Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless body fluid found within the tissue that surrounds the brain and spinal cord of all vertebrates.

White matter refers to areas of the central nervous system (CNS) that are mainly made up of myelinated axons, also called tracts. Long thought to be passive tissue, white matter affects learning and brain functions, modulating the distribution of action potentials, acting as a relay and coordinating communication between different brain regions.

Colpocephaly is a cephalic disorder involving the disproportionate enlargement of the occipital horns of the lateral ventricles and is usually diagnosed early after birth due to seizures. It is a nonspecific finding and is associated with multiple neurological syndromes, including agenesis of the corpus callosum, Chiari malformation, lissencephaly, and microcephaly. Although the exact cause of colpocephaly is not known yet, it is commonly believed to occur as a result of neuronal migration disorders during early brain development, intrauterine disturbances, perinatal injuries, and other central nervous system disorders. Individuals with colpocephaly have various degrees of motor disabilities, visual defects, spasticity, and moderate to severe intellectual disability. No specific treatment for colpocephaly exists, but patients may undergo certain treatments to improve their motor function or intellectual disability.

Systole is the part of the cardiac cycle during which some chambers of the heart contract after refilling with blood.

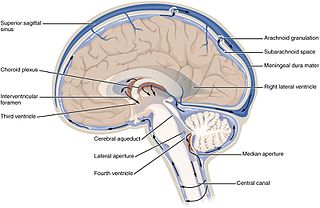
In neuroanatomy, the ventricular system is a set of four interconnected cavities known as cerebral ventricles in the brain. Within each ventricle is a region of choroid plexus which produces the circulating cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). The ventricular system is continuous with the central canal of the spinal cord from the fourth ventricle, allowing for the flow of CSF to circulate.

Neuropsychology is a branch of psychology concerned with how a person's cognition and behavior are related to the brain and the rest of the nervous system. Professionals in this branch of psychology focus on how injuries or illnesses of the brain affect cognitive and behavioral functions.

The third ventricle is one of the four connected ventricles of the ventricular system within the mammalian brain. It is a slit-like cavity formed in the diencephalon between the two thalami, in the midline between the right and left lateral ventricles, and is filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).

The brain is the central organ of the human nervous system, and with the spinal cord makes up the central nervous system. The brain consists of the cerebrum, the brainstem and the cerebellum. It controls most of the activities of the body, processing, integrating, and coordinating the information it receives from the sense organs, and making decisions as to the instructions sent to the rest of the body. The brain is contained in, and protected by, the skull bones of the head.

Glia, also called glial cells (gliocytes) or neuroglia, are non-neuronal cells in the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system that do not produce electrical impulses. The neuroglia make up more than one half the volume of neural tissue in the human body. They maintain homeostasis, form myelin in the peripheral nervous system, and provide support and protection for neurons. In the central nervous system, glial cells include oligodendrocytes, astrocytes, ependymal cells and microglia, and in the peripheral nervous system they include Schwann cells and satellite cells.

The choroid plexus, or plica choroidea, is a plexus of cells that arises from the tela choroidea in each of the ventricles of the brain. Regions of the choroid plexus produce and secrete most of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of the central nervous system. The choroid plexus consists of modified ependymal cells surrounding a core of capillaries and loose connective tissue. Multiple cilia on the ependymal cells move to circulate the cerebrospinal fluid.

Clinical neuropsychology is a sub-field of cognitive science and psychology concerned with the applied science of brain-behaviour relationships. Clinical neuropsychologists use this knowledge in the assessment, diagnosis, treatment, and or rehabilitation of patients across the lifespan with neurological, medical, neurodevelopmental and psychiatric conditions, as well as other cognitive and learning disorders. The branch of neuropsychology associated with children and young people is pediatric neuropsychology.

Diastole is the relaxed phase of the cardiac cycle when the chambers of the heart are refilling with blood. The contrasting phase is systole when the heart chambers are contracting. Atrial diastole is the relaxing of the atria, and ventricular diastole the relaxing of the ventricles.

The septum pellucidum is a thin, triangular, vertical double membrane separating the anterior horns of the left and right lateral ventricles of the brain. It runs as a sheet from the corpus callosum down to the fornix.

Radionuclide angiography is an area of nuclear medicine which specialises in imaging to show the functionality of the right and left ventricles of the heart, thus allowing informed diagnostic intervention in heart failure. It involves use of a radiopharmaceutical, injected into a patient, and a gamma camera for acquisition. A MUGA scan involves an acquisition triggered (gated) at different points of the cardiac cycle. MUGA scanning is also called equilibrium radionuclide angiocardiography, radionuclide ventriculography (RNVG), or gated blood pool imaging, as well as SYMA scanning.

The lateral ventricles are the two largest ventricles of the brain and contain cerebrospinal fluid. Each cerebral hemisphere contains a lateral ventricle, known as the left or right lateral ventricle, respectively.

A cerebral shunt is a device permanently implanted inside the head and body to drain excess fluid away from the brain. They are commonly used to treat hydrocephalus, the swelling of the brain due to excess buildup of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). If left unchecked, the excess CSF can lead to an increase in intracranial pressure (ICP), which can cause intracranial hematoma, cerebral edema, crushed brain tissue or herniation. The drainage provided by a shunt can alleviate or prevent these problems in patients with hydrocephalus or related diseases.

Intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH), also known as intraventricular bleeding, is a bleeding into the brain's ventricular system, where the cerebrospinal fluid is produced and circulates through towards the subarachnoid space. It can result from physical trauma or from hemorrhagic stroke.

An external ventricular drain (EVD), also known as a ventriculostomy or extraventricular drain, is a device used in neurosurgery to treat hydrocephalus and relieve elevated intracranial pressure when the normal flow of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) inside the brain is obstructed. An EVD is a flexible plastic catheter placed by a neurosurgeon or neurointensivist and managed by intensive care unit (ICU) physicians and nurses. The purpose of external ventricular drainage is to divert fluid from the ventricles of the brain and allow for monitoring of intracranial pressure. An EVD must be placed in a center with full neurosurgical capabilities, because immediate neurosurgical intervention can be needed if a complication of EVD placement, such as bleeding, is encountered.
The monitoring of intracranial pressure (ICP) is used in the treatment of a number of neurological conditions ranging from severe traumatic brain injury to stroke and brain bleeds. This process is called intracranial pressure monitoring. Monitoring is important as persistent increases in ICP is associated with worse prognosis in brain injuries due to decreased oxygen delivery to the injured area and risk of brain herniation.
















