
Compost is a mixture of ingredients used as plant fertilizer and to improve soil's physical, chemical, and biological properties. It is commonly prepared by decomposing plant and food waste, recycling organic materials, and manure. The resulting mixture is rich in plant nutrients and beneficial organisms, such as bacteria, protozoa, nematodes, and fungi. Compost improves soil fertility in gardens, landscaping, horticulture, urban agriculture, and organic farming, reducing dependency on commercial chemical fertilizers. The benefits of compost include providing nutrients to crops as fertilizer, acting as a soil conditioner, increasing the humus or humic acid contents of the soil, and introducing beneficial microbes that help to suppress pathogens in the soil and reduce soil-borne diseases.

Hydroponics is a type of horticulture and a subset of hydroculture which involves growing plants, usually crops or medicinal plants, without soil, by using water-based mineral nutrient solutions in an artificial environment. Terrestrial or aquatic plants may grow freely with their roots exposed to the nutritious liquid or the roots may be mechanically supported by an inert medium such as perlite, gravel, or other substrates.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to agriculture:

A land lab is an area of land that has been set aside for use in biological studies. Thus, it is literally an outdoor laboratory based on an area of land.

Vermicompost (vermi-compost) is the product of the decomposition process using various species of worms, usually red wigglers, white worms, and other earthworms, to create a mixture of decomposing vegetable or food waste, bedding materials, and vermicast. This process is called vermicomposting, with the rearing of worms for this purpose is called vermiculture.

Aquaponics is a food production system that couples aquaculture with hydroponics whereby the nutrient-rich aquaculture water is fed to hydroponically grown plants.

Aeroponics is the process of cultivating plants in an air or mist environment, eliminating the need for soil or an aggregate medium. The term "aeroponic" originates from the ancient Greek: aer (air) and ponos. It falls under the category of hydroponics, as water is employed in aeroponics to deliver nutrients to the plants.

A composting toilet is a type of dry toilet that treats human waste by a biological process called composting. This process leads to the decomposition of organic matter and turns human waste into compost-like material. Composting is carried out by microorganisms under controlled aerobic conditions. Most composting toilets use no water for flushing and are therefore called "dry toilets".

Organic fertilizers are fertilizers that are naturally produced. Fertilizers are materials that can be added to soil or plants, in order to provide nutrients and sustain growth. Typical organic fertilizers include all animal waste including meat processing waste, manure, slurry, and guano; plus plant based fertilizers such as compost; and biosolids. Inorganic "organic fertilizers" include minerals and ash. Organic refers to the Principles of Organic Agriculture, which determines whether a fertilizer can be used for commercial organic agriculture, not whether the fertilizer consists of organic compounds.

Vertical farming is the practice of growing crops in vertically and horizontally stacked layers. It often incorporates controlled-environment agriculture, which aims to optimize plant growth, and soilless farming techniques such as hydroponics, aquaponics, and aeroponics. Some common choices of structures to house vertical farming systems include buildings, shipping containers, underground tunnels, and abandoned mine shafts.

Deep water culture (DWC) is a hydroponic method of plant production by means of suspending the plant roots in a solution of nutrient-rich, oxygenated water. Also known as deep flow technique (DFT), floating raft technology (FRT), or raceway, this method uses a rectangular tank less than one foot deep filled with a nutrient-rich solution with plants floating in Styrofoam boards on top. This method of floating the boards on the nutrient solution creates a near friction-less conveyor belt of floating rafts. DWC, along with nutrient film technique (NFT), and aggregate culture, is considered to be one of the most common hydroponic systems used today. Typically, DWC is used to grow short-term, non-fruiting crops such as leafy greens and herbs. Supposedly, DWC was invented accidentally in 1998 by a legacy cannabis grower who goes by the name of “Snype." This occurred because “Snype” and his (unnamed) associate had to take a trip to Amsterdam and needed a way to feed their cannabis crop while they were away. They built nutrient and water reservoirs that would keep the plants thoroughly fed in their absence, and thusly the DWC system was born. However, this information is not backed up by any reliable source. English physician John Woodward is usually remembered as the first person to grow plants in water culture, although Woodward did note Robert Boyle was conducting similar experiments. Woodward's work was not specifically with DWC systems, however. This system was revised in 2010 to create RDWC. The large volume of water helps mitigate rapid changes in temperature, pH, electrical conductivity (EC), and nutrient solution composition.

Lightweight expanded clay aggregate (LECA) or expanded clay (exclay) is a lightweight aggregate made by heating clay to around 1,200 °C (2,190 °F) in a rotary kiln. The heating process causes gases trapped in the clay to expand, forming thousands of small bubbles and giving the material a porous structure. LECA has an approximately round or oblong shape due to circular movement in the kiln and is available in different sizes and densities. LECA is used to make lightweight concrete products and other uses.
Microponics, in agricultural practice, is a symbiotic integration of fish, plants, and micro-livestock within a semi-controlled environment, designed to enhance soil fertility and crop productivity. Coined by Gary Donaldson, an Australian urban farmer, in 2008, the term was used to describe his innovative concept of integrated backyard food production. While "microponics" had been previously used to refer to an obscure grafting method in hydroponics, Donaldson's application of the term was derived from the amalgamation of micro-livestock (micro-farming) and the cultivation of fish and plants, a practice commonly known as aquaponics.
Organic hydroponics is a hydroponics culture system based on organic agriculture concepts that does not use synthetic inputs such as fertilizers or pesticides. In organic hydroponics, nutrient solutions are derived from plant and animal material or naturally mined substances. Most studies on the topic have focused on the use of organic fertilizer.

Reuse of human excreta is the safe, beneficial use of treated human excreta after applying suitable treatment steps and risk management approaches that are customized for the intended reuse application. Beneficial uses of the treated excreta may focus on using the plant-available nutrients that are contained in the treated excreta. They may also make use of the organic matter and energy contained in the excreta. To a lesser extent, reuse of the excreta's water content might also take place, although this is better known as water reclamation from municipal wastewater. The intended reuse applications for the nutrient content may include: soil conditioner or fertilizer in agriculture or horticultural activities. Other reuse applications, which focus more on the organic matter content of the excreta, include use as a fuel source or as an energy source in the form of biogas.

The Sustainable Technology Optimization Research Center (STORC) is a research facility located on the California State University Sacramento campus. There are several players included in operations at the STORC including Sacramento State's Risk Management, the College of Engineering and Computer Science (ECS), and two professors in the Environmental Studies department Brook Murphy and Dudley Burton. The STORC facility is primarily maintained by California State University, Sacramento student interns and volunteers who use applied science and technology to address real world policy, food, health, and energy issues of present-day society. Research at the STORC encompasses engineering and science to test and evaluate new ideas and approaches of sustainable technology to solve environmental problems. Faculty and students address sustainability with an interdisciplinary studies approach. The STORC Vision is to become "an international resource for practical, scalable, and financially viable solutions in the area of sustainable technologies that are suitable for private and/or public sector operations related to the management of energy, food, water, and waste". The STORC Mission is "to demonstrate the operation of innovative commercially viable physical systems that are underpinned by sustainable technologies, and to disseminate the associated plans, public policy discourse, and scientific findings".

Anthroponics is a type of hydroponics system that uses human waste like urine as the source of nutrients for the cultivated plants. In general, the human urine or mixed waste is collected and stored for a period of time, before being applied either directly or passed through a biofilter before reaching the plants. As a form of organic hydroponics, anthroponics combines elements of both hydroponics and aquaponics systems.

Digeponics (pronounced die-jeh-ponics, as in digestion) is a method of agriculture which integrates the products of anaerobic digestion, including CO2 and digestate, with greenhouse cultivation of vegetables.
Home composting is the process of using household waste to make compost at home. Composting is the biological decomposition of organic waste by recycling food and other organic materials into compost. Home composting can be practiced within households for various environmental advantages, such as increasing soil fertility, reduce landfill and methane contribution, and limit food waste.
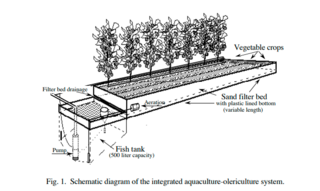
The Integrated Aqua-Vegeculture System (iAVs),also informally known as Sandponics, is a food production method that combines aquaculture and horticulture (olericulture). It was developed in the 1980s by Dr. Mark McMurtry and colleagues at North Carolina State University including Professor Doug Sanders, Paul V. Nelson and Dr. Merle Jensen. This system is one of the earliest instances of a closed-loop aquaponic system.















