Related Research Articles
In mathematics, an associative algebraA over a commutative ring K is a ring A together with a ring homomorphism from K into the center of A. This is thus an algebraic structure with an addition, a multiplication, and a scalar multiplication. The addition and multiplication operations together give A the structure of a ring; the addition and scalar multiplication operations together give A the structure of a module or vector space over K. In this article we will also use the term K-algebra to mean an associative algebra over K. A standard first example of a K-algebra is a ring of square matrices over a commutative ring K, with the usual matrix multiplication.
In mathematics, a chain complex is an algebraic structure that consists of a sequence of abelian groups and a sequence of homomorphisms between consecutive groups such that the image of each homomorphism is included in the kernel of the next. Associated to a chain complex is its homology, which describes how the images are included in the kernels.
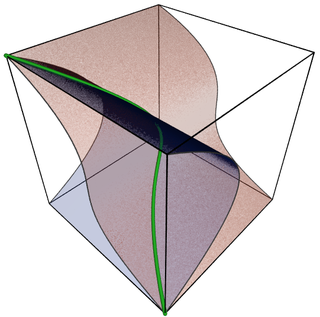
Algebraic varieties are the central objects of study in algebraic geometry, a sub-field of mathematics. Classically, an algebraic variety is defined as the set of solutions of a system of polynomial equations over the real or complex numbers. Modern definitions generalize this concept in several different ways, while attempting to preserve the geometric intuition behind the original definition.
Ring theory is the branch of mathematics in which rings are studied: that is, structures supporting both an addition and a multiplication operation. This is a glossary of some terms of the subject.
In mathematics, a Hopf algebra, named after Heinz Hopf, is a structure that is simultaneously an algebra and a coalgebra, with these structures' compatibility making it a bialgebra, and that moreover is equipped with an antihomomorphism satisfying a certain property. The representation theory of a Hopf algebra is particularly nice, since the existence of compatible comultiplication, counit, and antipode allows for the construction of tensor products of representations, trivial representations, and dual representations.
In mathematics, especially in the area of abstract algebra known as module theory, an injective module is a module Q that shares certain desirable properties with the Z-module Q of all rational numbers. Specifically, if Q is a submodule of some other module, then it is already a direct summand of that module; also, given a submodule of a module Y, any module homomorphism from this submodule to Q can be extended to a homomorphism from all of Y to Q. This concept is dual to that of projective modules. Injective modules were introduced in and are discussed in some detail in the textbook.

In mathematics, a group scheme is a type of object from algebraic geometry equipped with a composition law. Group schemes arise naturally as symmetries of schemes, and they generalize algebraic groups, in the sense that all algebraic groups have group scheme structure, but group schemes are not necessarily connected, smooth, or defined over a field. This extra generality allows one to study richer infinitesimal structures, and this can help one to understand and answer questions of arithmetic significance. The category of group schemes is somewhat better behaved than that of group varieties, since all homomorphisms have kernels, and there is a well-behaved deformation theory. Group schemes that are not algebraic groups play a significant role in arithmetic geometry and algebraic topology, since they come up in contexts of Galois representations and moduli problems. The initial development of the theory of group schemes was due to Alexander Grothendieck, Michel Raynaud and Michel Demazure in the early 1960s.
In commutative algebra, a Gorenstein local ring is a commutative Noetherian local ring R with finite injective dimension as an R-module. There are many equivalent conditions, some of them listed below, often saying that a Gorenstein ring is self-dual in some sense.
In mathematics, especially in the fields of representation theory and module theory, a Frobenius algebra is a finite-dimensional unital associative algebra with a special kind of bilinear form which gives the algebras particularly nice duality theories. Frobenius algebras began to be studied in the 1930s by Richard Brauer and Cecil Nesbitt and were named after Georg Frobenius. Tadashi Nakayama discovered the beginnings of a rich duality theory, . Jean Dieudonné used this to characterize Frobenius algebras. Frobenius algebras were generalized to quasi-Frobenius rings, those Noetherian rings whose right regular representation is injective. In recent times, interest has been renewed in Frobenius algebras due to connections to topological quantum field theory.

Ernst Witt was a German mathematician, one of the leading algebraists of his time.
In mathematics, Artin–Schreier theory is a branch of Galois theory, specifically a positive characteristic analogue of Kummer theory, for Galois extensions of degree equal to the characteristic p. Artin and Schreier introduced Artin–Schreier theory for extensions of prime degree p, and Witt generalized it to extensions of prime power degree pn.
In mathematics, a D-module is a module over a ring D of differential operators. The major interest of such D-modules is as an approach to the theory of linear partial differential equations. Since around 1970, D-module theory has been built up, mainly as a response to the ideas of Mikio Sato on algebraic analysis, and expanding on the work of Sato and Joseph Bernstein on the Bernstein–Sato polynomial.
In mathematics, a Witt vector is an infinite sequence of elements of a commutative ring. Ernst Witt showed how to put a ring structure on the set of Witt vectors, in such a way that the ring of Witt vectors over the finite field of prime order p is isomorphic to , the ring of p-adic integers. They have a highly non-intuitive structure upon first glance because their additive and multiplicative structure depends on an infinite set of recursive formulas which do not behave like addition and multiplication formulas for standard p-adic integers.
In mathematics, a Witt group of a field, named after Ernst Witt, is an abelian group whose elements are represented by symmetric bilinear forms over the field.
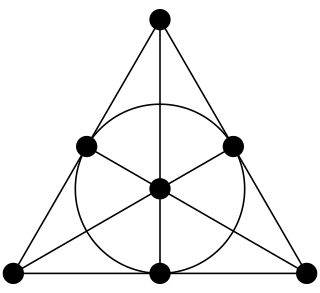
Algebraic combinatorics is an area of mathematics that employs methods of abstract algebra, notably group theory and representation theory, in various combinatorial contexts and, conversely, applies combinatorial techniques to problems in algebra.
In mathematics, a Dieudonné module introduced by Jean Dieudonné, is a module over the non-commutative Dieudonné ring, which is generated over the ring of Witt vectors by two special endomorphisms and called the Frobenius and Verschiebung operators. They are used for studying finite flat commutative group schemes.
In algebra, a λ-ring or lambda ring is a commutative ring together with some operations λn on it that behave like the exterior powers of vector spaces. Many rings considered in K-theory carry a natural λ-ring structure. λ-rings also provide a powerful formalism for studying an action of the symmetric functions on the ring of polynomials, recovering and extending many classical results.
This is a glossary for the terminology in a mathematical field of functional analysis.
References
- Demazure, Michel (1972), Lectures on p-divisible groups, Lecture Notes in Mathematics, vol. 302, Berlin, New York: Springer-Verlag, doi:10.1007/BFb0060741, ISBN 978-3-540-06092-5, MR 0344261
- Witt, Ernst (1937), "Zyklische Körper und Algebren der Characteristik p vom Grad pn. Struktur diskret bewerteter perfekter Körper mit vollkommenem Restklassenkörper der Charakteristik pn", Journal für die Reine und Angewandte Mathematik (in German), 176: 126–140, doi:10.1515/crll.1937.176.126