In economics and finance, arbitrage is the practice of taking advantage of a difference in prices in two or more markets – striking a combination of matching deals to capitalize on the difference, the profit being the difference between the market prices at which the unit is traded. When used by academics, an arbitrage is a transaction that involves no negative cash flow at any probabilistic or temporal state and a positive cash flow in at least one state; in simple terms, it is the possibility of a risk-free profit after transaction costs. For example, an arbitrage opportunity is present when there is the possibility to instantaneously buy something for a low price and sell it for a higher price.

Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) are business transactions in which the ownership of companies, business organizations, or their operating units are transferred to or consolidated with another company or business organization. This could happen through direct absorption, a merger, a tender offer or a hostile takeover. As an aspect of strategic management, M&A can allow enterprises to grow or downsize, and change the nature of their business or competitive position.
An initial public offering (IPO) or stock launch is a public offering in which shares of a company are sold to institutional investors and usually also to retail (individual) investors. An IPO is typically underwritten by one or more investment banks, who also arrange for the shares to be listed on one or more stock exchanges. Through this process, colloquially known as floating, or going public, a privately held company is transformed into a public company. Initial public offerings can be used to raise new equity capital for companies, to monetize the investments of private shareholders such as company founders or private equity investors, and to enable easy trading of existing holdings or future capital raising by becoming publicly traded.
Price discrimination is a microeconomic pricing strategy where identical or largely similar goods or services are sold at different prices by the same provider in different market segments. Price discrimination is distinguished from product differentiation by the more substantial difference in production cost for the differently priced products involved in the latter strategy. Price discrimination essentially relies on the variation in the customers' willingness to pay and in the elasticity of their demand. For price discrimination to succeed, a firm must have market power, such as a dominant market share, product uniqueness, sole pricing power, etc. All prices under price discrimination are higher than the equilibrium price in a perfectly competitive market. However, some prices under price discrimination may be lower than the price charged by a single-price monopolist. Price discrimination is utilized by the monopolist to recapture some deadweight loss. This Pricing strategy enables firms to capture additional consumer surplus and maximize their profits while benefiting some consumers at lower prices. Price discrimination can take many forms and is prevalent in many industries, from education and telecommunications to healthcare.
An electricity market is a system that enables the exchange of electrical energy, through an electrical grid. Historically, electricity has been primarily sold by companies that operate electric generators, and purchased by consumers or electricity retailers.
In marketing, product bundling is offering several products or services for sale as one combined product or service package. It is a common feature in many imperfectly competitive product and service markets. Industries engaged in the practice include telecommunications services, financial services, health care, information, and consumer electronics. A software bundle might include a word processor, spreadsheet, and presentation program into a single office suite. The cable television industry often bundles many TV and movie channels into a single tier or package. The fast food industry combines separate food items into a "meal deal" or "value meal".

Pricing is the process whereby a business sets the price at which it will sell its products and services, and may be part of the business's marketing plan. In setting prices, the business will take into account the price at which it could acquire the goods, the manufacturing cost, the marketplace, competition, market condition, brand, and quality of product.

Name your own price (NYOP) is a pricing strategy under which buyers make a suggestion for a product’s price and the transaction occurs only if a seller accepts this quoted price. What happens is that the seller waits for a potential buyer's offer and can then either accept or reject that 'named price' that the user had offered. As the Internet is continuously being developed and online marketplaces are becoming increasingly more popular, consumers have more choices in terms of product pricing. Popularized by the reverse auction pioneer, Priceline.com, such pricing strategy asks consumers to 'name their own price' for various products and services like air tickets, hotels, rental cars, etc. The first bid a consumer places and the subsequent bid increments express the consumer's willingness or unwillingness to haggle. "The economic argument is that the number of bids a consumer submits to win a product in a NYOP auction is determined by the bidder’s intention to trade off higher expected savings from haggling against the associated frictional costs". NYOP retailers do not post a price for their products, and the final price of the transaction is only determined via a "reverse auction process", and these are key features that distinguish hotels and travel intermediaries from NYOP retailers. Similarly, LetYouKnow, Inc. pioneered the application of its own patented matching method within confines of the reverse auction process, whereby consumers name their own price for new vehicles.

A Dutch auction is one of several similar types of auctions for buying or selling goods. Most commonly, it means an auction in which the auctioneer begins with a high asking price in the case of selling, and lowers it until some participant accepts the price, or it reaches a predetermined reserve price. This type of price auction is most commonly used for goods that are required to be sold quickly such as flowers, fresh produce, or tobacco. A Dutch auction has also been called a clock auction or open-outcry descending-price auction. This type of auction shows the advantage of speed since a sale never requires more than one bid. It is strategically similar to a first-price sealed-bid auction.
Yield management is a variable pricing strategy, based on understanding, anticipating and influencing consumer behavior in order to maximize revenue or profits from a fixed, time-limited resource. As a specific, inventory-focused branch of revenue management, yield management involves strategic control of inventory to sell the right product to the right customer at the right time for the right price. This process can result in price discrimination, in which customers consuming identical goods or services are charged different prices. Yield management is a large revenue generator for several major industries; Robert Crandall, former Chairman and CEO of American Airlines, gave yield management its name and has called it "the single most important technical development in transportation management since we entered deregulation."
Priceline.com is an online travel agency for finding discount rates for travel-related purchases such as airline tickets and hotel stays. The company facilitates the provision of travel services from its suppliers to its clients. Priceline.com is headquartered in Norwalk, Connecticut, United States and is wholly owned by Booking Holdings, which also owns Kayak.com, Booking.com and other sites. The company was founded in 1997. It operates in more than 200 countries and territories around the world and has partnerships with over 400 airlines and 300,000 hotels. Users can search for travel deals and discounts on the website, and in the past also offered the "Name Your Own Price" feature to bid on hotel rooms and flights.

A business can use a variety of pricing strategies when selling a product or service. To determine the most effective pricing strategy for a company, senior executives need to first identify the company's pricing position, pricing segment, pricing capability and their competitive pricing reaction strategy. Pricing strategies and tactics vary from company to company, and also differ across countries, cultures, industries and over time, with the maturing of industries and markets and changes in wider economic conditions.

Once the strategic plan is in place, retail managers turn to the more managerial aspects of planning. A retail mix is devised for the purpose of coordinating day-to-day tactical decisions. The retail marketing mix typically consists of six broad decision layers including product decisions, place decisions, promotion, price, personnel and presentation. The retail mix is loosely based on the marketing mix, but has been expanded and modified in line with the unique needs of the retail context. A number of scholars have argued for an expanded marketing, mix with the inclusion of two new Ps, namely, Personnel and Presentation since these contribute to the customer's unique retail experience and are the principal basis for retail differentiation. Yet other scholars argue that the Retail Format should be included. The modified retail marketing mix that is most commonly cited in textbooks is often called the 6 Ps of retailing.

Dynamic pricing, also referred to as surge pricing, demand pricing, or time-based pricing, is a revenue management pricing strategy in which businesses set flexible prices for products or services based on current market demands. It usually entails raising prices during periods of peak demand and lowering prices during periods of low demand.
A smart market is a periodic auction which is cleared by the operations research technique of mathematical optimization, such as linear programming. The smart market is operated by a market manager. Trades are not bilateral, between pairs of people, but rather to or from a pool. A smart market can assist market operation when trades would otherwise have significant transaction costs or externalities.
Return on investment (ROI) or return on costs (ROC) is the ratio between net income and investment. A high ROI means the investment's gains compare favourably to its cost. As a performance measure, ROI is used to evaluate the efficiency of an investment or to compare the efficiencies of several different investments. In economic terms, it is one way of relating profits to capital invested.
Customer to customer markets provide a way to allow customers to interact with each other. Traditional markets require business to customer relationships, in which a customer goes to the business in order to purchase a product or service. In customer to customer markets, the business facilitates an environment where customers can sell goods or services to each other. Other types of markets include business to business (B2B) and business to customer (B2C).
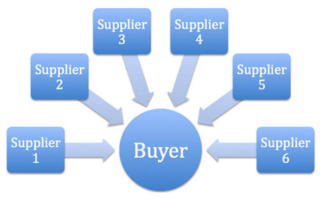
A reverse auction is a type of auction in which the traditional roles of buyer and seller are reversed. Thus, there is one buyer and many potential sellers. In an ordinary auction also known as a forward auction, buyers compete to obtain goods or services by offering increasingly higher prices. In contrast, in a reverse auction, the sellers compete to obtain business from the buyer and prices will typically decrease as the sellers underbid each other.

MadBid was a Gamified eCommerce and online auction website registered under Marcandi Ltd. in the United Kingdom. It was founded in 2008 by Juha Koski, Madhur Srivastava and Daniel Rovira. The company operates in ten European countries including the UK, Ireland, Spain, France, and Australia. However, in August 2018, Madbid closed down and ended all sales.
There are many types of e-commerce models, based on market segmentation, that can be used to conducted business online. The 6 types of business models that can be used in e-commerce include: Business-to-Consumer (B2C), Consumer-to-Business (C2B), Business-to-Business (B2B), Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C), Business-to-Administration (B2A), and Consumer-to-Administration








