Related Research Articles
Routing is the process of selecting a path for traffic in a network or between or across multiple networks. Broadly, routing is performed in many types of networks, including circuit-switched networks, such as the public switched telephone network (PSTN), and computer networks, such as the Internet.

A network interface controller is a computer hardware component that connects a computer to a computer network.
freedesktop.org (fd.o), formerly X Desktop Group (XDG), is a project to work on interoperability and shared base technology for free-software desktop environments for the X Window System (X11) and Wayland on Linux and other Unix-like operating systems. Although freedesktop.org produces specifications for interoperability, it is not a formal standards body.
Alliant Computer Systems Corporation was a computer company that designed and manufactured parallel computing systems. Together with Pyramid Technology and Sequent Computer Systems, Alliant's machines pioneered the symmetric multiprocessing market. One of the more successful companies in the group, over 650 Alliant systems were produced over their lifetime. The company was hit by a series of financial problems and went bankrupt in 1992.

The RapidIO architecture is a high-performance packet-switched electrical connection technology. It supports messaging, read/write and cache coherency semantics. Based on industry-standard electrical specifications such as those for Ethernet, RapidIO can be used as a chip-to-chip, board-to-board, and chassis-to-chassis interconnect.
In computing, a solution stack or software stack is a set of software subsystems or components needed to create a complete platform such that no additional software is needed to support applications. Applications are said to "run on" or "run on top of" the resulting platform.
In computing, ioctl is a system call for device-specific input/output operations and other operations which cannot be expressed by regular file semantics. It takes a parameter specifying a request code; the effect of a call depends completely on the request code. Request codes are often device-specific. For instance, a CD-ROM device driver which can instruct a physical device to eject a disc would provide an ioctl request code to do so. Device-independent request codes are sometimes used to give userspace access to kernel functions which are only used by core system software or still under development.
The Open Source Geospatial Foundation (OSGeo), is a non-profit non-governmental organization whose mission is to support and promote the collaborative development of open geospatial technologies and data. The foundation was formed in February 2006 to provide financial, organizational and legal support to the broader Libre/Free and open-source geospatial community. It also serves as an independent legal entity to which community members can contribute code, funding and other resources.

The Better Approach to Mobile Ad-hoc Networking (B.A.T.M.A.N.) is a routing protocol for multi-hop mobile ad hoc networks which is under development by the German "Freifunk" community and intended to replace the Optimized Link State Routing Protocol (OLSR) as OLSR did not meet the performance requirements of large-scale mesh deployments.
The Berkeley Packet Filter is a network tap and packet filter which permits computer network packets to be captured and filtered at the operating system level. It provides a raw interface to data link layers, permitting raw link-layer packets to be sent and received, and allows a userspace process to supply a filter program that specifies which packets it wants to receive. For example, a tcpdump process may want to receive only packets that initiate a TCP connection. BPF returns only packets that pass the filter that the process supplies. This avoids copying unwanted packets from the operating system kernel to the process, greatly improving performance. The filter program is in the form of instructions for a virtual machine, which are interpreted, or compiled into machine code by a just-in-time (JIT) mechanism and executed, in the kernel.
An AES instruction set is a set of instructions that are specifically designed to perform AES encryption and decryption operations efficiently. These instructions are typically found in modern processors and can greatly accelerate AES operations compared to software implementations. An AES instruction set includes instructions for key expansion, encryption, and decryption using various key sizes.

Node.js is a cross-platform, open-source JavaScript runtime environment that can run on Windows, Linux, Unix, macOS, and more. Node.js runs on the V8 JavaScript engine, and executes JavaScript code outside a web browser.

Dracut is a set of tools that provide enhanced functionality for automating the Linux boot process. The tool named dracut is used to create a Linux boot image (initramfs) by copying tools and files from an installed system and combining it with the Dracut framework, which is usually found in /usr/lib/dracut/modules.d.
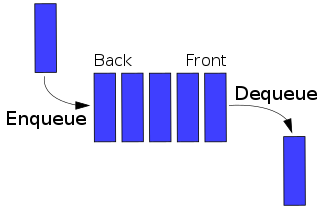
A network scheduler, also called packet scheduler, queueing discipline (qdisc) or queueing algorithm, is an arbiter on a node in a packet switching communication network. It manages the sequence of network packets in the transmit and receive queues of the protocol stack and network interface controller. There are several network schedulers available for the different operating systems, that implement many of the existing network scheduling algorithms.
The Data Plane Development Kit (DPDK) is an open source software project managed by the Linux Foundation. It provides a set of data plane libraries and network interface controller polling-mode drivers for offloading TCP packet processing from the operating system kernel to processes running in user space. This offloading achieves higher computing efficiency and higher packet throughput that is possible using the interrupt-driven processing provided in the kernel.
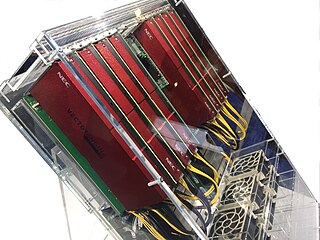
The NEC SX-Aurora TSUBASA is a vector processor of the NEC SX architecture family. Unlike previous SX supercomputers, the SX-Aurora TSUBASA is provided as a PCIe card, termed by NEC as a "Vector Engine" (VE). Eight VE cards can be inserted into a vector host (VH) which is typically a x86-64 server running the Linux operating system. The product has been announced in a press release on 25 October 2017 and NEC has started selling it in February 2018. The product succeeds the SX-ACE.
Secure Reliable Transport (SRT) is an open source video transport protocol that utilises the UDP transport protocol. The SRT Protocol specification is available as an Internet Draft from the IETF.
A graph neural network (GNN) belongs to a class of artificial neural networks for processing data that can be represented as graphs.

eBPF is a technology that can run programs in a privileged context such as the operating system kernel. It is the successor to the Berkeley Packet Filter filtering mechanism in Linux and is also used in non-networking parts of the Linux kernel as well.

Cilium is a cloud native technology for networking, observability, and security. It is based on the kernel technology eBPF, originally for better networking performance, and now leverages many additional features for different use cases. The core networking component has evolved from only providing a flat Layer 3 network for containers to including advanced networking features, like BGP and Service mesh, within a Kubernetes cluster, across multiple clusters, and connecting with the world outside Kubernetes. Hubble was created as the network observability component and Tetragon was later added for security observability and runtime enforcement. Cilium runs on Linux and is one of the first eBPF applications being ported to Microsoft Windows through the eBPF on Windows project.
References
- ↑ "What is VPP?". FD.io Wiki. 2017-05-27. Retrieved 2020-08-12.
- ↑ "Scalar vs Vector packet processing — The Vector Packet Processor 20.01 documentation". fd.io. Retrieved 2020-08-12.
- ↑ "[Guide] Intro to Vector Packet Processing (VPP)". PANTHEON.tech. 2020-01-03. Retrieved 2020-08-12.
- ↑ "VPP fd.io". wiki.fd.io. Linux Foundation . Retrieved 29 December 2016.
- ↑ "VPP Technology". fd.io. Retrieved 2020-08-12.