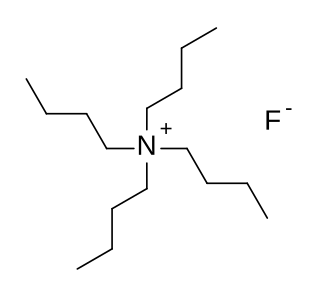
Tetra-n-butylammonium fluoride, commonly abbreviated to TBAF and n-Bu4NF, is a quaternary ammonium salt with the chemical formula (CH3CH2CH2CH2)4N+F−. It is commercially available as the white solid trihydrate and as a solution in tetrahydrofuran. TBAF is used as a source of fluoride ion in organic solvents.

A ketyl group in organic chemistry is an anion radical that contains a group R2C−O•. It is the product of the 1-electron reduction of a ketone.
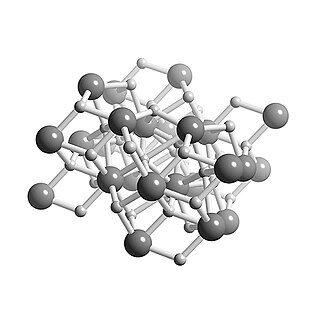
Calcium hydride is the chemical compound with the formula CaH2, an alkaline earth hydride. This grey powder reacts vigorously with water liberating hydrogen gas. CaH2 is thus used as a drying agent, i.e. a desiccant.
Air-free techniques refer to a range of manipulations in the chemistry laboratory for the handling of compounds that are air-sensitive. These techniques prevent the compounds from reacting with components of air, usually water and oxygen; less commonly carbon dioxide and nitrogen. A common theme among these techniques is the use of a fine (100–10−3 Torr) or high (10−3–10−6 Torr) vacuum to remove air, and the use of an inert gas: preferably argon, but often nitrogen.

Nickel(II) bis(acetylacetonate) is a coordination complex with the formula [Ni(acac)2]3, where acac is the anion C5H7O2− derived from deprotonation of acetylacetone. It is a dark green paramagnetic solid that is soluble in organic solvents such as toluene. It reacts with water to give the blue-green diaquo complex Ni(acac)2(H2O)2.

Ruthenium(III) acetylacetonate is a coordination complex with the formula Ru(O2C5H7)3. O2C5H7− is the ligand called acetylacetonate. This compound exists as a dark violet solid that is soluble in most organic solvents. It is used as a precursor to other compounds of ruthenium.

Tris(acetylacetonato) iron(III), often abbreviated Fe(acac)3, is a ferric coordination complex featuring acetylacetonate (acac) ligands, making it one of a family of metal acetylacetonates. It is a red air-stable solid that dissolves in nonpolar organic solvents.
Metal acetylacetonates are coordination complexes derived from the acetylacetonate anion (CH
3COCHCOCH−
3) and metal ions, usually transition metals. The bidentate ligand acetylacetonate is often abbreviated acac. Typically both oxygen atoms bind to the metal to form a six-membered chelate ring. The simplest complexes have the formula M(acac)3 and M(acac)2. Mixed-ligand complexes, e.g. VO(acac)2, are also numerous. Variations of acetylacetonate have also been developed with myriad substituents in place of methyl (RCOCHCOR′−). Many such complexes are soluble in organic solvents, in contrast to the related metal halides. Because of these properties, acac complexes are sometimes used as catalyst precursors and reagents. Applications include their use as NMR "shift reagents" and as catalysts for organic synthesis, and precursors to industrial hydroformylation catalysts. C
5H
7O−
2 in some cases also binds to metals through the central carbon atom; this bonding mode is more common for the third-row transition metals such as platinum(II) and iridium(III).

Vanadyl acetylacetonate is the chemical compound with the formula VO(acac)2, where acac– is the conjugate base of acetylacetone. It is a blue-green solid that dissolves in polar organic solvents. The coordination complex consists of the vanadyl group, VO2+, bound to two acac– ligands via the two oxygen atoms on each. Like other charge-neutral acetylacetonate complexes, it is not soluble in water.
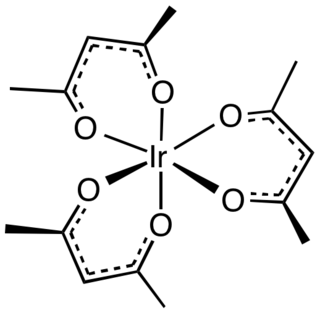
Iridium acetylacetonate is the iridium coordination complex with the formula Ir(O2C5H7)3, which is sometimes known as Ir(acac)3. The molecule has D3-symmetry. It is a yellow-orange solid that is soluble in organic solvents.

Zirconium acetylacetonate is the coordination complex with the formula Zr(C5H7O2)4. It is a common acetylacetonate of zirconium. It is a white solid that exhibits high solubility in nonpolar organic solvents, but not simple hydrocarbons.

Tris(acetylacetonato)cobalt(III) is the coordination complex with the formula Co(C5H7O2)3. Often abbreviated Co(acac)3, it is a green, diamagnetic solid that is soluble in organic solvents, but not in water. Owing to its solubility in organic solvents, tris(acetylacetonato)cobalt(III) is used to produce homogeneous catalysts by reduction.
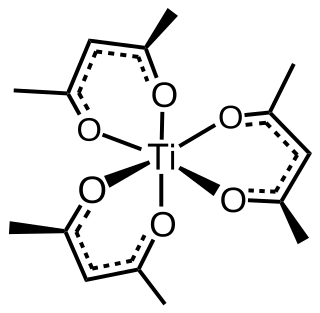
Tris(acetylacetonato)titanium(III), often abbreviated Ti(acac)3, is a coordination complex of titanium(III) featuring acetylacetonate (acac) ligands, making it one of a family of metal acetylacetonates. It is a blue air-sensitive solid that dissolves in nonpolar organic solvents. The compound is prepared by treating titanium trichloride with acetylacetone in the presence of base. Being paramagnetic, it gives a contact-shifted proton NMR signal at 60 ppm upfield of TMS assigned to the methyl group.

Tetraacetylethane is the organic compound with the nominal formula [CH(C(O)CH3)2]2. It is a white solid that has attracted interest as a precursor to heterocycles and metal complexes. It is prepared by oxidation of sodium acetylacetonate:

Praseodymium acetylacetonate is a coordination complex with the formula Pr(C3H7O2)3. This purported anhydrous acetylacetonate complex is widely discussed but only the dihydrate Pr(C3H7O2)3(H2O)2 has been characterized by X-ray crystallography.

















