Division is a taxonomic rank in biological classification that is used differently in zoology and in botany.

Edaphosauridae is a family of mostly large Late Carboniferous to Early Permian synapsids. Edaphosaur fossils are so far known only from North America and Europe.

Pachypleurosauria is an extinct clade of primitive sauropterygian reptiles from the Triassic period. Pachypleurosaurs vaguely resembled aquatic lizards, with elongate forms ranging in size from 0.2–1 metre (0.66–3.28 ft), with small heads, long necks, paddle-like limbs, and long, deep tails. The limb girdles are greatly reduced, so it is unlikely these animals could move about on land. The widely spaced peg-like teeth project at the front of the jaws, indicating that these animals fed on fish. In the species Prosantosaurus, it was observed that they fed on small fishes and crustaceans which they devoured entirely and that its teeth regrew after they broke off. This was the first observation of tooth replacement in a European pachypleurosaur, with the only other discovery of such an event having been made in China.

Eryopoidea is a clade of late Carboniferous and Permian temnospondyl amphibians, known from North America and Europe. Carroll (1998) includes no fewer than ten families, but Yates and Warren (2000) replaced this with a cladistic approach that includes three closely-related families, the Eryopidae, Parioxyidae and Zatrachydidae. They define the Eryopoidea as all members of Euskelia in which the choana are relatively rounded and the iliac blade is vertical. A similar definition is provided by Laurin and Steyer (2000).

Eryopidae were a group of medium to large amphibious temnospondyls, known from North America and Europe. They are defined as all eryopoids with interpterygoid vacuities that are rounded at the front; and large external nares. Not all of the genera previously included in the Eryopidae are retained under the cladistic revisions.

Trilophosaurs are lizard-like Triassic allokotosaur reptiles related to the archosaurs. The best known genus is Trilophosaurus, a herbivore up to 2.5 metres long. It had a short, unusually heavily built skull, equipped with massive, broad flattened cheek teeth with sharp shearing surfaces for cutting up tough plant material. Teeth are absent from the premaxilla and front of the lower jaw, which in life were probably equipped with a horny beak.

Araeoscelis is an extinct genus of reptile, and one of the earliest diapsids. Fossils have been found in the Nocona, Arroyo and Waggoner Ranch Formations in Texas, dating to the Early Permian. Two species have been described, A. casei and A. gracilis.

Ischigualastia is an extinct genus of large dicynodont therapsids that lived during the Late Carnian age and the Early Norian age of the Late Triassic Period. The genus was found in and named after the Ischigualasto Formation of the Ischigualasto-Villa Unión Basin in northwestern Argentina. It has been placed in the family Stahleckeriidae.

Tangasauridae is an extinct family of diapsids known from fossil specimens from Madagascar, Kenya and Tanzania that are Late Permian to Early Triassic in age. Fossils have been found of numerous specimens of common members of this family such as Hovasaurus in different stages of ontogenic development. Recent material from the Middle Sakamena Formation of the Morondava Basin of Madagascar that dates back to the early Triassic period suggests that the Tangasauridae were relatively unaffected by the Permian-Triassic extinction event.

Acherontemys is an extinct genus of turtle from Miocene of United States.

Dakotasuchus is a genus of goniopholidid mesoeucrocodylian. Its fossils have been recovered from the Cenomanian-age Upper Cretaceous Dakota Sandstone of Kansas. The type specimen was found in an iron-cemented sandstone concretion near Salina. This concretion was broken into two large pieces; more of the specimen was probably present originally, but by the time it was found only the torso and short portions of the neck and tail remained. Twenty pairs of bony scutes ran down the midline of the back. The vertebrae lacked the procoelous articulation of more derived crocodyliforms. Dakotasuchus had short broad shoulder blades, suggesting it had stout powerful forelimbs and perhaps terrestrial habits. M. G. Mehl, who described the genus, estimated the length of the type individual when complete to have been 3–4 metres (9.8–13.1 ft). The type species is D. kingi, named for Professor King, a former dean of Kansas Wesleyan University. Mehl did not classify his new genus to a more inclusive group than Mesosuchia. Robert Carroll assigned Dakotasuchus to Goniopholididae in 1988. In 2017, fossils of Dakotasuchus kingi which consisted of a coracoid, scutes, a dorsal vertebrate and postcranial bones were found in Utah, specifically in the Cedar Mountain Formation's Mussentuchit Member.
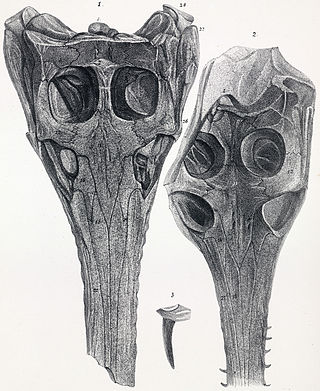
Anglosuchus is an extinct genus of pholidosaurid mesoeucrocodylian. Both species of Anglosuchus were originally assigned to the genus Steneosaurus by Richard Owen in 1884, but were later placed in the new genus. It was once thought to be a teleosaurid but later reassigned to the family Pholidosauridae.
Atlantosuchus is an extinct genus of dyrosaurid crocodylomorph from Morocco. One defining characteristic that distinguishes it from other long-snouted dyrosaurids was its proportionally elongate snout, the longest in proportion to body size of any dyrosaurid. Rhabdognathus, a hyposaurine dyrosaurid, is believed to have been the closest relative of the genus.
Hoplosuchus is a genus of crocodylomorph belonging to Protosuchidae. It is so far only known definitely from one specimen, a skeleton collected from sandstone of the Upper Jurassic-age Morrison Formation rocks at Dinosaur National Monument, Utah, during road construction. The individual was small, approximately 20 centimetres (7.9 in) long, although it may have been very young. It is the basalmost crocodyliform of the Morrison Formation, as suggested by such attributes as still having antorbital fenestrae in the skull. The limbs were relatively long, suggesting that the animal was terrestrial. Two rows of bony scutes ran down the back. The crowns of the teeth are not well preserved, so the diet cannot be determined with certainty. Given its small size, it probably ate insects and small vertebrates; it may have been carnivorous or omnivorous.
Baharijodon is an extinct genus of trematochampsid crocodylomorph. It is known from the Bahariya Formation in Egypt, which dates back to the Cenomanian stage of the Late Cretaceous. The genus is known from a single tooth, which was first figured by Ernst Stromer in 1933, and then named as a new genus of the family Goniopholididae by Oskar Kuhn in 1936. In 1979, Éric Buffetaut and P. Taquet instead referred the tooth to Trematochampsidae.
Coelosuchus is an extinct genus of goniopholidid mesoeucrocodylian. Fossils have been found from the Graneros Shale of the Benton Group in Wyoming, and are of Cenomanian age. It was slightly over 1 meter in length.

Crocodilaemus is an extinct genus of pholidosaurid mesoeucrocodylian. Fossils have been found from the Cerin Lagerstätte of eastern France and are of late Kimmeridgian age. The depositional environment in Cerin at the time is thought to have been the bottom of a lagoon that was enclosed by an emergent reef complex, evidence of the shallow tropical sea that covered much of western Europe during the Jurassic period.
Pseudocyonopsis is a member of the extinct family Amphicyonidae, a terrestrial carnivore belonging to the order Caniformia.

Pseudhesperosuchus is a genus of sphenosuchian, a type of basal crocodylomorph, the clade that comprises the crocodilians and their closest kin. It is known from a partial skeleton and skull found in rocks of the Late Triassic (Norian-age) Los Colorados Formation of the Ischigualasto-Villa Unión Basin in northwestern Argentina.

Eutatus is an extinct genus of large armadillos of the family Chlamyphoridae. It was endemic to South America from the Early Miocene to Late Pleistocene, living from 17.5 Ma-11,000 years ago, with possible survival into the early Holocene and existing for approximately 17.49 million years. Based on carbon isotope ratios, it is thought to have been an herbivore that fed on grasses.














