
Alexander III of Macedon, commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. A member of the Argead dynasty, he was born in Pella—a city in Ancient Greece—in 356 BC. He succeeded his father King Philip II to the throne at the age of 20, and spent most of his ruling years conducting a lengthy military campaign throughout Western Asia and Northeastern Africa. By the age of thirty, he had created one of the largest empires in history, stretching from Greece to northwestern India. He was undefeated in battle and is widely considered to be one of history's most successful military commanders.

Macedonian is an Eastern South Slavic language. Spoken as a first language by around two million people, it serves as the official language of North Macedonia. Most speakers can be found in the country and its diaspora, with a smaller number of speakers throughout the transnational region of Macedonia. Macedonian is also a recognized minority language in parts of Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Romania, and Serbia and it is spoken by emigrant communities predominantly in Australia, Canada and the United States.
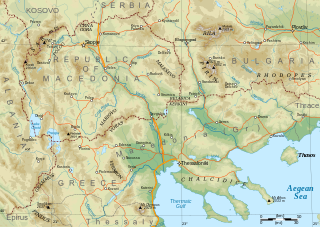
Macedonia is a geographical and historical region of the Balkan Peninsula in Southeast Europe. Its boundaries have changed considerably over time; however, it came to be defined as the modern geographical region by the mid 19th century. Today the region is considered to include parts of six Balkan countries: Greece, North Macedonia, Bulgaria, and smaller parts in Albania, Serbia, and Kosovo. It covers approximately 67,000 square kilometres (25,869 sq mi) and has a population of 4.76 million.

Skopje is the capital and largest city of North Macedonia. It is the country's political, cultural, economic, and academic centre.

Macedonia, also called Macedon, was an ancient kingdom on the periphery of Archaic and Classical Greece, and later the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. The kingdom was founded and initially ruled by the royal Argead dynasty, which was followed by the Antipatrid and Antigonid dynasties. Home to the ancient Macedonians, the earliest kingdom was centered on the northeastern part of the Greek peninsula, and bordered by Epirus to the west, Paeonia to the north, Thrace to the east and Thessaly to the south.

Macedonians are a nation and a South Slavic ethnic group native to the region of Macedonia in Southeast Europe. They speak the Macedonian language, a South Slavic language. About two thirds of all ethnic Macedonians live in North Macedonia and there are also communities in a number of other countries.

The North Macedonia national football team represents Macedonia in men's international football, and is administered by the Football Federation of North Macedonia. The team play their home matches at the Toše Proeski Arena in Skopje.

Macedonia most commonly refers to:

The Socialist Republic of Macedonia, or SR Macedonia, commonly referred to as Socialist Macedonia or YugoslavMacedonia, was one of the six constituent countries of the post-WWII Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, and a nation state of the Macedonians. After the transition of the political system to parliamentary democracy in 1990, the Republic changed its official name to Republic of Macedonia in 1991, and with the beginning of the breakup of Yugoslavia, it declared itself an independent country and held a referendum on 8 September 1991 on which a sovereign and independent state of Macedonia, with a right to enter into any alliance with sovereign states of Yugoslavia was approved.

The Football Federation of Macedonia ; ФФМ/FFM, is the governing body of football in North Macedonia based in Skopje.

The Macedonians were an ancient tribe that lived on the alluvial plain around the rivers Haliacmon and lower Axios in the northeastern part of mainland Greece. Essentially an ancient Greek people, they gradually expanded from their homeland along the Haliacmon valley on the northern edge of the Greek world, absorbing or driving out neighbouring non-Greek tribes, primarily Thracian and Illyrian. They spoke Ancient Macedonian, a language closely related to Ancient Greek or a Doric Greek dialect, although the prestige language of the region was at first Attic and then Koine Greek. Their religious beliefs mirrored those of other Greeks, following the main deities of the Greek pantheon, although the Macedonians continued Archaic burial practices that had ceased in other parts of Greece after the 6th century BC. Aside from the monarchy, the core of Macedonian society was its nobility. Similar to the aristocracy of neighboring Thessaly, their wealth was largely built on herding horses and cattle.
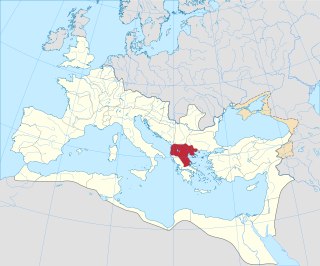
The Roman province of Macedonia was officially established in 146 BC, after the Roman general Quintus Caecilius Metellus defeated Andriscus of Macedon, the last self-styled king of the ancient kingdom of Macedonia in 148 BC, and after the four client republics established by Rome in the region were dissolved. The province incorporated the former kingdom of Macedonia with the addition of Epirus, Thessaly, and parts of Illyria, Paeonia and Thrace. This created a much larger administrative area, to which the name of 'Macedonia' was still applied.

Goran Pandev is a Macedonian professional footballer who plays as a forward for Italian club Genoa. He is the captain of the North Macedonia national football team, and is the country's all-time top scorer with 38 goals.

Macedonia is a geographic and administrative region of Greece, in the southern Balkans. Macedonia is the largest and second-most-populous Greek region, with a population of 2.38 million in 2017. The region is highly mountainous, with most major urban centres such as Thessaloniki and Kavala being concentrated on its southern coastline. Together with Thrace, and sometimes also Thessaly and Epirus, it is part of Northern Greece. Greek Macedonia encompasses entirely the southern part of the region of Macedonia, making up 51% of the total area of the region. It also contains Mount Athos, an autonomous monastic region of Greece. Macedonia forms part of Greece's national frontier with three countries: Bulgaria to the northeast, North Macedonia to the north, and Albania to the northwest.

Macedonian nationalism is a general grouping of nationalist ideas and concepts among ethnic Macedonians that were first formed in the late 19th century among separatists seeking the autonomy of the region of Macedonia from the Ottoman Empire. The idea evolved during the early 20th century alongside the first expressions of ethnic nationalism among the Slavs of Macedonia. The separate Macedonian nation gained recognition after World War II when the "Socialist Republic of Macedonia" was created as part of Yugoslavia. Afterwards the Macedonian historiography has established historical links between the ethnic Macedonians and events and Bulgarian figures from the Middle Ages up to the 20th century. Following the independence of the Republic of Macedonia in the late 20th century, issues of Macedonian national identity have become contested by the country's neighbours, as some adherents to aggressive Macedonian nationalism, called Macedonism, hold more extreme beliefs such as an unbroken continuity between ancient Macedonians, and modern ethnic Macedonians, and views connected to the irredentist concept of a United Macedonia, which involves territorial claims on a large portion of Greece, along with smaller regions of Albania, Bulgaria, Kosovo and Serbia.
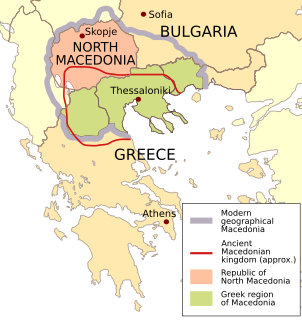
The use of the country name "Macedonia" was disputed between Greece and Macedonia between 1991 and 2019. The dispute was a source of instability in the Western Balkans for 25 years. It was resolved through negotiations between Athens and Skopje, mediated by the United Nations, resulting in the Prespa agreement, which was signed on June 17, 2018. Pertinent to its background is an early 20th-century multifaceted dispute and armed conflict that formed part of the background to the Balkan Wars. The specific naming dispute, although an existing issue in Yugoslav–Greek relations since World War II, was reignited after the breakup of Yugoslavia and the newly gained independence of the former Socialist Republic of Macedonia in 1991. Since then, it was an ongoing issue in bilateral and international relations until it was settled with the Prespa agreement in June 2018, the subsequent ratification by the Macedonian and Greek parliaments in late 2018 and early 2019, and the official renaming of Macedonia to North Macedonia in February 2019.
The Macedonian First League is the top-tier basketball competition in the Republic of North Macedonia organized by the Basketball Federation of North Macedonia. Macedonian Republic League was transformed in to top division level Macedonian Basketball First League. After the transformation teams from the higher level federal Leagues joined the Macedonian First League.
Slavic speakers are a linguistic minority population in the northern Greek region of Macedonia, who are mostly concentrated in certain parts of the peripheries of West and Central Macedonia, adjacent to the territory of the state of North Macedonia. The language called "Slavic" in the context of Greece is generally called "Macedonian" or "Macedonian Slavic" otherwise. Some members have formed their own emigrant communities in neighbouring countries, as well as further abroad.

North Macedonia, officially the Republic of North Macedonia, is a country in Southeast Europe. It gained independence in 1991 as one of the successor states of Yugoslavia. North Macedonia is a landlocked country bordering with Kosovo to the northwest, Serbia to the north, Bulgaria to the east, Greece to the south, and Albania to the west. It constitutes approximately the northern third of the larger geographical region of Macedonia. Skopje, the capital and largest city, is home to a quarter of the country's 2.06 million population. The majority of the residents are ethnic Macedonians, a South Slavic people. Albanians form a significant minority at around 25%, followed by Turks, Romani, Serbs, Bosniaks, and Aromanians.

The Argead dynasty was an ancient Macedonian royal house of Dorian Greek provenance. They were the founders and the ruling dynasty of the kingdom of Macedon from about 700 to 310 BC.














