Related Research Articles

The Iapydes were an ancient people who dwelt north of and inland from the Liburnians, off the Adriatic coast and eastwards of the Istrian peninsula. They occupied the interior of the country between the Colapis (Kupa) and Oeneus (Una) rivers, and the Velebit mountain range which separated them from the coastal Liburnians. Their territory covered the central inlands of modern Croatia and Una River Valley in today's Bosnia and Herzegovina. Archaeological documentation confirms their presence in these countries at least from 9th century BC, and they persisted in their area longer than a millennium. The ancient written documentation on inland Iapydes is scarcer than on the adjacent coastal peoples that had more frequent maritime contacts with ancient Greeks and Romans.
The Scordisci were a Celtic Iron Age cultural group centered in the territory of present-day Serbia, at the confluence of the Savus (Sava), Dravus (Drava), Margus (Morava) and Danube rivers. They were historically notable from the beginning of the third century BC until the turn of the common era, and consolidated into a tribal state. At their zenith, their core territory stretched over regions comprising parts of present-day Serbia, Croatia, Bulgaria and Romania, while their influence spread even further. After the Roman conquest in the 1st century AD, their territories were included into the Roman provinces of Pannonia, Moesia and Dacia.
The Delmatae, alternatively Dalmatæ, during the Roman period, were a group of Illyrian tribes in Dalmatia, contemporary southern Croatia and western Bosnia and Herzegovina. The region of Dalmatia takes its name from the tribe.
The Amantini was the name of a Pannonian Illyrian tribe.
Celticisation, or Celticization, was historically the process of conquering and assimilating by the ancient Celts. Today, as the Celtic inhabited-areas significantly differ, the term still refers to making something Celtic, usually focusing around the Celtic nations and their languages.
Caravantius, an Illyrian, was half brother to Gentius, the last Illyrian king of the Ardiaean State. In 168 BC he fought with his brother against the Cavii.
Plator the Illyrian was brother to King Gentius, the last Illyrian king of the Ardiaean State.
Etuta was an Illyrian queen of the Ardiaean Kingdom, married to Gentius. Etuta was a Dardanian princess, the daughter of Monunius II of Dardania.
Catari was the name of a tribe belonging to the Venetic peoples that are sometimes confused with Illyrians.
Promona was an ancient city inhabited by the Illyrians. Promona was the location a Roman cohort in the territory of the Delmatae. The location is the modern-day village of Tepljuh, north of Drnis.

The Illyrian Kingdom is the name of a country that existed on the Western part of the Balkan Peninsula in ancient times and represented an alliance of Illyrian tribes.
The history of Illyrian warfare of the Illyrians spans from the beginning of the 2nd millennium BC up to the 1st century AD in the region of Illyria and in southern Italy where the Iapygian civilization flourished.
Epidaurus or Epidauros was an ancient Greek colony founded sometime in the 6th century BC, renamed to Epidaurum during Roman rule in 228 BC, when it was part of the province of Illyricum, later Dalmatia. It is located at the modern-day Cavtat in Croatia, 15 km (9 mi) south of Dubrovnik.
Celegeri were a Celtic tribe, together with the Dindari a branch of the Scordisci that migrated to Illyria after the Gallic invasion of the Balkans in 279 BC. They inhabited Moesia Superior, and are registered by Pliny as living between the Dardanoi and the Triballi. They appear in north-westernmost Thrace in the 1st century BC. They were replaced by the Romanized Thracio-Celtic Tricornenses.
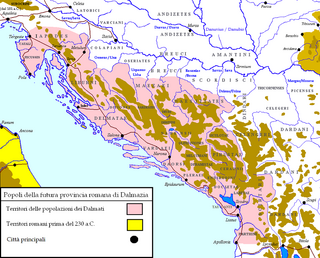
Mazaei or Maezaei were a sub-tribe of the Illyrians, autochthonous to the interior of today's Bosnia and Herzegovina, settled mainly in the Sana river basin, the middle course of Vrbas, and around the Vrbanja and Ugar rivers.
This article contains information about Illyrian vocabulary. No Illyrian texts survive, so sources for identifying Illyrian words have been identified by Hans Krahe as being of four kinds: inscriptions, glosses of Illyrian words in classical texts, names—including proper names, toponyms and river names—and Illyrian loanwords in other languages. The last category has proven particularly contentious. The names occur in sources that range over more than a millennium, including numismatic evidence, as well as posited original forms of placenames. The Messapian language, which may be related, does have a small attested corpus, but it is not in this page's scope due to the uncertainty about its relationship to Illyrian.

The Azali were a Pannonian Illyrian people. They originally lived in Pannonia, northern Illyria. They were one of the tribal groups which revolted in the Bellum Batonianum and like other Pannonian Illyrians, they were forcibly moved out of the region. The exact date of the resettlement is unclear as the Transdanubian area, where they were settled, passed under Roman control after the Illyrian revolt. The Azali were settled in the Roman frontier between the Celtic Boii and Eravisci. In their new homeland they were organized as a civitas. Their chief settlement was Brigetio, contemporary Szőny.
This is a list of Illyrian rulers from the Ardiean-Labeatan dynasty:
References
- ↑ Wilkes, J. J. The Illyrians, 1992, ISBN 0-631-19807-5,page 81,"... " In Roman Pannonia the Latobici and Varciani who dwelt east of the Venetic Catari in the upper Sava valley were Celtic but the Colapiani of ..."
- ↑ Wilkes, J. J. The Illyrians, 1992, ISBN 0-631-19807-5,page 256, "... established among the predominantly Celtic communities of the Latobici and Varciani. Only later, in the reign of Trajan (AD 98-117), does the Roman citizenship begin to appear among the ..."