Related Research Articles

NLC India Limited (NLC) is a central public sector undertaking under the administrative control of the Ministry of Coal, Government of India. It annually produces about 30 million tonnes of lignite from opencast mines at Neyveli in the state of Tamil Nadu in southern India and at Barsingsar in Bikaner district of Rajasthan state. The lignite is used at pithead thermal power stations of 3640 MW installed capacity to produce electricity. Its joint venture has a 1000 MW thermal power station using coal. Lately, it has diversified into renewable energy production and installed 1404 MW solar power plant to produce electricity from photovoltaic (PV) cells and 51 MW electricity from windmills.

Rajasthan is a mineral-rich state and has a diversified economy having agriculture, mining and tourism as its main engines of growth. The state mines produce gold, silver, sandstone, limestone, marble, rock phosphate, copper and lignite. It is the second-largest producer of cement and contributes one tenth of the salt produced in India.
Rajasthan State Mines & Minerals Limited (RSMML) is a public sector enterprise of the Government of Rajasthan and primarily engaged in Mining and Marketing of High Grade Rock phosphate, Lignite, Limestone & Gypsum (Non-Metallic minerals) through its mines located at various locations in Rajasthan. RSMML is a multiple location organization which originated from a private company Bikaner Gypsum limited (BGL) founded in the year 1947 in Bikaner district of Rajasthan. In 1969 after discovery of rock phosphate in Jhamarkotra (Udaipur), BGL took over operations at Jhamarkotra mines. To enhance and stabilize the profit of company, government of Rajasthan acquired majority of shares and company’s name was changed to Rajasthan state of Mines and Minerals Limited. RSMML has divided its functions according to the respective minerals. It is engaged in the mining of the 4 minerals gypsum, rock phosphate, limestone and lignite at 4 different locations.
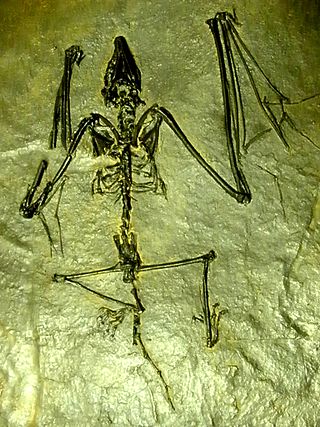
Archaeonycteris is an archaic bat genus whose fossilised remains have been found in Germany, France, England and India.

Sadbhav Engineering Limited (SEL) is an Indian civil engineering and construction company headquartered in Ahmedabad. Founded in 1988 by Vishnubhai M. Patel, the company has implemented projects in the construction of roads & highways, bridges, mining and irrigation-supporting infrastructure. The company worked for clients including NHAI, DMRC, Sardar Sarovar Narmada Nigam, Coal India, L&T, HCC, Punj Lloyd and various others.
Indobune is an extinct genus of ungulate endemic to Asia during the Eocene from 55.8—48.6 Ma, living for approximately 7.2 million years.

Giral Lignite Power Plant (GLPL) or Giral Lignite Thermal Power Station (GLTPP) is a wholly owned subsidiary of Rajasthan Rajya Vidyut Utpadan Nigam Limited (RRVUNL). RRVUNL is a state government owned corporation working in field of power generation.
Kutch Lignite Thermal Power Station is Gujarat State Electricity Corporation Limited's only lignite based power plant.

Gujarat Mineral Development Corporation Limited (GMDC) is a major Indian state-owned minerals and lignite mining company based in Ahmedabad. GMDC was founded in 1963.
Eobarbourula delfinoi is an extinct toad which existed in what is now Gujarat, India, during the Middle Ypresian age of the early Eocene. It was described by Annelise Folie, Rajendra S. Rana, Kenneth D. Rose, Ashok Sahni, Kishor Kumar, Lachham Singh and Thierry Smith in 2012, and is the only species in the genus Eobarbourula. The name of the genus is a combination of "Eo", referring to the epoch in which the animal existed, and Barbourula, the generic name of the jungle toads, while the specific epithet refers to Massimo Delfino, an Italian paleontologist.
Indorana is an extinct genus of lissamphibians which existed in what is now India during the Early Eocene. The type and only known species is Indorana prasadi.
Indohyaenodon is an extinct genus of placental mammals from family Indohyaenodontidae within extinct order Hyaenodonta, that lived during the early Eocene in India.
Surat Thermal Power Station is lignite-based thermal power plant. It is located at Nani Naroli village in Surat, Gujarat. The power plant is run by state owned Gujarat Industrial Power Corporation Limited (GIPCL).
Marcgodinotius is a genus of adapiform primate that lived in Asia during the early Eocene. It is a monotypic genus, the only species being Marcgodinotius indicus. Another adapiform primate Suratius robustus was found in the same horizon. Anthrasimias may be a junior synonym of Marcgodinotius and Anthrasimias gujaratensis a junior synonym of Marcgodinotius indicus.
Indiagama is an extinct genus of agamid lizard known from the type species Indiagama gujarata from the early Eocene of India. Indiagama was named in 2013 on the basis of a single lower jaw from the Cambay Shale in Gujarat. The rectangular shape of its teeth distinguish it from all other agamids, living and extinct.
Suratagama is an extinct genus of agamid lizard known from the type species Suratagama neeraae from the early Eocene of India. It was named in 2013 on the basis of three isolated jaw bones from the Cambay Shale in Gujarat.
Heterodontagama is an extinct genus of iguanian lizard from the Early Eocene of India. It belongs to the extinct family Priscagamidae, which is otherwise only known from the Late Cretaceous of Mongolia. The type species Heterodontagama borsukae was named in 2013 from several isolated upper and lower jaws found in an exposure of the Cambay Shale in an open-pit coal mine in Gujarat.
Protonycteris was a primitive bat genus in the family Archaeonycteridae with a sole species, Protonycteris gunnelli, found in Vastan Lignite Mine (Ypresian), in India.
Cambaytheriidae is a family of primitive four or five-toed ungulates native to the Indian subcontinent. They lived during the Early Eocene epoch and are distinguished by the presence of bunodont teeth suitable for eating tough vegetation. They are related to, but distinct from, the early perissodactyls, and may also be closely related to the anthracobunids as a sister group to the Perissodactyla.

Sunil Bajpai is the Chair Professor of Vertebrate Paleontology in the Department of Earth Sciences, Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee. He is in service as a professor at IIT Roorkee since 1st January 1996 till September 2026. He also served as the director of the Birbal Sahni Institute of Palaeosciences from January 2013 to July 2018.
References
- ↑ "Vastan Lignite and Limestone Mine | Mine | Gujarat Industries Power Company Ltd".
- ↑ "Why Bats Are One of Evolution's Greatest Puzzles". Pocket. Retrieved 2020-11-27.